Preventive maintenance involves scheduled inspections and routine servicing to prevent equipment failures before they occur, while predictive maintenance uses data analytics and real-time monitoring to foresee potential issues and address them just in time. By adopting predictive maintenance, your operations can minimize downtime and reduce maintenance costs through timely interventions based on actual equipment conditions.
Table of Comparison
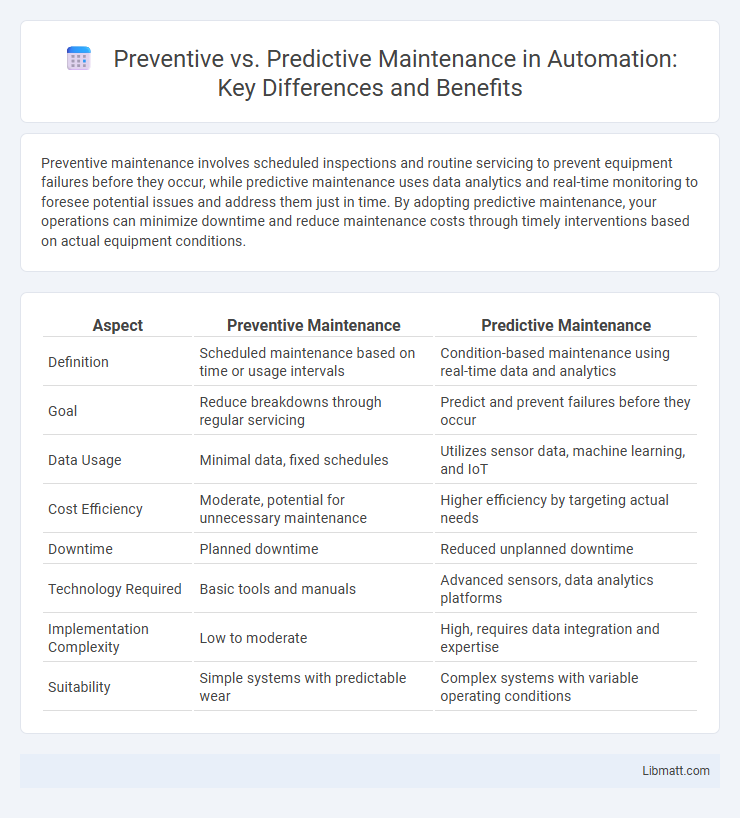
| Aspect | Preventive Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled maintenance based on time or usage intervals | Condition-based maintenance using real-time data and analytics |
| Goal | Reduce breakdowns through regular servicing | Predict and prevent failures before they occur |
| Data Usage | Minimal data, fixed schedules | Utilizes sensor data, machine learning, and IoT |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate, potential for unnecessary maintenance | Higher efficiency by targeting actual needs |
| Downtime | Planned downtime | Reduced unplanned downtime |
| Technology Required | Basic tools and manuals | Advanced sensors, data analytics platforms |
| Implementation Complexity | Low to moderate | High, requires data integration and expertise |
| Suitability | Simple systems with predictable wear | Complex systems with variable operating conditions |
Introduction to Maintenance Strategies
Preventive maintenance involves scheduled inspections and routine servicing to reduce equipment failure and extend asset lifespan. Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and condition monitoring technologies to forecast when maintenance is needed, minimizing downtime and optimizing resource use. Choosing the right strategy enhances your operational efficiency and reduces unexpected repair costs.
Defining Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance involves regularly scheduled inspections and servicing of equipment to reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures and extend asset lifespan. It relies on time-based intervals or usage metrics to perform tasks such as lubrication, adjustments, and parts replacement before problems arise. Your maintenance strategy benefits from preventive maintenance by minimizing downtime and maintaining consistent operational performance.
Understanding Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and advanced analytics to monitor equipment health, enabling early detection of potential failures before they occur. By analyzing sensor data, vibration patterns, and temperature fluctuations, predictive maintenance optimizes repair schedules, reduces downtime, and extends asset lifespan. This approach contrasts with preventive maintenance, which relies on fixed intervals rather than condition-based insights.
Key Differences Between Preventive and Predictive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance involves scheduled inspections and routine servicing based on time or usage intervals to prevent equipment failures, while predictive maintenance utilizes real-time data and condition monitoring techniques such as vibration analysis and thermal imaging to forecast equipment issues before they occur. Preventive maintenance relies on fixed maintenance schedules regardless of equipment condition, whereas predictive maintenance triggers interventions only when specific indicators show signs of potential failure. The key difference lies in efficiency and cost-effectiveness, as predictive maintenance reduces unnecessary maintenance actions and minimizes unplanned downtime by addressing issues proactively.
Advantages of Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance extends equipment lifespan by scheduling regular inspections and servicing before failures occur, reducing unexpected downtime and costly repairs. It enhances operational efficiency by maintaining optimal performance levels through consistent upkeep and early detection of wear and tear. Preventive maintenance also improves safety standards by addressing potential hazards proactively, minimizing the risk of accidents and compliance violations.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance enhances equipment reliability by using real-time data analytics and IoT sensors to detect potential failures before they occur, reducing unplanned downtime by up to 50%. This approach extends asset lifespan and optimizes maintenance schedules, leading to cost savings of 20-30% compared to traditional preventive methods. Key industries leveraging predictive maintenance include manufacturing, energy, and transportation, where improved operational efficiency directly impacts productivity and safety.
Challenges of Each Maintenance Approach
Preventive maintenance faces challenges such as scheduling inefficiencies and unnecessary part replacements, which lead to increased labor costs and downtime. Predictive maintenance struggles with high initial investment in sensors and data analytics infrastructure, alongside the complexity of accurately interpreting sensor data to prevent false alarms or missed failures. Both approaches demand skilled personnel and continuous monitoring to optimize equipment reliability and operational efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Preventive vs Predictive
Preventive maintenance typically incurs higher costs due to scheduled part replacements and routine inspections regardless of equipment condition, leading to potential unnecessary expenses. Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and condition monitoring to minimize downtime and avoid premature part replacements, resulting in lower overall maintenance costs. Your organization can achieve significant cost savings by adopting predictive maintenance strategies that optimize resource allocation and extend asset lifespan.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Strategy
Choosing the right maintenance strategy involves evaluating the specific needs of your equipment and operational environment. Preventive maintenance schedules regular inspections and part replacements to minimize unexpected failures, ideal for assets with predictable wear patterns. Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and condition monitoring to anticipate failures, providing a more cost-efficient and targeted approach when your systems allow for continuous performance tracking.
Future Trends in Maintenance Practices
Future trends in maintenance practices emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance predictive maintenance capabilities, enabling real-time condition monitoring and precise failure prediction. Emerging technologies such as IoT sensors and digital twins provide granular data analytics that improve asset performance and reduce downtime. Your maintenance strategy will increasingly rely on these advancements to shift from routine preventive actions to dynamic, data-driven predictive interventions that optimize operational efficiency.
Preventive vs Predictive Maintenance Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com