An IO Expander increases the number of input/output pins available on a microcontroller, allowing you to connect more devices without altering the microcontroller itself. A Multiplexer, on the other hand, selects one input from multiple signals to send to a single output line, optimizing the use of limited input pins by time-sharing connections.
Table of Comparison
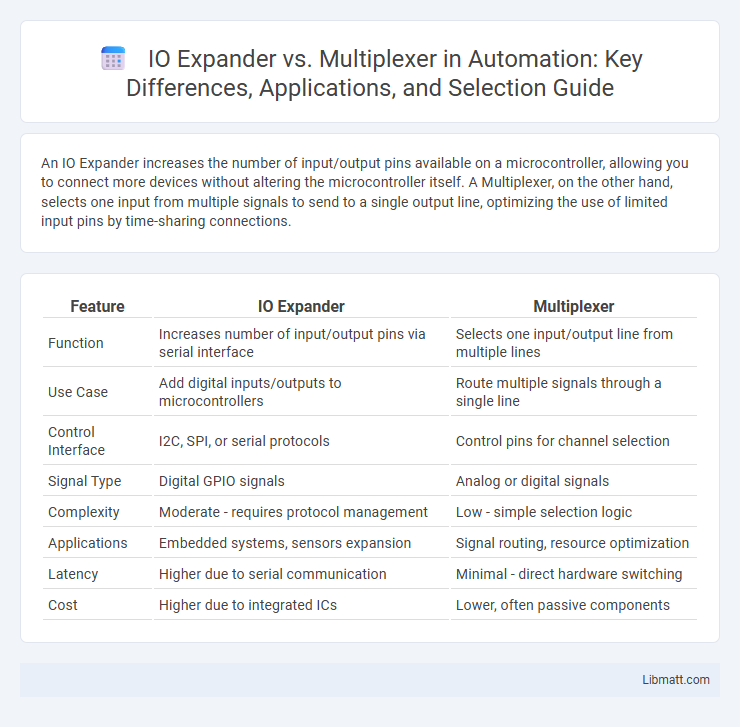
| Feature | IO Expander | Multiplexer |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Increases number of input/output pins via serial interface | Selects one input/output line from multiple lines |
| Use Case | Add digital inputs/outputs to microcontrollers | Route multiple signals through a single line |
| Control Interface | I2C, SPI, or serial protocols | Control pins for channel selection |
| Signal Type | Digital GPIO signals | Analog or digital signals |
| Complexity | Moderate - requires protocol management | Low - simple selection logic |
| Applications | Embedded systems, sensors expansion | Signal routing, resource optimization |
| Latency | Higher due to serial communication | Minimal - direct hardware switching |
| Cost | Higher due to integrated ICs | Lower, often passive components |
Introduction to IO Expanders and Multiplexers
IO expanders increase the number of input/output pins available on microcontrollers, enabling control of more devices with fewer microcontroller pins. Multiplexers select one input signal from many for data transmission, optimizing signal routing and resource usage. Both components are essential in embedded systems to manage multiple inputs and outputs efficiently while reducing wiring complexity.
What is an IO Expander?
An IO Expander is an integrated circuit that increases the number of input/output pins available on a microcontroller or processor, allowing for control of more devices using fewer microcontroller pins. It communicates typically via protocols like I2C or SPI, enabling the expansion of digital inputs or outputs without adding complexity to the main controller. Unlike multiplexers that select one signal from many, IO Expanders provide parallel access to multiple signals, facilitating simultaneous control and monitoring of numerous peripherals.
What is a Multiplexer?
A multiplexer (MUX) is a digital switch that selects one input from multiple data lines and forwards it to a single output, enabling efficient data routing in electronic circuits. It reduces the number of I/O pins required by allowing multiple signals to share a single output line, controlled by select lines. Unlike an IO expander, which increases the number of input/output pins available, a multiplexer primarily focuses on channel selection and signal gating.
Core Functions and Applications
IO Expanders increase the number of input/output pins available on a microcontroller, enabling Your system to control more peripherals such as sensors, LEDs, or switches without expanding hardware complexity. Multiplexers select one input signal from multiple inputs to send to a single output line, optimizing signal management in data acquisition or communication systems. Both components enhance interface efficiency, with IO Expanders suited for GPIO extension and Multiplexers ideal for channel selection in signal routing applications.
IO Expander vs Multiplexer: Key Differences
IO Expanders increase the number of input/output pins available on a microcontroller, enabling the control of multiple devices with fewer MCU pins by using communication protocols like I2C or SPI. Multiplexers select one input signal from multiple inputs to pass to a single output line, optimizing the use of limited input channels by switching between signals rather than expanding PIN count. Key differences include IO Expanders providing parallel input/output expansion, while Multiplexers offer selection between multiple signals, both enhancing microcontroller interfacing but addressing different hardware constraints.
Advantages of Using IO Expanders
IO expanders increase the number of input/output pins available on microcontrollers, allowing Your projects to handle more sensors or actuators without upgrading the main controller. They often use protocols like I2C or SPI, offering efficient communication with minimal pin usage, which reduces wiring complexity. Compared to multiplexers, IO expanders provide independent pin control, enabling simultaneous operation of multiple inputs or outputs.
Benefits of Multiplexers in Circuit Design
Multiplexers streamline circuit design by enabling multiple input signals to share a single communication line, significantly reducing the number of required input/output pins. They enhance signal routing efficiency and minimize hardware complexity, lowering costs and improving scalability in embedded systems. Multiplexers also facilitate faster data processing by enabling selective signal transmission, which optimizes performance in complex electronic applications.
Choosing Between IO Expander and Multiplexer
Choosing between an IO Expander and a Multiplexer depends on your specific input/output needs and hardware constraints. An IO Expander increases the number of available GPIO pins via I2C or SPI interfaces, ideal for adding multiple sensors or buttons without complex wiring. A Multiplexer, on the other hand, allows you to select one signal from several inputs, optimizing limited pin usage for applications like analog sensor reading or digital input scanning.
Common Use Cases and Examples
IO expanders are commonly used in microcontroller projects to increase the number of input/output pins, enabling connection of multiple sensors, LEDs, or switches without redesigning the main board. Multiplexers are frequently employed in applications requiring selection between several input signals, such as reading multiple analog sensors with a single analog-to-digital converter (ADC) channel. Typical examples include using an IO expander like the MCP23017 for keypad matrices and a 74HC4051 multiplexer for signal routing in data acquisition systems.
Conclusion: Which Solution Fits Your Needs?
IO Expanders provide additional input/output pins by communicating via protocols like I2C or SPI, making them ideal for applications requiring numerous discrete signals with minimal wiring complexity. Multiplexers allow multiple signals to share a single input or output line, optimizing pin usage when sequential access to signals is acceptable and cost constraints are critical. Your choice depends on whether simultaneous access to multiple pins (favoring IO Expanders) or time-shared access to signals (favoring Multiplexers) better suits your project requirements.
IO Expander vs Multiplexer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com