Point to Point topology establishes a direct connection between two devices, ensuring fast and secure data transfer with minimal latency. Bus topology connects multiple devices via a single communication line, which can be cost-effective but may lead to data collisions and network slowdowns as your system expands.
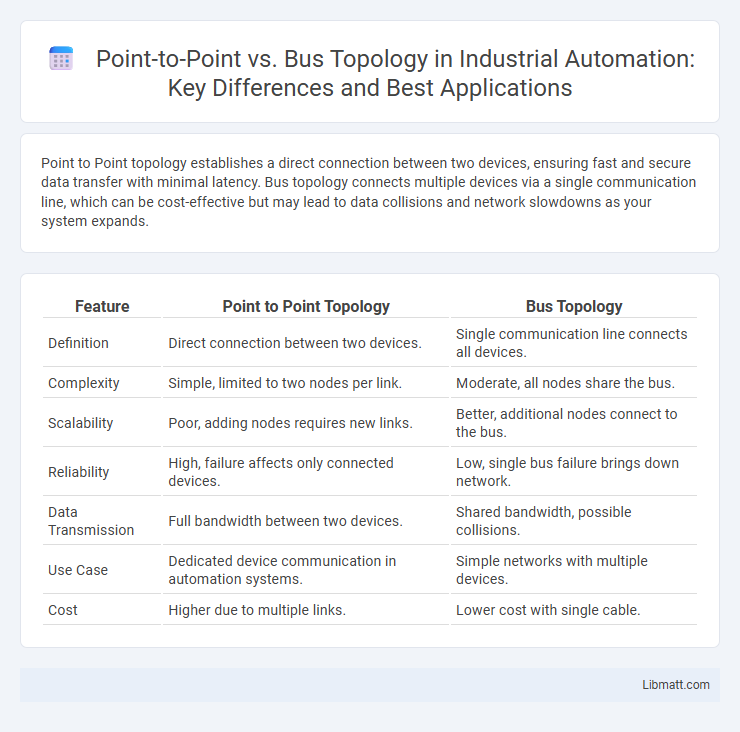
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Point to Point Topology | Bus Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct connection between two devices. | Single communication line connects all devices. |
| Complexity | Simple, limited to two nodes per link. | Moderate, all nodes share the bus. |
| Scalability | Poor, adding nodes requires new links. | Better, additional nodes connect to the bus. |
| Reliability | High, failure affects only connected devices. | Low, single bus failure brings down network. |
| Data Transmission | Full bandwidth between two devices. | Shared bandwidth, possible collisions. |
| Use Case | Dedicated device communication in automation systems. | Simple networks with multiple devices. |
| Cost | Higher due to multiple links. | Lower cost with single cable. |
Introduction to Network Topologies
Network topologies define the arrangement of devices and data paths in a network, crucial for efficient communication and performance. Point to Point topology involves direct connections between two devices, offering simplicity and dedicated bandwidth, ideal for secure, low-latency links. Bus topology connects multiple nodes along a shared communication line, optimizing cost and setup but potentially causing data collisions and limited scalability.
Overview of Point to Point Topology
Point to Point topology directly connects two devices through a dedicated communication link, ensuring exclusive and reliable data transmission with minimal latency. This topology is highly efficient for simple, low-complexity networks where a direct and secure connection is required, such as in device-to-device communication or small-scale setups. Its straightforward design reduces the chances of collisions and makes troubleshooting easier compared to more complex topologies like bus or star.
Overview of Bus Topology
Bus topology connects all devices to a single central cable called the bus or backbone, allowing data to travel in both directions along the line. This configuration is cost-effective and easy to implement for small networks but often suffers from limited scalability and potential data collisions. Your network performance can degrade significantly if the main cable fails, making troubleshooting and maintenance more challenging compared to alternative topologies.
Key Differences Between Point to Point and Bus Topology
Point to Point topology involves a direct communication link between two devices, ensuring dedicated bandwidth and simple data transfer. Bus topology connects multiple devices on a single communication line, where all nodes share the same data path, which can lead to data collisions and requires terminators at both ends of the bus. Point to Point offers higher security and reliability due to the exclusive connection, while Bus topology is more cost-effective and easier to implement for small networks but less scalable and prone to network failures if the main bus line is damaged.
Advantages of Point to Point Topology
Point to Point topology offers direct communication between two devices, ensuring high-speed data transfer and low latency without interference. This topology simplifies troubleshooting and enhances security by isolating connections, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Its straightforward architecture supports reliable and dedicated bandwidth, making it ideal for critical and real-time applications.
Advantages of Bus Topology
Bus topology offers cost-effective installation and requires less cable than other network structures, making it ideal for small networks. It simplifies network expansion since devices can be easily connected to the main cable without complex configurations. Your network benefits from straightforward troubleshooting due to the linear layout, enhancing overall maintenance efficiency.
Limitations of Point to Point Topology
Point to Point topology faces limitations such as restricted scalability since each connection links only two devices, making network expansion costly and complex. It lacks flexibility for adding new devices, as every additional node requires a new dedicated line, leading to increased cabling and hardware expenses. Your network may encounter inefficiencies in larger environments due to the impracticality of managing numerous individual connections.
Limitations of Bus Topology
Bus topology faces significant limitations including a single point of failure, where a break in the main cable disrupts the entire network. It suffers from data collisions and signal degradation as more devices are connected, reducing overall performance and network reliability. Scalability is restricted due to difficulty in troubleshooting and network expansion, making bus topology less suitable for larger or more dynamic environments compared to point-to-point topology.
Use Cases and Applications
Point to Point topology is ideal for direct, private communication between two devices, frequently used in telephone lines, dedicated data links, and fiber optic connections where secure, high-speed transfers are crucial. Bus topology suits small networks with minimal device connections, commonly found in legacy Ethernet LANs, where simple setup and cost-efficiency are prioritized despite scalability limitations. Choosing Point to Point enhances reliability in critical systems like financial transactions, while Bus topology supports lightweight networks such as small office environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Topology
Choosing the right topology depends on your network size, complexity, and communication needs. Point to Point topology offers direct, high-speed connections ideal for simple, dedicated links, while Bus topology supports multiple devices on a single communication line, suited for smaller networks with limited traffic. Evaluating factors like scalability, fault tolerance, and maintenance will help you determine the most efficient and cost-effective topology for your specific environment.
Point to Point vs Bus Topology Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com