Profibus offers robust fieldbus communication for industrial automation with high reliability and speed, ideal for real-time data exchange in manufacturing environments. Profinet enhances network flexibility by integrating Ethernet technology, supporting seamless connectivity and improved diagnostics for your industrial Ethernet applications.
Table of Comparison
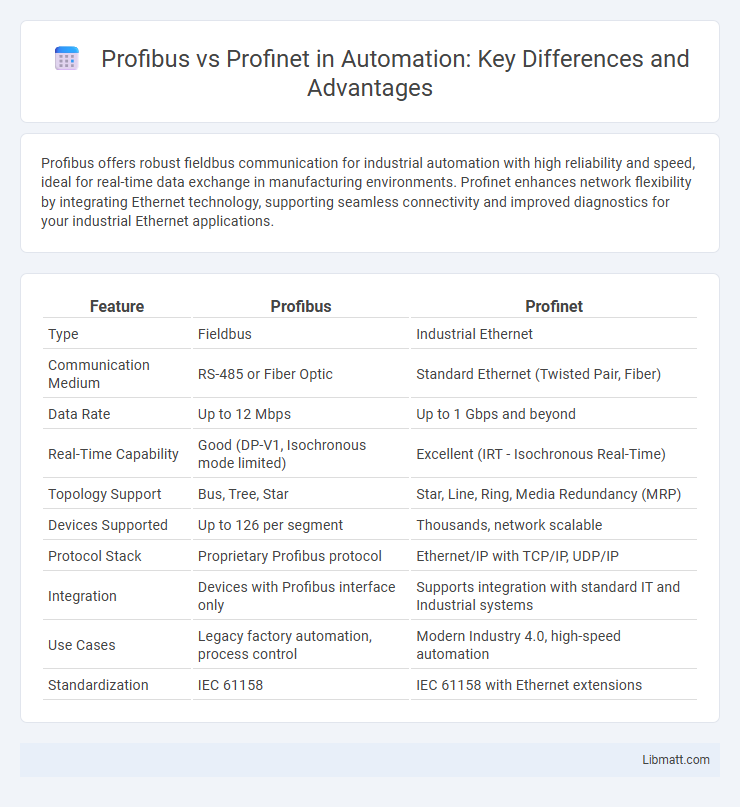
| Feature | Profibus | Profinet |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Fieldbus | Industrial Ethernet |
| Communication Medium | RS-485 or Fiber Optic | Standard Ethernet (Twisted Pair, Fiber) |
| Data Rate | Up to 12 Mbps | Up to 1 Gbps and beyond |
| Real-Time Capability | Good (DP-V1, Isochronous mode limited) | Excellent (IRT - Isochronous Real-Time) |
| Topology Support | Bus, Tree, Star | Star, Line, Ring, Media Redundancy (MRP) |
| Devices Supported | Up to 126 per segment | Thousands, network scalable |
| Protocol Stack | Proprietary Profibus protocol | Ethernet/IP with TCP/IP, UDP/IP |
| Integration | Devices with Profibus interface only | Supports integration with standard IT and Industrial systems |
| Use Cases | Legacy factory automation, process control | Modern Industry 4.0, high-speed automation |
| Standardization | IEC 61158 | IEC 61158 with Ethernet extensions |
Introduction to Profibus and Profinet
Profibus is a widely used fieldbus communication protocol designed for real-time automation in industrial environments, enabling devices to communicate efficiently over serial networks. Profinet, on the other hand, is an advanced Ethernet-based protocol that supports faster data transmission and greater flexibility for complex automation systems. Your choice between Profibus and Profinet depends on the required network speed, scalability, and integration with modern industrial Ethernet standards.
Historical Development and Evolution
Profibus, developed in the 1980s by a consortium including Siemens and Bosch, emerged as one of the first standardized fieldbus systems for industrial automation, enabling reliable communication between sensors, actuators, and controllers. Profinet, introduced in the early 2000s as an Ethernet-based successor, leverages standard TCP/IP protocols to provide faster data transmission, real-time communication, and enhanced interoperability in modern industrial networks. The evolution from Profibus to Profinet reflects the industry's shift from serial communication to Ethernet technology, accommodating the increasing demand for higher bandwidth and integration with IT systems.
Core Technologies and Architectures
Profibus relies on a master-slave architecture using RS-485 or fiber optic physical layers, implementing a deterministic cyclic communication for real-time industrial automation. Profinet, built on Ethernet protocols, utilizes a scalable client-server and producer-consumer model supporting real-time and isochronous real-time data exchange via TCP/IP and UDP. Core technologies in Profibus focus on fieldbus standards optimized for device-level communication, while Profinet emphasizes integration with IT networks, high bandwidth, and flexibility for Industry 4.0 applications.
Communication Protocols Explained
Profibus and Profinet are industrial communication protocols designed for automation systems, with Profibus based on serial communication using RS-485, while Profinet utilizes Ethernet for faster data transfer and real-time performance. Profibus supports cyclic and acyclic data exchange suited for decentralized automation, whereas Profinet offers enhanced diagnostics, scalability, and seamless integration with IT networks. Understanding the protocols' specifications helps optimize your industrial network's reliability and speed in process control environments.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Profibus offers data transmission speeds up to 12 Mbps, making it suitable for moderate-speed industrial automation applications, while Profinet utilizes Ethernet technology, supporting speeds up to 100 Mbps or higher, enabling faster real-time communication and higher bandwidth for complex processes. Profinet's performance advantage lies in its ability to handle large volumes of data with minimal latency, improving network responsiveness and system efficiency. Your choice should consider the required communication speed and system complexity, with Profinet preferred for high-performance, time-critical environments.
Network Topologies and Scalability
Profibus supports linear, star, and tree network topologies, offering flexibility but with limited scalability due to its master-slave communication structure. Profinet, utilizing Ethernet technology, enables more complex topologies like ring, star, and line, providing superior scalability and real-time capabilities essential for larger industrial networks. Your choice between Profibus and Profinet impacts network expansion potential and the ability to integrate diverse automation devices efficiently.
Compatibility and Integration
Profibus and Profinet differ significantly in compatibility and integration within industrial automation environments; Profibus uses a serial communication protocol ideal for legacy systems, while Profinet employs Ethernet-based technology supporting real-time data exchange and enhanced network flexibility. Profinet provides superior integration with modern IT infrastructures, enabling seamless interoperability with Industrial Ethernet devices and higher data throughput. Many industrial setups adopt Profinet for new installations yet maintain Profibus networks for existing equipment, leveraging gateways and protocol converters to ensure system compatibility.
Application Areas and Industry Use Cases
Profibus is predominantly used in manufacturing automation and process control environments, offering reliable communication for sensors, actuators, and PLCs in industries like automotive and pharmaceuticals. Profinet excels in industrial Ethernet applications, enabling real-time data exchange and integrating complex automation systems in sectors such as robotics, conveyor systems, and factory automation. Your choice between Profibus and Profinet depends on the network infrastructure requirements and the level of flexibility needed for Industry 4.0 implementations.
Security Features and Considerations
Profibus primarily focuses on robust real-time communication but lacks advanced native security features, making it more susceptible to unauthorized access and cyber threats in industrial environments. Profinet incorporates built-in security mechanisms such as device authentication, integrity checks, and encryption to protect data and ensure secure communication across networks. Your industrial automation security strategy benefits significantly from leveraging Profinet's comprehensive security features to safeguard critical infrastructure against evolving cyber risks.
Future Trends and Industry Adoption
Profibus and Profinet are evolving to meet future industrial automation demands, with Profinet gaining significant traction due to its Ethernet-based architecture, which supports higher data speeds and enhanced integration with Industry 4.0 technologies. Industry adoption is increasingly favoring Profinet for its scalability, real-time communication capabilities, and compatibility with IoT platforms, making it suitable for smart factories and digital transformation initiatives. Your choice between Profibus and Profinet should consider long-term industry trends emphasizing network flexibility, speed, and interoperability to ensure future-proof automation solutions.
Profibus vs Profnet Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com