Local control offers immediate, hands-on management of devices or systems within close proximity, ensuring quicker response times and enhanced security. Your choice between local and remote control depends on the need for convenience, accessibility, and the level of direct oversight required.
Table of Comparison
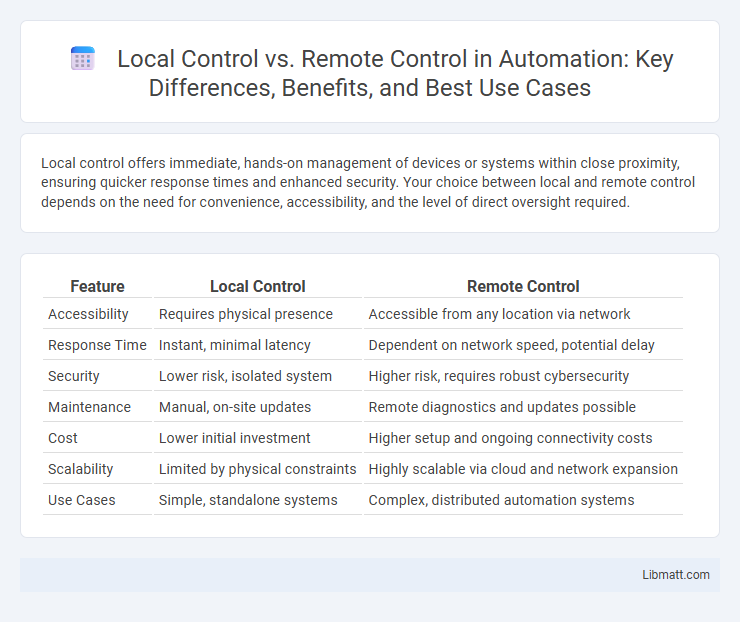
| Feature | Local Control | Remote Control |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Requires physical presence | Accessible from any location via network |
| Response Time | Instant, minimal latency | Dependent on network speed, potential delay |
| Security | Lower risk, isolated system | Higher risk, requires robust cybersecurity |
| Maintenance | Manual, on-site updates | Remote diagnostics and updates possible |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher setup and ongoing connectivity costs |
| Scalability | Limited by physical constraints | Highly scalable via cloud and network expansion |
| Use Cases | Simple, standalone systems | Complex, distributed automation systems |
Introduction to Local Control vs Remote Control
Local control involves managing devices or systems directly on-site, allowing immediate interaction and real-time adjustments without network dependency. Remote control enables operation from a distant location through internet or network connections, offering convenience and access to systems beyond physical reach. Both approaches play critical roles in automation, security, and operational efficiency across industries such as manufacturing, IT, and smart home technologies.
Defining Local Control Systems
Local control systems are designed to operate directly at the site of the equipment or process, enabling immediate response and real-time management without dependency on external communication networks. These systems utilize sensors, controllers, and actuators in close proximity, ensuring low latency and high reliability in critical industrial and manufacturing environments. The primary advantage of local control lies in its ability to maintain continuous operation during network outages or remote access failures.
Understanding Remote Control Technologies
Remote control technologies utilize wireless communication methods such as infrared, radio frequency (RF), Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi to operate devices from a distance, enhancing convenience and accessibility. These technologies enable real-time command transmission between a controller and a device, supporting applications from consumer electronics like TVs and drones to industrial automation systems. Advances in IoT integration and mobile app development further optimize remote control capabilities, allowing seamless device management across diverse environments.
Key Differences Between Local and Remote Control
Local control operates directly at the device or machine site, enabling immediate response with minimal latency and enhanced security through physical access. Remote control relies on network connectivity to manage devices from distant locations, offering greater flexibility and scalability but potentially introducing latency and cybersecurity risks. The choice between local and remote control depends on factors like operational environment, response time requirements, and security considerations.
Advantages of Local Control
Local control offers faster response times and enhanced reliability by eliminating dependence on network connectivity. It provides greater security since control commands remain within the local system, reducing vulnerability to external attacks. Your operations benefit from simplified troubleshooting and maintenance, as direct access to equipment enables immediate adjustments and monitoring.
Benefits of Remote Control
Remote control systems offer significant benefits by enabling users to operate devices and manage processes from virtually any location, increasing flexibility and operational efficiency. They reduce the need for on-site presence, lowering labor costs and minimizing downtime through immediate troubleshooting and adjustments. Enhanced security features and real-time monitoring capabilities further contribute to improved system reliability and faster response times.
Limitations of Local Control
Local control systems often face limitations such as restricted operational range, slower response times, and increased vulnerability to human error due to manual intervention. These constraints can lead to inefficiencies in monitoring and adjusting complex processes, especially when real-time data access and swift decision-making are crucial. Your ability to manage expansive or distributed systems remotely becomes significantly hindered when relying solely on local control methods.
Challenges of Remote Control
Remote control poses challenges such as signal latency, which can disrupt real-time operations and reduce system responsiveness. Network reliability and security concerns also affect the consistent performance and protection of remote-controlled devices. Your ability to manage these issues depends on robust infrastructure and effective cybersecurity measures.
Choosing Between Local and Remote Control: Factors to Consider
Choosing between local and remote control depends on factors such as response time, security requirements, and system accessibility. Local control offers faster response and higher security by limiting access, while remote control provides flexibility and convenience for managing systems from different locations. Evaluate your operational needs, network reliability, and potential risks to determine the best control method for your applications.
Future Trends in Control Systems
Future trends in control systems emphasize the integration of AI-powered remote control with enhanced local control stability to maximize efficiency and responsiveness. Advanced IoT devices facilitate seamless communication between local controllers and cloud platforms, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time decision-making. Your control strategy will increasingly leverage hybrid architectures combining edge computing and centralized intelligence for optimized automation solutions.
Local Control vs Remote Control Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com