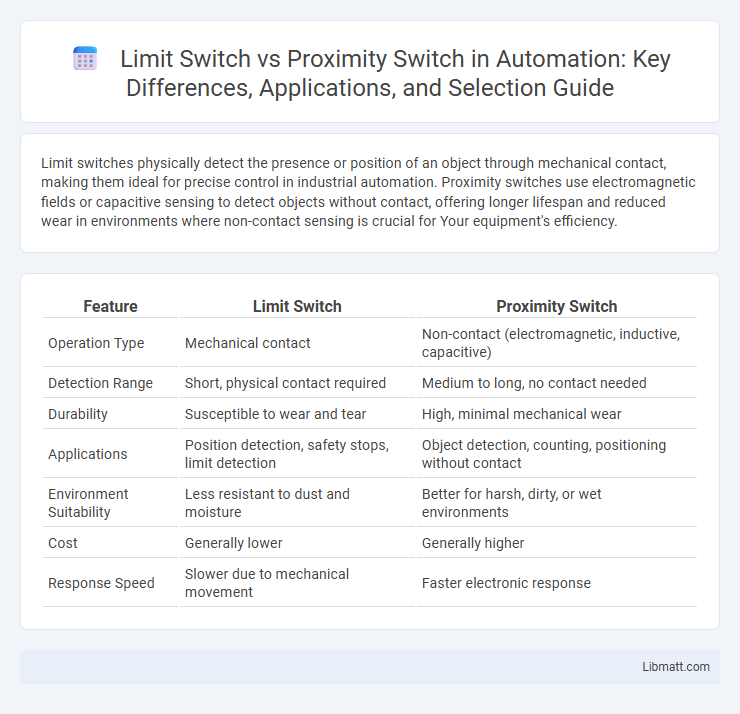
Limit switches physically detect the presence or position of an object through mechanical contact, making them ideal for precise control in industrial automation. Proximity switches use electromagnetic fields or capacitive sensing to detect objects without contact, offering longer lifespan and reduced wear in environments where non-contact sensing is crucial for Your equipment's efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Limit Switch | Proximity Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Type | Mechanical contact | Non-contact (electromagnetic, inductive, capacitive) |
| Detection Range | Short, physical contact required | Medium to long, no contact needed |
| Durability | Susceptible to wear and tear | High, minimal mechanical wear |
| Applications | Position detection, safety stops, limit detection | Object detection, counting, positioning without contact |
| Environment Suitability | Less resistant to dust and moisture | Better for harsh, dirty, or wet environments |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Response Speed | Slower due to mechanical movement | Faster electronic response |
Introduction to Limit Switches and Proximity Switches
Limit switches are electromechanical devices designed to detect the physical presence or position of an object by making direct contact, commonly used in industrial automation to control machinery and ensure safety. Proximity switches operate without physical contact, using electromagnetic fields or capacitive sensing to detect the presence of nearby objects, offering high durability and fast response times in various applications. Both switches serve critical roles in manufacturing processes, with limit switches excelling in mechanical position detection and proximity switches providing non-contact sensing solutions.
Working Principle of Limit Switches
Limit switches operate through physical contact, detecting the presence or position of an object by mechanically triggering an internal switch when an object pushes or passes a lever, plunger, or roller actuator. This mechanical movement changes the electrical state of the switch, sending a signal to control equipment or machinery. Your automation system relies on this direct physical interaction for precise position control in applications such as conveyor systems, safety interlocks, and end-of-travel detection.
Working Principle of Proximity Switches
Proximity switches operate on the principle of detecting the presence or absence of an object without physical contact by utilizing electromagnetic fields, capacitance changes, or inductive coupling. These switches emit a sensing field, and when a metallic or conductive target enters this field, the switch changes its output state to signal detection. Your automation system benefits from enhanced durability and reduced mechanical wear due to this contactless detection method.
Key Differences Between Limit Switches and Proximity Switches
Limit switches are electromechanical devices that require physical contact to detect the position or presence of an object, providing precise end-of-travel signals in machinery. Proximity switches utilize electromagnetic fields or capacitive sensing to detect objects without contact, enabling non-intrusive operation and longer lifespan in harsh environments. Key differences include their sensing method, durability, response time, and suitability for applications involving physical contact versus non-contact detection.
Types of Limit Switches
Limit switches come in various types, including plunger, roller lever, and whisker arm switches, each designed for specific mechanical actuation methods. These switches physically detect the presence or position of an object by direct contact, providing reliable on/off signals in industrial automation. Your choice of limit switch depends on application requirements such as operating environment, actuation force, and mounting constraints.
Types of Proximity Switches
Proximity switches include inductive, capacitive, ultrasonic, and photoelectric types, each designed to detect specific materials or objects without physical contact. Inductive proximity switches sense metallic objects through electromagnetic fields, while capacitive switches detect both metallic and non-metallic materials by sensing changes in capacitance. Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves for distance measurement and detection of various materials, whereas photoelectric switches rely on light beams to detect object presence or absence.
Applications of Limit Switches
Limit switches are widely used in industrial automation to detect the physical presence or position of objects, ensuring precise control of machinery movements. Common applications include machine safety interlocks, conveyor belt end detection, and elevator door positioning, where reliable mechanical contact feedback is essential. Your equipment benefits from limit switches by providing accurate limits for moving parts, preventing mechanical overtravel and costly damage.
Applications of Proximity Switches
Proximity switches are widely used in industrial automation for object detection, positioning, and speed monitoring without physical contact, enhancing durability and reducing wear. Common applications include conveyor systems, robotic arms, and safety interlocks in manufacturing processes. Their ability to sense metal, plastic, or other materials makes them ideal for automated assembly lines and machine tool control.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Limit vs Proximity Switch
Limit switches offer precise mechanical actuation and reliable position detection with clear on/off signals, making them ideal for harsh environments and machinery safety controls. Proximity switches provide non-contact detection, reducing wear and maintenance while enabling faster response times and longer lifespan, though they can be sensitive to environmental factors such as metal interference or dirt. Your choice depends on application requirements for durability, accuracy, and maintenance considerations, weighing the mechanical robustness of limit switches against the convenience and longevity of proximity sensors.
How to Choose Between Limit Switch and Proximity Switch
Choosing between a limit switch and a proximity switch depends on factors such as the operating environment, desired detection type, and durability requirements. Limit switches are ideal for applications needing physical contact to detect position or motion, offering reliable mechanical feedback in harsh conditions. Proximity switches excel in non-contact detection, providing faster response times and longer lifespan, especially in environments where contamination or wear could impact performance.
Limit Switch vs Proximity Switch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com