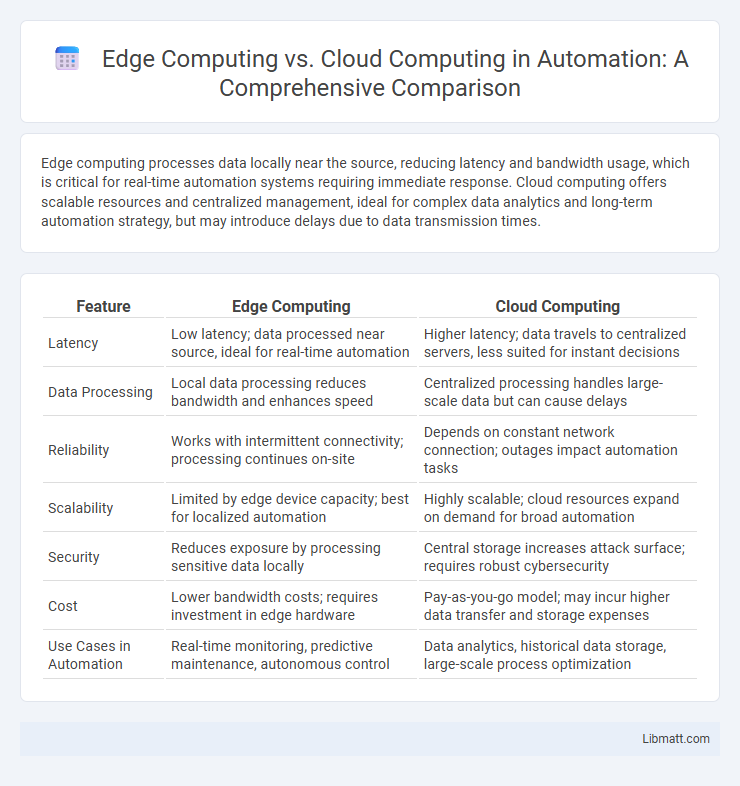
Edge computing processes data locally near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage, which is critical for real-time automation systems requiring immediate response. Cloud computing offers scalable resources and centralized management, ideal for complex data analytics and long-term automation strategy, but may introduce delays due to data transmission times.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Low latency; data processed near source, ideal for real-time automation | Higher latency; data travels to centralized servers, less suited for instant decisions |
| Data Processing | Local data processing reduces bandwidth and enhances speed | Centralized processing handles large-scale data but can cause delays |
| Reliability | Works with intermittent connectivity; processing continues on-site | Depends on constant network connection; outages impact automation tasks |
| Scalability | Limited by edge device capacity; best for localized automation | Highly scalable; cloud resources expand on demand for broad automation |
| Security | Reduces exposure by processing sensitive data locally | Central storage increases attack surface; requires robust cybersecurity |
| Cost | Lower bandwidth costs; requires investment in edge hardware | Pay-as-you-go model; may incur higher data transfer and storage expenses |
| Use Cases in Automation | Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, autonomous control | Data analytics, historical data storage, large-scale process optimization |
Introduction: Automation’s Evolution with Edge and Cloud Computing
Edge computing enhances automation by processing data closer to where it's generated, reducing latency and improving real-time responsiveness in industrial applications. Cloud computing offers scalable resources and centralized data management, enabling extensive analytics and machine learning for optimizing automated systems. Your automation strategy benefits from combining edge's low-latency processing with the cloud's powerful computational capabilities for comprehensive efficiency and innovation.
Defining Cloud Computing in Automation
Cloud Computing in automation delivers scalable, on-demand access to centralized computing resources, enabling seamless integration and management of automated processes across distributed systems. It supports real-time data analytics and remote control of devices by leveraging virtualized infrastructure hosted on the internet, reducing the need for local hardware. Your automation workflows benefit from cloud services through enhanced flexibility, cost efficiency, and rapid deployment.
Understanding Edge Computing for Automated Systems
Edge computing processes data locally on devices or nearby servers, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making essential for automated systems. Unlike cloud computing, which relies on centralized data centers, edge computing enhances system reliability and bandwidth efficiency by minimizing data transfer. Your automated system benefits from faster response times and improved privacy by leveraging edge computing for critical tasks.
Key Differences: Edge vs Cloud in Automation
Edge computing processes data locally on devices or nearby servers, reducing latency crucial for real-time automation tasks, while cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote data centers, offering scalability and vast storage capacity. In automation, edge computing enables faster decision-making and reduces dependence on constant internet connectivity, whereas cloud computing excels in handling complex analytics and long-term data storage. Choosing between edge and cloud depends on your automation needs for speed, data volume, and network reliability.
Latency and Real-Time Processing in Automation
Edge computing significantly reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, enabling faster decision-making crucial for real-time automation tasks such as industrial robotics and autonomous vehicles. Cloud computing, while offering scalable resources and extensive data storage, often experiences higher latency due to data transmission to centralized servers, which can delay time-sensitive responses. Automation systems demanding immediate data processing and minimal delay increasingly rely on edge computing to optimize performance and ensure real-time operational efficiency.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
Edge computing enhances data security and privacy in automation by processing sensitive information locally, reducing exposure to potential breaches during transmission. Cloud computing relies on centralized servers that may increase vulnerability to cyberattacks but offer robust encryption and compliance measures for large-scale data storage. Your automation system benefits from a hybrid approach that leverages edge computing for real-time, secure data handling and cloud computing for comprehensive analytics and long-term storage.
Scalability and Deployment Flexibility
Edge computing offers enhanced deployment flexibility by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage, which is crucial for real-time automation systems. Cloud computing provides superior scalability, enabling businesses to dynamically allocate resources and handle vast amounts of data across distributed networks. Your automation infrastructure benefits from a hybrid approach that leverages edge for immediate responsiveness and cloud for expansive, scalable processing.
Cost Implications in Edge and Cloud Automation
Edge computing reduces latency and bandwidth costs by processing data closer to the source, which minimizes the need for continuous data transfer to centralized cloud servers. Cloud computing offers scalability and lower upfront infrastructure investments but can lead to higher ongoing expenses due to data storage, transmission, and processing fees. Your choice between edge and cloud automation should consider the trade-offs between real-time processing costs and scalable resource management.
Industry Use Cases: Edge vs Cloud in Automation
Edge computing enables real-time data processing for automation in industries like manufacturing, where low latency is crucial for robotic control and predictive maintenance. Cloud computing offers scalable storage and powerful analytics, ideal for large-scale data aggregation and machine learning in sectors such as supply chain management and smart grids. Your automation strategy benefits from combining edge's rapid response capabilities with cloud's extensive computational resources to optimize operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Computing Model for Your Automation Needs
Edge computing processes data locally on devices or nearby servers, reducing latency and enhancing real-time automation control, which is crucial for time-sensitive industrial applications. Cloud computing offers vast scalability, centralized data management, and powerful analytics, ideal for automations requiring extensive data processing and integration across multiple locations. Your choice between edge and cloud computing depends on the balance between latency requirements, data volume, security concerns, and the complexity of your automation tasks.
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing (in automation) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com