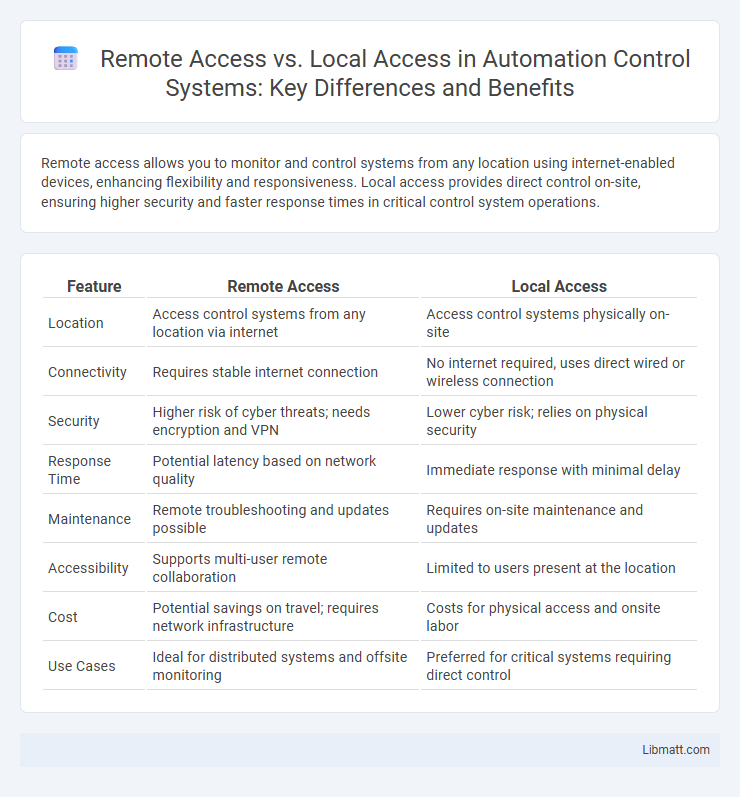
Remote access allows you to monitor and control systems from any location using internet-enabled devices, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness. Local access provides direct control on-site, ensuring higher security and faster response times in critical control system operations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Remote Access | Local Access |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Access control systems from any location via internet | Access control systems physically on-site |
| Connectivity | Requires stable internet connection | No internet required, uses direct wired or wireless connection |
| Security | Higher risk of cyber threats; needs encryption and VPN | Lower cyber risk; relies on physical security |
| Response Time | Potential latency based on network quality | Immediate response with minimal delay |
| Maintenance | Remote troubleshooting and updates possible | Requires on-site maintenance and updates |
| Accessibility | Supports multi-user remote collaboration | Limited to users present at the location |
| Cost | Potential savings on travel; requires network infrastructure | Costs for physical access and onsite labor |
| Use Cases | Ideal for distributed systems and offsite monitoring | Preferred for critical systems requiring direct control |
Introduction to Access Control Systems
Access control systems manage entry permissions to physical or digital environments, ensuring security and operational efficiency. Remote access allows users to control systems from any location via secure networks, while local access requires physical presence at the control point. Understanding these differences helps you optimize security protocols and system responsiveness based on specific operational needs.
Defining Remote Access in Control Systems
Remote access in control systems enables operators to monitor and manage industrial processes or machinery from geographically dispersed locations using secure network connections. This capability leverages technologies such as VPNs, encrypted protocols, and specialized software to ensure real-time data exchange and command execution without physical presence. Remote access enhances operational efficiency, rapid troubleshooting, and centralized management, contrasting with local access that requires direct on-site interaction with control system interfaces.
Understanding Local Access in Control Systems
Local access in control systems refers to the direct interaction with machinery or devices at the physical site, enabling operators to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot without relying on external networks. This method ensures lower latency, enhanced security by reducing exposure to cyber threats, and immediate response times critical for real-time control applications. Understanding local access is essential for environments requiring precise, dependable control where network connectivity may be limited or unreliable.
Key Differences Between Remote and Local Access
Remote access in control systems enables users to monitor and manage operations from any location via secure internet connections, while local access requires physical presence at the control site. Key differences include latency, security risks, and accessibility; remote access introduces potential cybersecurity vulnerabilities but offers flexibility and real-time data exchange, whereas local access provides direct control with minimal network delay and enhanced protection against external threats. The choice between remote and local access depends on factors such as operational complexity, need for immediate intervention, and organizational security policies.
Security Implications: Remote vs Local Access
Remote access control systems expose your network to a broader attack surface, increasing vulnerability to cyber threats such as unauthorized intrusions and data breaches. Local access limits exposure by restricting control to physically present users, reducing risks associated with external hacking attempts. Implementing robust authentication and encryption protocols is essential to secure both remote and local access environments effectively.
Performance and Reliability Considerations
Remote access in control systems often faces latency and potential network disruptions that can affect real-time performance and system responsiveness, while local access offers lower latency and higher reliability due to direct connection to the control hardware. Local control systems minimize latency and data packet loss, ensuring consistent real-time monitoring and faster response times critical for safety and operational efficiency. Performance optimization relies on minimizing communication delays and ensuring uninterrupted signal integrity, making local access preferable for mission-critical applications where reliability and real-time control are paramount.
Costs and Infrastructure Requirements
Remote access control systems typically involve higher initial setup costs due to the need for secure network infrastructure, VPNs, or cloud services, but reduce ongoing expenses by minimizing on-site staffing and maintenance. Local access systems require substantial investment in physical infrastructure such as cabling, dedicated hardware, and on-premise servers, leading to higher maintenance and upgrade costs over time. Both approaches impact total cost of ownership differently, with remote access offering scalability and lower long-term infrastructure expenses, while local access demands robust on-site resources and continuous technical support.
Use Cases: When to Choose Remote or Local Access
Remote access suits scenarios requiring system monitoring or control from distant locations, ideal for managing distributed control systems or troubleshooting without onsite presence. Local access is essential when direct, real-time interaction with equipment ensures safety and precision, such as during system commissioning or critical maintenance tasks. Your choice depends on factors like urgency, physical security, and the need for immediate feedback in control operations.
Emerging Trends in Access Control Systems
Emerging trends in access control systems highlight a growing shift from traditional local access methods to more sophisticated remote access solutions powered by cloud computing and IoT integration. Remote access enables real-time monitoring and control of security systems from anywhere, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness in modern facilities. Your organization can benefit from adaptive access controls that use AI-driven analytics to detect anomalies and improve overall security posture.
Best Practices for Secure Access Management
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is essential for both remote and local access in control systems to enhance security and prevent unauthorized entry. Segmentation of networks and strict access controls limit exposure, ensuring users only access necessary resources based on roles. Continuous monitoring and regular audits help detect anomalies and enforce compliance with security policies to maintain secure access management.
Remote Access vs Local Access (control systems) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com