Extraction involves removing specific compounds from a solid or liquid mixture through techniques like solvent use or mechanical separation, while infusion extracts flavors or active ingredients by soaking materials in a hot or cold liquid over time. Your choice between extraction and infusion depends on the desired concentration and properties of the final product.
Table of Comparison
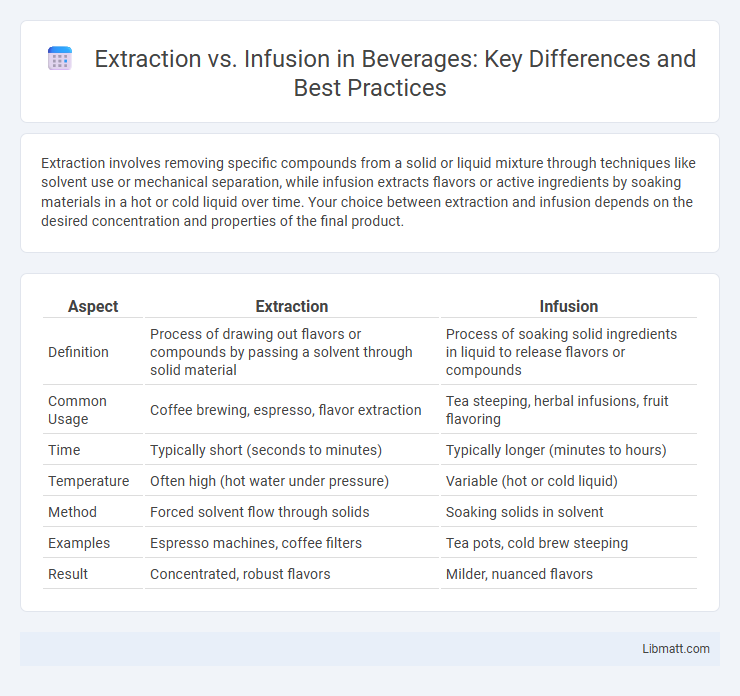
| Aspect | Extraction | Infusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of drawing out flavors or compounds by passing a solvent through solid material | Process of soaking solid ingredients in liquid to release flavors or compounds |
| Common Usage | Coffee brewing, espresso, flavor extraction | Tea steeping, herbal infusions, fruit flavoring |
| Time | Typically short (seconds to minutes) | Typically longer (minutes to hours) |
| Temperature | Often high (hot water under pressure) | Variable (hot or cold liquid) |
| Method | Forced solvent flow through solids | Soaking solids in solvent |
| Examples | Espresso machines, coffee filters | Tea pots, cold brew steeping |
| Result | Concentrated, robust flavors | Milder, nuanced flavors |
Understanding Extraction and Infusion
Extraction involves drawing out specific compounds from a substance using solvents or heat to concentrate flavors or active ingredients efficiently. Infusion, on the other hand, gently soaks ingredients in a liquid over time, allowing flavors to meld slowly and develop depth without intense heat. Your choice between extraction and infusion depends on the desired intensity and speed of flavor release in culinary or herbal applications.
Key Differences Between Extraction and Infusion
Extraction involves separating specific compounds from a material using solvents, solutes, or physical processes to obtain concentrated active ingredients, while infusion relies on steeping substances in a liquid to transfer flavors or beneficial properties. Extraction typically targets precise, potent elements from raw materials, providing higher purity, whereas infusion produces milder, more nuanced profiles by soaking ingredients over time. Your choice depends on whether you need a concentrated extract or a gentle infusion for culinary, medicinal, or aromatic applications.
Common Methods of Extraction
Common methods of extraction include solvent extraction, steam distillation, and cold pressing, each tailored to separate specific compounds from plant material or other substances. Solvent extraction utilizes chemicals like ethanol or hexane to dissolve desired compounds, while steam distillation captures volatile oils by vaporizing them with steam. Cold pressing mechanically presses ingredients, particularly in citrus fruits, to release essential oils without heat, preserving delicate aromatic compounds.
Popular Techniques of Infusion
Popular techniques of infusion include cold brew, where ingredients steep in cold water over an extended period, and hot infusion, which uses boiling water to rapidly extract flavors. Steam infusion utilizes vapor to capture delicate aromas without overheating, preserving subtle taste profiles. Alcohol infusion combines spirits with botanicals or fruits to create concentrated extracts used in cocktails and culinary applications.
Suitable Ingredients for Extraction
Extraction is ideal for robust ingredients like roots, barks, and seeds that require solvent or heat to release their active compounds effectively. Ingredients such as ginseng root, cinnamon bark, and coffee beans benefit significantly from extraction methods to maximize potency and concentration. Infusion, by contrast, is better suited for delicate parts like leaves and flowers, but your choice should favor extraction when targeting durable, dense materials for optimal results.
Best Materials for Infusion
Stainless steel, glass, and ceramic are the best materials for infusion due to their non-reactive properties, which preserve the flavor and integrity of herbs or teas. Silicone and BPA-free plastic can also be suitable, offering durability and heat resistance without altering the infusion's taste. Avoid metals like aluminum or copper that may react with acidic compounds, compromising the quality and safety of the infusion.
Flavor Profiles: Extraction vs. Infusion
Extraction involves drawing out flavors through processes like brewing or steeping, resulting in a concentrated and robust flavor profile that highlights the core characteristics of the ingredient. Infusion gently imparts subtle and complex notes by soaking ingredients in a liquid over time, often creating a more balanced and nuanced taste experience. Understanding the difference in extraction versus infusion helps you tailor flavor intensity and aroma to match your desired culinary or beverage outcome.
Tools and Equipment Needed
Extraction typically requires tools such as grinders, filters, and extraction machines designed to separate essential compounds from raw materials, including solvents for chemical extraction and pressure-based systems like espresso machines. Infusion often involves simpler equipment like teapots, infusers, or jars, where raw materials steep in a liquid medium, commonly hot water, allowing flavors and compounds to dissolve gradually. Both methods rely on temperature control devices, such as kettles or heating elements, to optimize the process for maximum yield and quality.
Applications in Culinary and Beverages
Extraction and infusion techniques are essential in culinary and beverage applications for enhancing flavor profiles and aroma. Extraction efficiently isolates concentrated essences, such as espresso shots or cold brew coffee, delivering intense taste and richness. Infusion infuses delicate flavors slowly into liquids, like herbal teas or flavored oils, allowing your dishes and drinks to develop subtle, layered aromas.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Extraction involves pulling active compounds from materials using solvents or mechanical processes, ideal for concentrated potency, while infusion gently releases flavors or properties by soaking ingredients in a liquid, best suited for delicate blends. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize strength and purity, favoring extraction, or prefer subtle, harmonious flavors that infusion offers. Understanding these differences ensures you select the most effective method for maximizing the desired qualities in your preparations.
Extraction vs infusion Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com