A tertiary air duct supplies additional air to improve combustion efficiency, while a cooler vent regulates temperature by allowing excess heat to escape. Understanding the difference helps you optimize airflow for better system performance and energy savings.
Table of Comparison
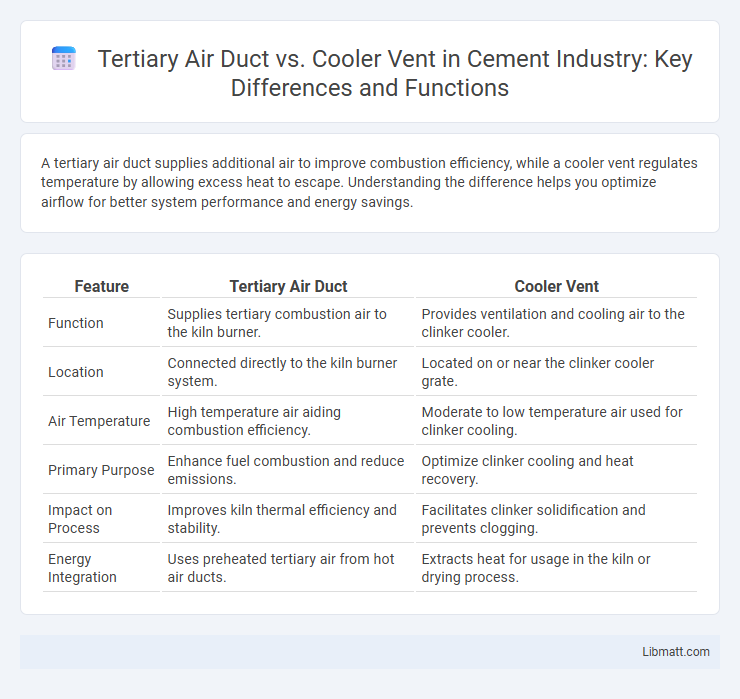
| Feature | Tertiary Air Duct | Cooler Vent |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Supplies tertiary combustion air to the kiln burner. | Provides ventilation and cooling air to the clinker cooler. |
| Location | Connected directly to the kiln burner system. | Located on or near the clinker cooler grate. |
| Air Temperature | High temperature air aiding combustion efficiency. | Moderate to low temperature air used for clinker cooling. |
| Primary Purpose | Enhance fuel combustion and reduce emissions. | Optimize clinker cooling and heat recovery. |
| Impact on Process | Improves kiln thermal efficiency and stability. | Facilitates clinker solidification and prevents clogging. |
| Energy Integration | Uses preheated tertiary air from hot air ducts. | Extracts heat for usage in the kiln or drying process. |
Introduction to Tertiary Air Ducts and Cooler Vents
Tertiary air ducts are designed to distribute conditioned air efficiently within HVAC systems, enhancing airflow control and energy performance in large commercial buildings. Cooler vents serve as outlets that regulate temperature by allowing cooled air to enter specific zones, improving occupant comfort and ventilation effectiveness. Both components are critical in optimizing indoor air quality and thermal management through precise air distribution strategies.
Key Functions of Tertiary Air Ducts
Tertiary air ducts play a crucial role in industrial furnaces by distributing secondary combustion air precisely to enhance fuel combustion efficiency and reduce emissions. They ensure optimal temperature control and uniform heat distribution, improving energy savings and operational performance. Unlike cooler vents that primarily facilitate heat dissipation, tertiary air ducts specifically optimize airflow for better combustion dynamics.
Core Purposes of Cooler Vents
Cooler vents primarily regulate airflow to maintain optimal temperature and prevent overheating in HVAC systems or industrial equipment. These vents ensure efficient heat dissipation by directing cool air into specific areas, enhancing overall system performance and reliability. You can optimize your system's thermal management by selecting cooler vents tailored to your cooling requirements rather than relying solely on tertiary air ducts.
Design Differences: Tertiary Air Duct vs Cooler Vent
Tertiary air ducts are designed to channel excess air within HVAC systems, typically featuring rigid construction for controlled airflow and integration with secondary ductwork, whereas cooler vents prioritize directed airflow distribution with adjustable louvers for user comfort. The tertiary air duct's primary role focuses on system efficiency and pressure balance, while cooler vents emphasize localized temperature control and occupant ventilation. Understanding these design differences helps optimize your building's air circulation and energy use.
Material Selection for Air Ducts and Vents
Material selection for tertiary air ducts typically involves durable metals like galvanized steel or aluminum, ensuring high resistance to corrosion and prolonged lifespan in industrial environments. Cooler vents often incorporate materials such as stainless steel or reinforced plastic composites to withstand temperature fluctuations and moisture exposure while maintaining air quality. Your choice between these materials depends on factors like environmental conditions, budget, and required durability for optimal HVAC system performance.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Tertiary air ducts enhance combustion efficiency by delivering additional oxygen directly to the flame zone, resulting in more complete fuel burning and reduced emissions. Cooler vents primarily function to regulate temperature by circulating cooler air, which can improve overall system durability but do not significantly impact combustion performance. Comparing both, tertiary air ducts directly boost thermal efficiency and combustion quality, while cooler vents mainly support system longevity and temperature control.
Application Areas in Industrial Settings
Tertiary air ducts play a critical role in industrial settings by providing precise control of airflow in combustion processes, enhancing efficiency in boilers, furnaces, and ovens. Cooler vents are primarily used in industrial cooling systems, facilitating heat dissipation in machinery such as air compressors, heat exchangers, and refrigeration units. Your choice between tertiary air ducts and cooler vents depends on whether the application requires optimized combustion air supply or effective temperature regulation in equipment cooling.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Tertiary air ducts require regular inspection and cleaning to prevent blockages that can reduce airflow efficiency and increase operational costs. Cooler vents demand routine maintenance to ensure proper cooling performance, with particular attention to dust accumulation that can compromise heat exchange. You should evaluate the ease of access and maintenance frequency for both systems to optimize reliability and minimize downtime.
Energy Consumption Impacts
Tertiary air ducts typically improve airflow efficiency by reducing pressure drops, which can lower energy consumption of HVAC systems compared to traditional cooler vents. Cooler vents often cause uneven distribution of conditioned air, leading to increased operation time and higher energy use. Optimizing tertiary air duct design minimizes energy waste by enhancing air delivery and reducing compressor and fan workloads in cooling systems.
Choosing the Right System: Factors to Consider
When choosing between a tertiary air duct and a cooler vent, consider airflow requirements, system efficiency, and space constraints to ensure optimal performance. Your decision should factor in the specific cooling needs, installation complexity, and maintenance demands of each system. Evaluating these key elements guarantees enhanced climate control and energy savings tailored to your environment.
Tertiary Air Duct vs Cooler Vent Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com