The primary difference between a tertiary air duct and a secondary air duct lies in their functions within an HVAC system, where the secondary air duct distributes air from the main supply to specific zones, and the tertiary air duct further refines this distribution by delivering conditioned air to localized areas or equipment. Understanding the role of each duct can help optimize Your system's airflow efficiency and improve overall comfort.
Table of Comparison
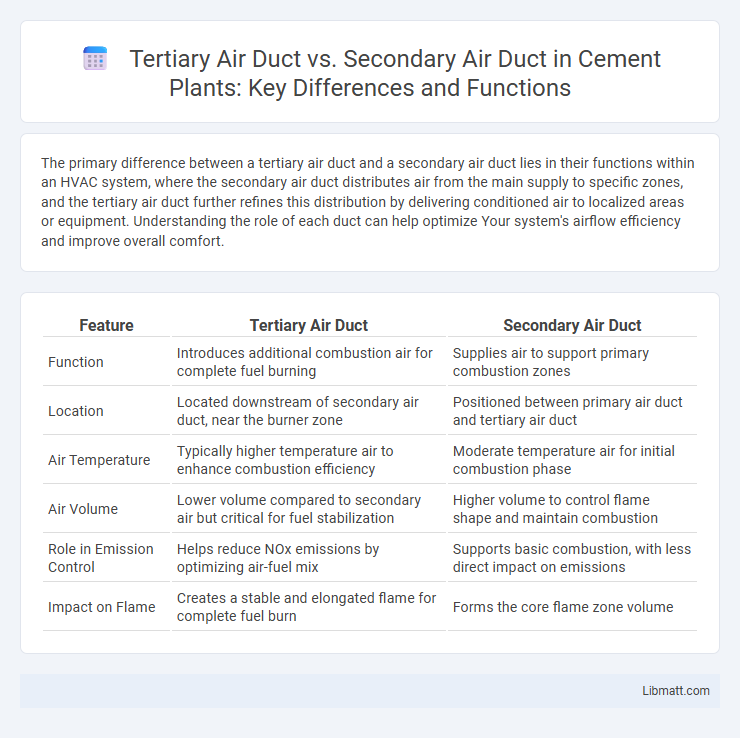
| Feature | Tertiary Air Duct | Secondary Air Duct |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Introduces additional combustion air for complete fuel burning | Supplies air to support primary combustion zones |
| Location | Located downstream of secondary air duct, near the burner zone | Positioned between primary air duct and tertiary air duct |
| Air Temperature | Typically higher temperature air to enhance combustion efficiency | Moderate temperature air for initial combustion phase |
| Air Volume | Lower volume compared to secondary air but critical for fuel stabilization | Higher volume to control flame shape and maintain combustion |
| Role in Emission Control | Helps reduce NOx emissions by optimizing air-fuel mix | Supports basic combustion, with less direct impact on emissions |
| Impact on Flame | Creates a stable and elongated flame for complete fuel burn | Forms the core flame zone volume |
Introduction to Air Duct Systems
Tertiary air ducts and secondary air ducts serve distinct roles within comprehensive air duct systems that manage airflow and combustion efficiency. Tertiary air ducts deliver additional oxygen at specific combustion stages, enhancing complete fuel burning and reducing emissions, while secondary air ducts supply the initial excess air needed to support primary combustion. Understanding these differences helps you optimize heating systems, improve energy efficiency, and maintain cleaner exhaust emissions in industrial or residential applications.
Overview of Secondary Air Ducts
Secondary air ducts distribute preheated air from the primary air system to various zones in a building, improving energy efficiency and indoor air quality. These ducts are typically larger in diameter compared to tertiary air ducts and play a crucial role in maintaining balanced ventilation and temperature control. Your HVAC system's performance heavily relies on the proper installation and maintenance of secondary air ducts to ensure optimal airflow and comfort.
Overview of Tertiary Air Ducts
Tertiary air ducts serve as an advanced stage in the air supply system, delivering conditioned air directly to more specific zones compared to secondary air ducts, which distribute air from the main ducts to larger areas. These ducts optimize ventilation efficiency by enabling precise temperature and airflow control within targeted spaces, reducing energy consumption and improving indoor air quality. Typically smaller in diameter, tertiary air ducts integrate with HVAC systems to enhance airflow distribution and occupant comfort in complex building layouts.
Functional Differences Between Secondary and Tertiary Air Ducts
Secondary air ducts primarily distribute conditioned air from the main supply to various zones within a building, ensuring balanced airflow and temperature control. Tertiary air ducts, on the other hand, serve more specific functions, such as directing air to localized areas or specialized equipment for enhanced ventilation or filtration. Understanding the functional differences between these ducts helps optimize your HVAC system's efficiency and indoor air quality.
Design Considerations for Secondary and Tertiary Ducts
Design considerations for secondary air ducts involve ensuring uniform air distribution to optimize combustion efficiency and reduce emissions, often requiring larger cross-sectional areas and smooth bends to minimize pressure loss. Tertiary air ducts demand precise control of air staging to enhance NOx reduction, necessitating smaller, strategically placed outlets for targeted mixing in high-temperature zones. Your choice between secondary and tertiary ducts influences overall boiler performance, emphasizing the importance of tailored sizing, materials, and positioning to meet specific operational goals.
Applications in Industrial Systems
Tertiary air ducts are primarily used in cement kilns and rotary dryers to introduce additional air for combustion control and temperature regulation, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Secondary air ducts supply combustion air directly to burners in industrial furnaces and boilers, ensuring optimal flame stability and complete fuel combustion. Understanding the distinct roles of tertiary and secondary air ducts can help you optimize air distribution in complex industrial heating systems for enhanced performance.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Tertiary air ducts improve combustion efficiency by introducing additional oxygen at a later stage, enhancing fuel burnout and reducing emissions compared to secondary air ducts, which supply the initial combustion air. The precise control of tertiary air flow allows better temperature distribution in the furnace, increasing thermal performance and minimizing unburnt fuel. Optimizing your system with tertiary air ducts can lead to higher energy efficiency and lower operational costs.
Maintenance Requirements and Challenges
Tertiary air ducts typically require more frequent inspections and cleaning due to their complex routing and exposure to higher particulate matter, leading to increased maintenance challenges compared to secondary air ducts. Secondary air ducts have simpler designs and more accessible locations, which generally result in easier maintenance with fewer operational disruptions. Understanding these differences helps you plan maintenance schedules effectively and reduce downtime in HVAC systems.
Common Problems and Solutions
Tertiary air ducts often face issues such as clogging and uneven air distribution, which can be resolved by regular cleaning and installing adjustable dampers to balance airflow. Secondary air ducts commonly suffer from leaks and poor insulation, leading to energy loss and reduced system efficiency; sealing leaks with mastic and enhancing insulation are effective solutions. Both duct types benefit from routine inspections to detect and fix problems early, ensuring optimal HVAC performance.
Selecting the Right Air Duct for Your System
Choosing the right air duct for your system depends on the specific function and design requirements; tertiary air ducts primarily control emissions in combustion engines by introducing air to the exhaust stream, while secondary air ducts supply air to the combustion chamber to enhance fuel burning efficiency. Your selection should consider factors such as engine type, emission regulations, and desired performance outcomes. Understanding the distinct roles of tertiary and secondary air ducts ensures optimal airflow management and compliance with environmental standards.
Tertiary air duct vs Secondary air duct Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com