Limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) offers enhanced sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and utilizing abundant raw materials compared to traditional Portland cement. Your choice of LC3 supports lower environmental impact while maintaining comparable strength and durability in construction applications.
Table of Comparison
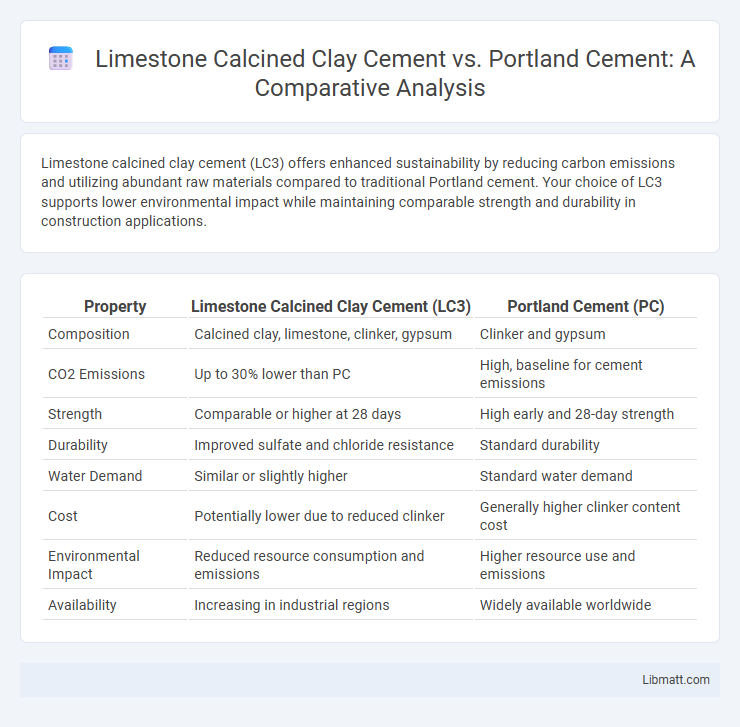
| Property | Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3) | Portland Cement (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcined clay, limestone, clinker, gypsum | Clinker and gypsum |
| CO2 Emissions | Up to 30% lower than PC | High, baseline for cement emissions |
| Strength | Comparable or higher at 28 days | High early and 28-day strength |
| Durability | Improved sulfate and chloride resistance | Standard durability |
| Water Demand | Similar or slightly higher | Standard water demand |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to reduced clinker | Generally higher clinker content cost |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced resource consumption and emissions | Higher resource use and emissions |
| Availability | Increasing in industrial regions | Widely available worldwide |
Introduction to Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3) and Portland Cement
Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3) combines calcined clay and limestone to significantly reduce CO2 emissions compared to traditional Portland cement by lowering clinker content. Portland cement, widely used in construction, primarily consists of clinker produced through energy-intensive processes that release high levels of carbon dioxide. Your choice of LC3 promotes sustainability while maintaining similar mechanical properties and durability to Portland cement.
Composition and Raw Materials Comparison
Limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) comprises a blend of about 50% clinker, 30% calcined clay, and 15% limestone, reducing reliance on clinker compared to Portland cement, which is primarily composed of 95% clinker and 5% gypsum. Calcined clay in LC3 enhances pozzolanic reactions, improving durability and reducing carbon emissions by lowering the clinker content. The raw materials for LC3 include abundant and low-cost calcined clay and limestone, offering a more sustainable alternative to the energy-intensive clinker used predominantly in Portland cement.
Environmental Impact and CO2 Emissions
Limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) significantly reduces CO2 emissions compared to traditional Portland cement by replacing a portion of clinker with limestone and calcined clay, lowering the carbon footprint by up to 30%. The production of LC3 requires less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases due to the lower clinker factor and the use of abundant, locally sourced calcined clay. This environmentally optimized cement offers a sustainable alternative, contributing to climate change mitigation by reducing the cement industry's overall carbon emissions.
Energy Efficiency in Production Processes
Limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) requires significantly less energy during production compared to Portland cement due to its lower clinker content, which reduces the need for high-temperature kiln operations. The substitution of clinker with calcined clay and limestone decreases carbon dioxide emissions by minimizing fuel consumption and raw material extraction. This energy-efficient process not only lowers environmental impact but also offers a sustainable alternative for the construction industry.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Performance
Limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) exhibits comparable or superior mechanical strength to Portland cement, with improved early and long-term compressive strength due to synergistic hydration reactions. Its enhanced durability performance includes increased resistance to chloride penetration and reduced permeability, leading to better protection against carbonation and sulfate attack. Using LC3 can extend the lifespan of your structures while supporting sustainable construction practices.
Workability and Setting Time Differences
Limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) exhibits improved workability compared to Portland cement due to its finer particle size and enhanced particle packing, which reduces water demand. LC3 typically has a longer setting time, as the pozzolanic reactions between calcined clay and limestone proceed more gradually than the hydration of Portland cement. Your construction projects can benefit from LC3's extended setting time by allowing more time for placement and finishing without compromising early strength development.
Cost-effectiveness and Resource Availability
Limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) offers significant cost-effectiveness compared to Portland cement by reducing clinker content, which lowers energy consumption and raw material expenses. The use of abundant calcined clay and limestone expands resource availability, easing the dependency on limited high-grade limestone deposits required for traditional Portland cement. This combination leads to sustainability benefits and economic savings, making LC3 an attractive alternative in large-scale construction projects.
Applications and Suitability for Construction Projects
Limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) excels in sustainability-focused construction projects due to its lower carbon footprint and improved durability compared to traditional Portland cement. LC3 is particularly suitable for large-scale infrastructure and precast elements where enhanced resistance to chemical attacks and reduced heat of hydration are critical. Your choice of cement can impact project longevity and environmental compliance, making LC3 ideal for green building initiatives.
Challenges and Limitations of LC3 and Portland Cement
Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3) faces challenges such as limited industrial-scale production and variability in clay quality, which can affect consistency and performance in your construction projects. Portland cement, while widely used, presents environmental limitations including high CO2 emissions and energy consumption during manufacture. Both materials encounter issues with standardization and acceptance in regulatory codes, impacting widespread adoption and application.
Future Prospects and Adoption in the Construction Industry
Limestone calcined clay cement (LC3) offers significant environmental advantages over traditional Portland cement by reducing CO2 emissions up to 30-40% during production, which aligns with the construction industry's increasing focus on sustainability. The growing regulatory pressure for greener building materials and the demand for cost-effective, durable alternatives drive the accelerated adoption of LC3 in infrastructure and commercial projects worldwide. Continued research and development, combined with supportive policies, position LC3 as a pivotal material in achieving carbon-neutral construction goals and a resilient future for the cement sector.
Limestone calcined clay cement vs Portland cement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com