Mill internals include various components such as liners, lifters, and diaphragms that protect the mill shell and enhance grinding efficiency by controlling the movement of the grinding media. Mill liners specifically serve as protective plates that reduce wear and impact damage, extending the lifespan of your milling equipment.
Table of Comparison
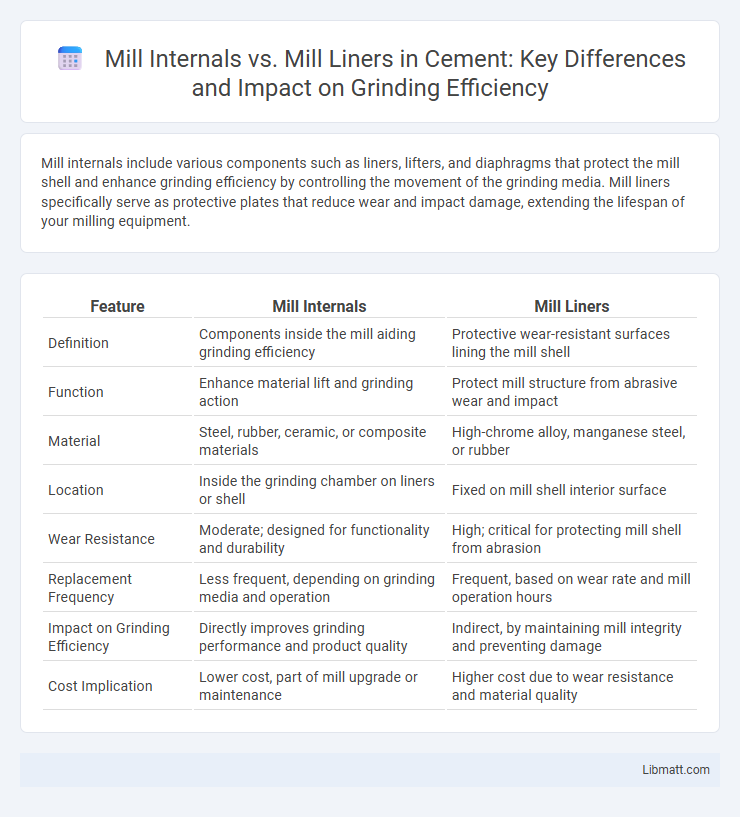
| Feature | Mill Internals | Mill Liners |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Components inside the mill aiding grinding efficiency | Protective wear-resistant surfaces lining the mill shell |
| Function | Enhance material lift and grinding action | Protect mill structure from abrasive wear and impact |
| Material | Steel, rubber, ceramic, or composite materials | High-chrome alloy, manganese steel, or rubber |
| Location | Inside the grinding chamber on liners or shell | Fixed on mill shell interior surface |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate; designed for functionality and durability | High; critical for protecting mill shell from abrasion |
| Replacement Frequency | Less frequent, depending on grinding media and operation | Frequent, based on wear rate and mill operation hours |
| Impact on Grinding Efficiency | Directly improves grinding performance and product quality | Indirect, by maintaining mill integrity and preventing damage |
| Cost Implication | Lower cost, part of mill upgrade or maintenance | Higher cost due to wear resistance and material quality |
Introduction to Mill Internals and Mill Liners
Mill internals refer to the essential components inside grinding mills, including lifters, diaphragm plates, and discharge grids, designed to enhance grinding efficiency and material flow. Mill liners are a critical part of mill internals, serving as protective surfaces that absorb impact and abrasion from the grinding media and ore. The selection of mill liners influences grinding performance, mill lifespan, and energy consumption, making them vital for optimizing mill operation.
Defining Mill Internals: Components and Functions
Mill internals consist of various components such as lifters, diaphragm plates, grates, and grinding media that play crucial roles in material grinding and processing efficiency. These parts optimize the grinding action by controlling the motion of the grinding media, facilitating material flow, and protecting the mill shell from wear. Proper design and selection of mill internals enhance throughput, reduce energy consumption, and extend the lifespan of mill liners.
Understanding Mill Liners: Role and Significance
Mill liners are critical components installed inside grinding mills to protect the shell from wear and to enhance grinding efficiency by lifting and cascading the charge within the mill. These liners, designed from durable materials like manganese steel or rubber, influence the mill's grinding performance, energy consumption, and overall lifespan. Understanding your mill's liner configurations and material options ensures optimized milling operations tailored to specific ore characteristics and processing goals.
Key Differences Between Mill Internals and Mill Liners
Mill internals refer to the components inside a grinding mill, such as lifters and diaphragms, designed to improve grinding efficiency and protect the mill shell from wear. Mill liners are heavy-duty plates installed along the interior shell of the mill to provide abrasion resistance and extend the equipment's lifespan. The key difference lies in function: mill internals optimize grinding performance, while mill liners primarily serve as protective wear surfaces.
Material Composition: Mill Internals vs Mill Liners
Mill internals are typically composed of metal and rubber composites designed to protect grinding media and enhance milling efficiency, whereas mill liners are primarily made from high-chrome alloys, manganese steel, or rubber to provide wear resistance and impact absorption. The material composition of mill internals emphasizes durability against abrasive forces and chemical corrosion inside the mill chamber, while mill liners focus on protecting the mill shell from damage and reducing maintenance frequency. Selecting the appropriate materials for mill internals and mill liners directly influences operational lifespan, grinding performance, and energy consumption in mineral processing.
Impact on Grinding Efficiency
Mill internals, including lifters and diaphragm plates, play a crucial role in the grinding process by influencing the motion and trajectory of grinding media, thereby enhancing impact and abrasion efficiencies. Mill liners protect the mill shell and contribute to optimal grinding by maintaining proper grinding media charge and reducing wear, which directly affects throughput and energy consumption. Optimizing both mill internals and liners improves grinding efficiency by maximizing particle size reduction and minimizing operational downtime.
Maintenance and Replacement Considerations
Mill internals, including lifters, diaphragms, and charge breakers, require regular inspection to prevent wear and maintain grinding efficiency, while mill liners primarily protect the shell and absorb impact from grinding media. Maintenance of mill internals often involves partial replacement or repair during routine shutdowns, whereas mill liners typically demand full replacement when wear reaches critical levels to avoid equipment damage. You should carefully assess the condition of both components, as timely maintenance and replacement minimize downtime and extend the overall lifespan of a grinding mill.
Cost Analysis: Mill Internals vs Mill Liners
Mill internals such as lifters, diaphragm plates, and discharge grates often incur higher initial costs but contribute to improved grinding efficiency and reduced wear rates, leading to lower maintenance expenses over time. Mill liners, while typically less expensive upfront, may require more frequent replacement and can increase operational downtime, impacting overall cost-effectiveness. Evaluating your specific grinding operation's requirements and wear patterns is essential for a balanced cost analysis between mill internals and mill liners.
Innovations and Advancements in Mill Internals and Liners
Innovations in mill internals and liners enhance grinding efficiency and equipment longevity through the development of high-chromium alloys, composite rubber-metal materials, and modular designs that reduce maintenance downtime. Advanced castings and profile optimizations improve wear resistance and energy consumption, while intelligent monitoring systems enable real-time condition assessment for predictive maintenance. These technological advancements directly contribute to higher throughput, reduced operational costs, and improved process control in mineral processing industries.
Choosing the Right Mill Protection Solution
Choosing the right mill protection solution depends on understanding the distinct roles of mill internals and mill liners; mill internals manage the grinding media movement, while mill liners protect the mill shell from wear and optimize grinding efficiency. Selecting appropriate materials and designs for mill liners extends equipment life, reduces maintenance costs, and improves overall mill performance. Your choice should balance durability, compatibility with the grinding process, and operational conditions to ensure maximum protection and productivity.
Mill Internals vs Mill Liners Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com