Sulphate Resisting Cement is specially formulated to withstand high sulfate environments, making it ideal for foundations and marine structures exposed to aggressive soils or water. Portland Pozzolana Cement enhances durability and reduces permeability by incorporating pozzolanic materials, benefiting Your construction projects through improved long-term strength and resistance to chemical attacks.
Table of Comparison
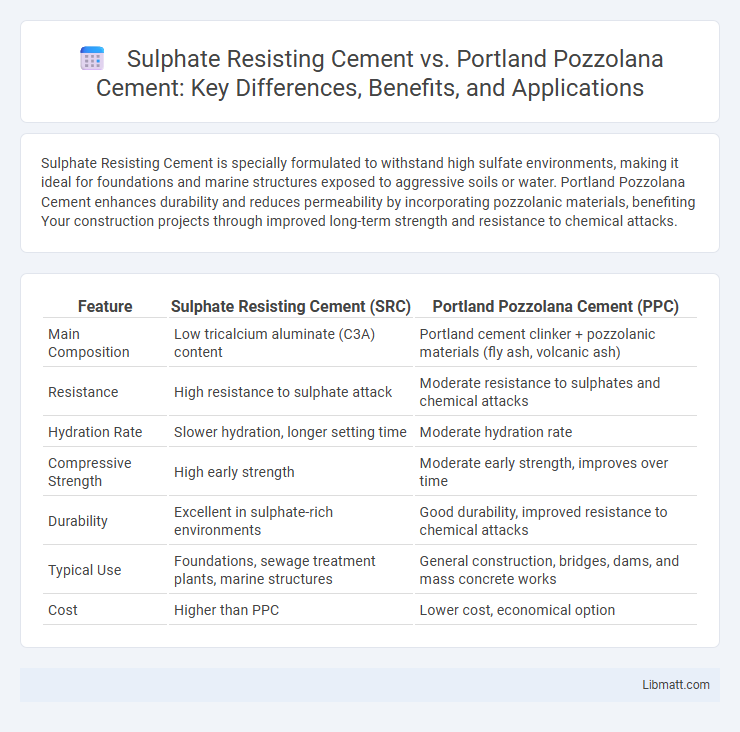
| Feature | Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) | Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Main Composition | Low tricalcium aluminate (C3A) content | Portland cement clinker + pozzolanic materials (fly ash, volcanic ash) |
| Resistance | High resistance to sulphate attack | Moderate resistance to sulphates and chemical attacks |
| Hydration Rate | Slower hydration, longer setting time | Moderate hydration rate |
| Compressive Strength | High early strength | Moderate early strength, improves over time |
| Durability | Excellent in sulphate-rich environments | Good durability, improved resistance to chemical attacks |
| Typical Use | Foundations, sewage treatment plants, marine structures | General construction, bridges, dams, and mass concrete works |
| Cost | Higher than PPC | Lower cost, economical option |
Introduction to Sulphate Resisting Cement and Portland Pozzolana Cement
Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) is specifically formulated to withstand high sulfate concentrations, commonly used in environments exposed to groundwater or soil containing sulfates. Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) incorporates pozzolanic materials like fly ash, enhancing durability and minimizing permeability, making it suitable for hydraulic structures and marine applications. Both cement types improve concrete longevity but target different environmental challenges through chemical composition and microstructural enhancements.
Chemical Composition Differences
Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) contains lower amounts of tricalcium aluminate (C3A), typically less than 5%, which significantly reduces its vulnerability to sulfate attack, enhancing its durability in aggressive environments. Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) incorporates pozzolanic materials like fly ash, which react with calcium hydroxide to form additional calcium silicate hydrates, improving long-term strength and reducing permeability but having a higher C3A content than SRC. The chemical composition differences primarily impact the resistance to sulfate-induced expansion and improve sulfate resistance in SRC compared to the more generalized strength and durability benefits offered by PPC.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) is manufactured by limiting the tri-calcium aluminate (C3A) content to reduce sulfate attack, typically involving the use of raw materials with low alumina and special clinker burning conditions. Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) is produced by grinding Portland cement clinker together with pozzolanic materials such as fly ash, volcanic ash, or silica fumes, which enhance strength and durability by reacting with calcium hydroxide during hydration. Your choice between SRC and PPC should consider the manufacturing differences that directly influence sulfate resistance and long-term performance in aggressive environments.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) demonstrates superior resistance to sulfate attacks, making it ideal for structures exposed to aggressive sulfate environments, while Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) offers enhanced durability and reduced permeability due to pozzolanic materials. SRC typically exhibits lower heat of hydration, resulting in less thermal cracking, whereas PPC provides improved long-term strength and better resistance to chemical corrosion. Your choice between these cements should consider the specific environmental exposure and the desired balance between mechanical strength and chemical durability.
Resistance to Sulphate Attack
Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) offers superior resistance to sulphate attack compared to Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) due to its low tri-calcium aluminate (C3A) content, which minimizes the formation of expansive compounds in sulphate-rich environments. PPC contains pozzolanic materials that enhance durability by reducing permeability, but its resistance to sulphate attack is moderate and less effective in highly aggressive sulphate conditions. For structures exposed to high sulphate concentrations, SRC is preferred to ensure long-term durability and prevent deterioration like cracking and spalling.
Durability and Longevity
Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) offers superior durability in aggressive sulfate environments by minimizing the formation of expansive compounds that cause concrete deterioration. Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) enhances longevity through the pozzolanic reaction, which improves resistance to chemical attacks and reduces permeability. SRC is ideal for sulfate-rich soils and groundwater, while PPC provides enhanced durability in moderate exposure conditions and general construction.
Applications and Suitable Uses
Sulphate Resisting Cement is ideal for structures exposed to high sulfate environments such as sewage treatment plants, marine constructions, and foundations in sulfate-rich soils, offering superior resistance to sulfate attack. Portland Pozzolana Cement is suitable for general construction like residential buildings, bridges, and dams, providing enhanced durability and reduced permeability due to the pozzolanic material. Your choice depends on exposure conditions, with Sulphate Resisting Cement preferred for aggressive sulfate environments and Portland Pozzolana Cement for improved long-term strength in normal conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) offers superior durability in sulfate-rich environments, reducing structural deterioration and minimizing frequent repairs that contribute to carbon emissions, thereby supporting sustainability goals. Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) incorporates industrial by-products like fly ash, lowering clinker content and CO2 emissions during production, which enhances its eco-friendly profile. For your construction projects, choosing between SRC and PPC involves balancing sulfate resistance requirements with environmental impact considerations.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) generally incurs higher initial costs compared to Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) due to its specialized formulation to combat sulfate attacks. However, SRC's enhanced durability in aggressive sulfate environments reduces long-term maintenance and repair expenses, offering economic advantages in infrastructure exposed to high sulfate levels. PPC provides a cost-effective alternative for standard construction with moderate sulfate presence, balancing initial outlay and performance in typical conditions.
Summary: Which Cement to Choose?
Sulphate Resisting Cement is ideal for structures exposed to high sulfate concentrations, such as sewage treatment plants and coastal constructions, due to its enhanced durability against sulfate attack. Portland Pozzolana Cement offers improved long-term strength and reduced permeability, making it suitable for general construction and mass concrete works where sulfate exposure is moderate. Choose Sulphate Resisting Cement for aggressive sulfate environments and Portland Pozzolana Cement for better durability and cost-effectiveness in less severe conditions.
Sulphate Resisting Cement vs Portland Pozzolana Cement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com