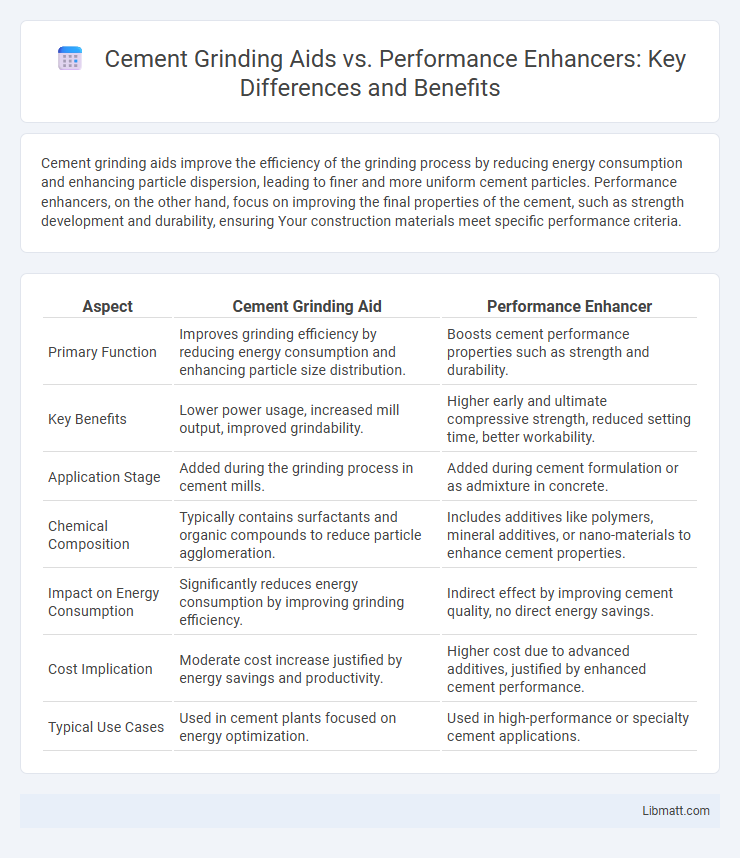
Cement grinding aids improve the efficiency of the grinding process by reducing energy consumption and enhancing particle dispersion, leading to finer and more uniform cement particles. Performance enhancers, on the other hand, focus on improving the final properties of the cement, such as strength development and durability, ensuring Your construction materials meet specific performance criteria.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cement Grinding Aid | Performance Enhancer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Improves grinding efficiency by reducing energy consumption and enhancing particle size distribution. | Boosts cement performance properties such as strength and durability. |
| Key Benefits | Lower power usage, increased mill output, improved grindability. | Higher early and ultimate compressive strength, reduced setting time, better workability. |
| Application Stage | Added during the grinding process in cement mills. | Added during cement formulation or as admixture in concrete. |
| Chemical Composition | Typically contains surfactants and organic compounds to reduce particle agglomeration. | Includes additives like polymers, mineral additives, or nano-materials to enhance cement properties. |
| Impact on Energy Consumption | Significantly reduces energy consumption by improving grinding efficiency. | Indirect effect by improving cement quality, no direct energy savings. |
| Cost Implication | Moderate cost increase justified by energy savings and productivity. | Higher cost due to advanced additives, justified by enhanced cement performance. |
| Typical Use Cases | Used in cement plants focused on energy optimization. | Used in high-performance or specialty cement applications. |
Introduction: Understanding Cement Grinding Aids and Performance Enhancers
Cement grinding aids increase grinding efficiency by reducing particle agglomeration and minimizing energy consumption during the cement milling process. Performance enhancers improve the final cement properties, such as strength development and setting time, by optimizing the hydration process. Both additives play crucial roles in achieving higher productivity and better cement quality in industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Grinding Aids and Performance Enhancers
Grinding aids primarily improve cement particle dispersion during milling, reducing energy consumption and enhancing grinding efficiency, while performance enhancers focus on boosting the final product's properties such as strength development and setting time control. Key differences lie in their functional impact: grinding aids optimize the milling process, whereas performance enhancers modify cement hydration and durability characteristics. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the right additive for your cement production goals.
Chemical Composition of Cement Grinding Aids
Cement grinding aids typically contain organic compounds such as amines, glycol ethers, and alcohols that reduce energy consumption by minimizing particle agglomeration during grinding. Performance enhancers often include proprietary blends of surfactants and dispersants designed to improve cement hydration and strength development beyond mere grinding efficiency. Your choice between a grinding aid and a performance enhancer depends on the desired chemical interaction with clinker minerals and the specific optimization of cement properties.
Typical Components of Performance Enhancers
Performance enhancers for cement grinding typically contain organic compounds such as amines, glycols, and lignosulfonates that reduce particle coating and improve mill throughput. These components work by minimizing agglomeration and optimizing energy transfer during grinding, leading to finer particle size distribution and improved cement quality. Unlike basic grinding aids, performance enhancers often include tailored surfactants and dispersants that enhance cement hydration and strength development.
Mechanism of Action: How Grinding Aids Work
Grinding aids function by reducing the surface energy of cement particles, which minimizes particle agglomeration and enhances grinding efficiency. These chemicals adsorb onto clinker surfaces, improving mill throughput by preventing coating and ball packing within the mill. Performance enhancers optimize the hydration process by modifying the microstructure of cement, leading to improved strength development and durability.
Performance Enhancers: Functional Benefits in Cement Production
Performance enhancers in cement production improve grinding efficiency by reducing energy consumption and increasing mill throughput. These additives optimize particle size distribution and enhance cement strength development by promoting better particle packing and hydration. Their functional benefits lead to a more consistent cement quality and improved durability in concrete applications.
Impact on Cement Quality and Strength
Cement grinding aids improve grinding efficiency by reducing energy consumption and enhancing particle dispersion, which leads to finer cement particles and improved early strength development in concrete. Performance enhancers, on the other hand, specifically target the hydration process and microstructure refinement, resulting in higher long-term strength and durability of the cementitious material. Your choice between these additives will influence both the immediate workability and the ultimate performance of the cement in structural applications.
Energy Consumption: Reducing Costs with Additives
Cement grinding aids and performance enhancers both play crucial roles in reducing energy consumption during the milling process, significantly lowering operational costs. Grinding aids improve particle dispersion, decreasing the energy required to grind raw materials, while performance enhancers optimize hydration rates, contributing to faster strength development and overall efficiency. Understanding the specific benefits of these additives ensures your cement production process remains cost-effective and energy-efficient.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
Cement grinding aids and performance enhancers play distinct roles in optimizing cement production efficiency while addressing environmental and regulatory considerations. Grinding aids typically reduce energy consumption and lower emissions by improving mill productivity and decreasing clinker consumption, aligning with stringent environmental standards. Your selection between these additives should factor in compliance with regional regulations on chemical use and emissions, ensuring sustainable and eco-friendly cement manufacturing practices.
Choosing the Right Additive: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right additive between cement grinding aids and performance enhancers depends on specific operational goals such as improving mill efficiency, reducing energy consumption, or enhancing final product properties. Key factors to consider include the chemical compatibility with cement components, impact on particle size distribution, and influence on setting time and strength development. Evaluating cost-effectiveness alongside environmental regulations ensures optimal additive choice for sustainable cement production.
Cement Grinding Aid vs Performance Enhancer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com