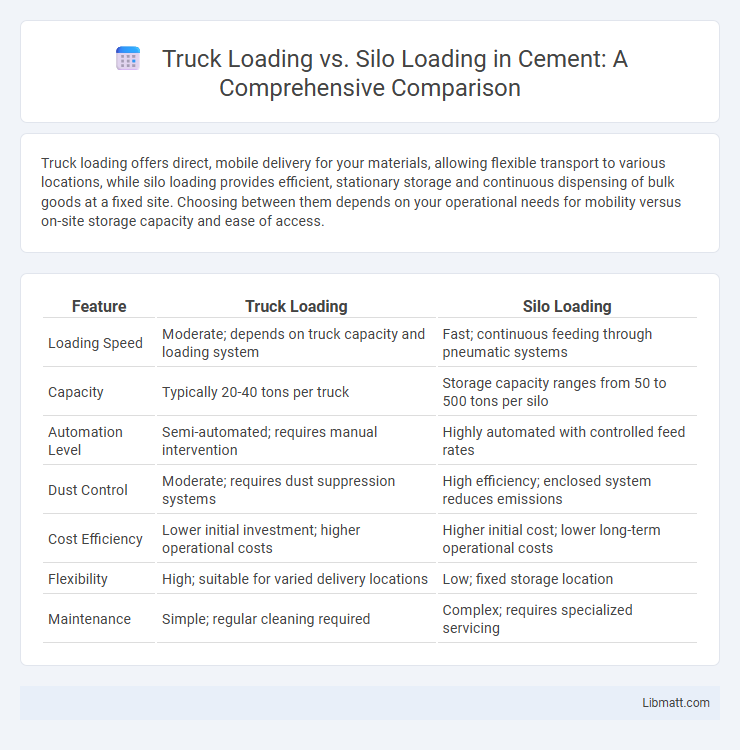
Truck loading offers direct, mobile delivery for your materials, allowing flexible transport to various locations, while silo loading provides efficient, stationary storage and continuous dispensing of bulk goods at a fixed site. Choosing between them depends on your operational needs for mobility versus on-site storage capacity and ease of access.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Truck Loading | Silo Loading |
|---|---|---|
| Loading Speed | Moderate; depends on truck capacity and loading system | Fast; continuous feeding through pneumatic systems |
| Capacity | Typically 20-40 tons per truck | Storage capacity ranges from 50 to 500 tons per silo |
| Automation Level | Semi-automated; requires manual intervention | Highly automated with controlled feed rates |
| Dust Control | Moderate; requires dust suppression systems | High efficiency; enclosed system reduces emissions |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial investment; higher operational costs | Higher initial cost; lower long-term operational costs |
| Flexibility | High; suitable for varied delivery locations | Low; fixed storage location |
| Maintenance | Simple; regular cleaning required | Complex; requires specialized servicing |
Introduction to Truck Loading and Silo Loading
Truck loading involves transferring bulk materials into trucks for transportation, ensuring efficient and timely delivery to various destinations. Silo loading refers to the process of depositing bulk materials into vertical storage silos designed for long-term storage and controlled dispensing. Both methods play crucial roles in supply chain management, tailored to specific storage and distribution needs.
Definitions and Core Differences
Truck loading involves transferring bulk materials directly into trucks for immediate transport, whereas silo loading refers to storing bulk materials in large vertical containers for later use or distribution. The core difference lies in the purpose and process: truck loading emphasizes rapid, temporary containment for shipment, while silo loading prioritizes long-term storage and controlled dispensing. Your choice between these methods impacts logistics efficiency and material handling strategies.
Equipment and Technology Overview
Truck loading utilizes automated conveyor belts and hydraulic lifts designed for quick, flexible material transfer directly into vehicle beds, optimizing turnaround time. Silo loading employs air pressure systems and rotary valves to pneumatically move bulk materials into sealed storage, preserving product quality and minimizing contamination. Advanced sensors and real-time monitoring technologies enhance accuracy and efficiency in both loading methods, ensuring precise inventory management.
Operational Workflow Comparison
Truck loading involves direct transfer of bulk materials into vehicles, enabling flexible delivery schedules and on-demand dispatch, while silo loading utilizes vertical storage tanks for continuous, automated filling that supports large-scale inventory management. Your operational workflow with truck loading requires coordination of loading docks, precise timing for arrivals, and adherence to weight limits, whereas silo loading demands integrated monitoring systems to control flow rates and maintain product quality. Efficiency in truck loading is enhanced by quick turnaround times, whereas silo loading emphasizes steady throughput and minimal manual intervention.
Efficiency and Throughput Analysis
Truck loading offers flexible and fast turnaround times, ideal for variable shipment sizes, with throughput rates typically ranging from 30 to 60 tons per hour depending on equipment and material flow. Silo loading ensures continuous material handling with minimal downtime, often achieving higher throughput of 100 to 200 tons per hour, making it efficient for bulk storage and steady supply chains. Efficiency analysis shows silo loading minimizes labor and loading errors, while truck loading provides versatile deployment but may experience bottlenecks in high-demand scenarios.
Safety Considerations for Each Method
Truck loading requires rigorous safety protocols such as securing the vehicle, proper weight distribution, and using personal protective equipment to prevent accidents during material transfer. Silo loading prioritizes containment measures to avoid dust explosions and ensures the structural integrity of the silo to prevent collapse or spillage. Both methods demand continuous monitoring for toxic gas emissions and adherence to industry regulations like OSHA standards to safeguard workers and the environment.
Cost Implications and ROI
Truck loading typically incurs higher operational costs due to labor intensity and time requirements, while silo loading offers a more automated and efficient process, leading to lower ongoing expenses. Investing in silo loading infrastructure often yields a higher ROI by minimizing loading times and reducing product loss during transfer. Your choice between these methods should consider upfront capital versus long-term savings and efficiency gains.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Truck loading generates higher greenhouse gas emissions due to increased fuel consumption and traffic congestion, contributing significantly to air pollution in urban areas. Silo loading offers a more environmentally sustainable alternative by minimizing particulate emissions and reducing noise pollution through enclosed handling systems. Life cycle assessments indicate that silo loading decreases carbon footprint and resource use, promoting greener logistics solutions.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Truck loading excels in industries requiring flexible, on-demand bulk material transport such as agriculture, construction, and mining, offering rapid loading and easy mobility. Silo loading suits industries like grain storage, cement production, and chemical manufacturing by providing long-term, high-capacity storage with controlled dispensing. Your choice depends on whether your operation prioritizes mobility and quick turnaround or centralized, large-scale storage with precise inventory management.
Future Trends in Bulk Material Loading
Future trends in bulk material loading emphasize automation and real-time monitoring, enhancing efficiency in both truck loading and silo loading systems. Integration of IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics optimizes load accuracy and reduces material waste during bulk handling processes. Energy-efficient equipment and sustainable practices are increasingly adopted to meet environmental regulations and lower operational costs.
Truck Loading vs Silo Loading Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com