High alumina cement offers rapid strength development and enhanced resistance to chemical attack compared to Portland cement, making it ideal for specialized industrial applications. Your choice depends on the project's requirements, as Portland cement provides slower curing but excellent durability for general construction.
Table of Comparison
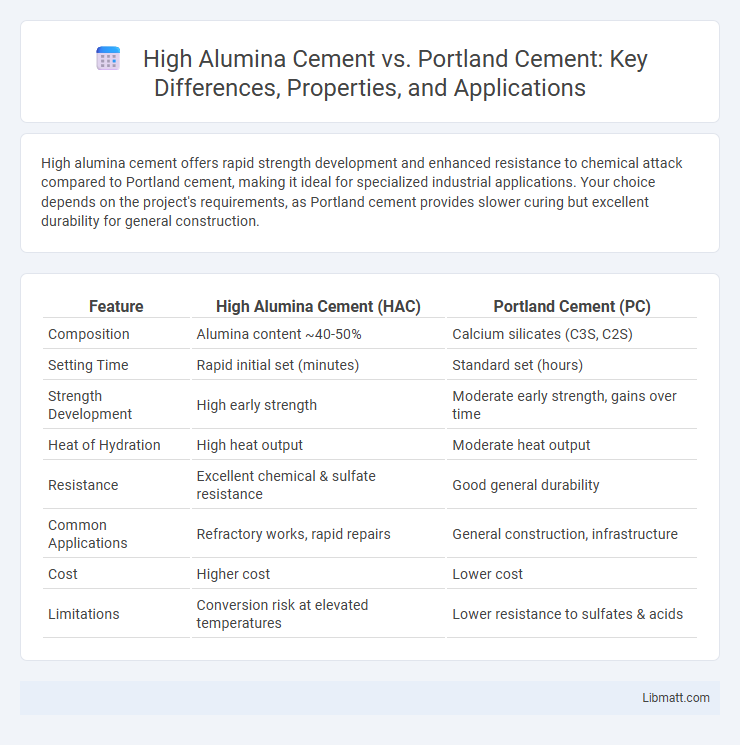
| Feature | High Alumina Cement (HAC) | Portland Cement (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alumina content ~40-50% | Calcium silicates (C3S, C2S) |
| Setting Time | Rapid initial set (minutes) | Standard set (hours) |
| Strength Development | High early strength | Moderate early strength, gains over time |
| Heat of Hydration | High heat output | Moderate heat output |
| Resistance | Excellent chemical & sulfate resistance | Good general durability |
| Common Applications | Refractory works, rapid repairs | General construction, infrastructure |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Limitations | Conversion risk at elevated temperatures | Lower resistance to sulfates & acids |
Introduction to High Alumina Cement and Portland Cement
High alumina cement, also known as calcium aluminate cement, contains high percentages of alumina typically ranging from 40% to 60%, distinguishing it from Portland cement, which primarily consists of calcium silicates. High alumina cement exhibits rapid strength gain and exceptional resistance to chemical attack and high temperatures, making it suitable for refractory applications and aggressive environments. Portland cement remains the most widely used cement globally, favored for its balanced strength development, versatility, and cost-effectiveness in conventional construction projects.
Chemical Composition Differences
High alumina cement contains 40-60% alumina (Al2O3) which contributes to its rapid strength gain and resistance to chemical corrosion, while Portland cement primarily consists of calcium silicates like tricalcium silicate (C3S) and dicalcium silicate (C2S), responsible for its slower hydration and strength development. The high alumina content in your construction material improves refractory properties and sulfate resistance, contrasting with Portland cement's higher lime (CaO) and silica (SiO2) content that favors general construction applications. Understanding these chemical composition differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate cement type tailored to specific environmental and structural requirements.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
High alumina cement is produced by sintering a mixture of bauxite and limestone at temperatures around 1,600degC, resulting in a clinker rich in calcium aluminates, whereas Portland cement is manufactured by heating a blend of limestone and clay between 1,450degC and 1,500degC to form alite and belite phases. Unlike Portland cement's emphasis on silicate minerals formed through calcination and subsequent grinding, high alumina cement's manufacturing process prioritizes rapid fusion and cooling to preserve reactive calcium aluminate compounds. Understanding these distinct processes can help you select the appropriate cement type based on strength development and chemical resistance requirements.
Setting Times and Early Strength
High alumina cement exhibits significantly faster setting times compared to Portland cement, with initial set occurring within 30 minutes to 2 hours, ideal for rapid repair works. Its early strength development is rapid, often achieving high compressive strength within 24 hours, whereas Portland cement typically requires 7 days to reach similar strength levels. Your construction projects can benefit from high alumina cement's quick setting and strength gain when fast turnaround and early load-bearing capacity are critical.
Durability and Resistance to Chemical Attack
High alumina cement exhibits superior durability in aggressive environments due to its enhanced resistance to chemical attack, particularly from sulfates and acids, compared to Portland cement. Its unique composition allows it to maintain strength and integrity under high-temperature and corrosive conditions where Portland cement may degrade through leaching or sulfate attack. This makes high alumina cement ideal for industrial applications requiring prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals and extreme environments.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
High alumina cement is commonly used in refractory applications, rapid repair works, and environments requiring high early strength and resistance to chemical attacks, such as sewage treatment plants and marine structures. Portland cement is widely applied in general construction projects, including residential buildings, bridges, and pavements due to its balanced strength development and durability. Your choice between these cements should consider the specific environmental conditions and the required curing time for optimal performance.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
High alumina cement offers superior performance in extreme conditions due to its rapid strength development and excellent resistance to high temperatures, chemical attack, and sulfate environments compared to Portland cement. Your projects exposed to severe thermal shocks or aggressive chemicals benefit from high alumina cement's durability and longevity. Portland cement, while versatile, typically underperforms in such harsh environments, making high alumina cement the preferred choice for specialized applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
High alumina cement produces lower CO2 emissions during manufacturing compared to Portland cement, contributing to reduced environmental impact. Its rapid strength gain allows for faster construction cycles, minimizing energy consumption and resource use. You can support sustainability efforts by choosing high alumina cement for projects requiring eco-friendly materials and accelerated timelines.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
High alumina cement generally incurs higher initial costs compared to Portland cement due to specialized raw materials and manufacturing processes. However, its superior chemical resistance and rapid strength gain can reduce overall project timelines and maintenance expenses, providing economic benefits in specific applications. Evaluating your project's performance requirements and lifecycle costs helps determine the most cost-effective choice between high alumina cement and Portland cement.
Choosing the Right Cement for Your Project
High alumina cement offers superior resistance to chemical attack and rapid strength development, making it ideal for refractory applications and structures exposed to aggressive environments. Portland cement remains the most widely used option for general construction due to its balanced cost, availability, and strength characteristics suitable for residential and commercial projects. Selecting the right cement depends on project requirements such as exposure conditions, strength timeline, and durability needs to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
High alumina cement vs Portland cement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com