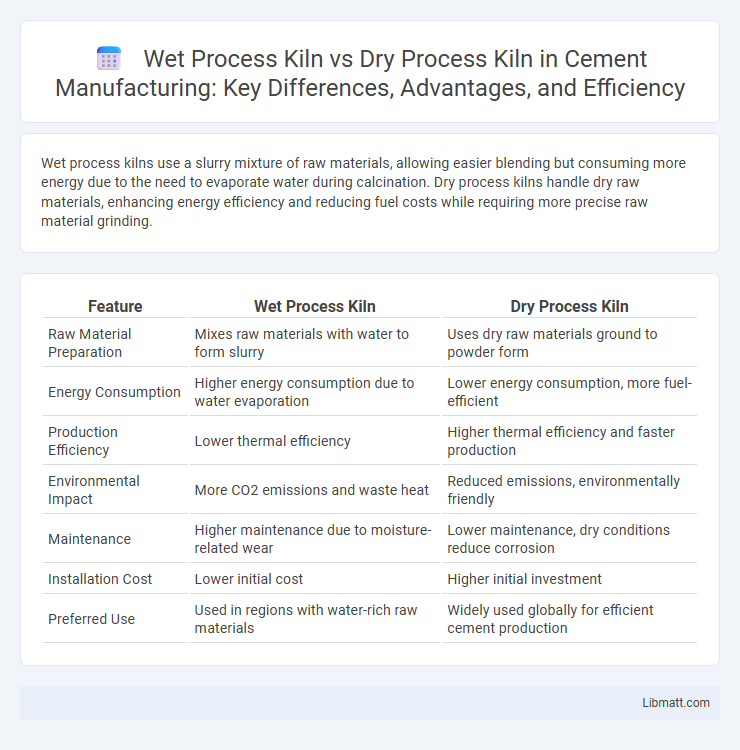
Wet process kilns use a slurry mixture of raw materials, allowing easier blending but consuming more energy due to the need to evaporate water during calcination. Dry process kilns handle dry raw materials, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing fuel costs while requiring more precise raw material grinding.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wet Process Kiln | Dry Process Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Preparation | Mixes raw materials with water to form slurry | Uses dry raw materials ground to powder form |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy consumption due to water evaporation | Lower energy consumption, more fuel-efficient |
| Production Efficiency | Lower thermal efficiency | Higher thermal efficiency and faster production |
| Environmental Impact | More CO2 emissions and waste heat | Reduced emissions, environmentally friendly |
| Maintenance | Higher maintenance due to moisture-related wear | Lower maintenance, dry conditions reduce corrosion |
| Installation Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
| Preferred Use | Used in regions with water-rich raw materials | Widely used globally for efficient cement production |
Introduction to Cement Kiln Processes
Cement kiln processes primarily consist of wet and dry methods, differentiated by the form of raw material preparation before heating. The wet process kiln uses a slurry of raw materials, resulting in higher fuel consumption due to the energy required to evaporate water, while the dry process kiln employs dry powdered raw materials, enhancing thermal efficiency and reducing emissions. Advances in dry process technologies contribute to lower operational costs and environmental impact, making it the preferred method in modern cement manufacturing.
Overview of Wet Process Kilns
Wet process kilns utilize a slurry of raw materials with high moisture content, typically around 30-40%, which improves mixing and homogenization during cement production. These kilns consume more energy due to the additional heat required to evaporate water but allow for easier material handling and better control over the raw mix consistency. Your choice between wet and dry process kilns depends on factors such as energy efficiency requirements, raw material characteristics, and production scale.
Overview of Dry Process Kilns
Dry process kilns use a dry raw material mixture with less moisture compared to wet process kilns, resulting in lower energy consumption and higher thermal efficiency. These kilns incorporate preheaters and precalciners to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce greenhouse gas emissions during cement production. The dry process technology dominates modern cement manufacturing due to its cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits.
Key Differences Between Wet and Dry Process Kilns
Wet process kilns use slurry-based raw materials, requiring more energy due to water evaporation, while dry process kilns handle dry powdered raw materials, enhancing fuel efficiency. Wet kilns typically have longer retention times and higher heat consumption, whereas dry kilns operate at higher temperatures with preheaters and precalciners to reduce energy use. The dry process kiln's technological advancements lead to lower CO2 emissions and improved overall productivity compared to the traditional wet process kiln.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Wet process kilns consume significantly more energy compared to dry process kilns due to the additional fuel required to evaporate the water content in the raw material slurry. Dry process kilns use preheated and dried raw materials, resulting in lower fuel consumption and higher thermal efficiency. Optimizing your cement production with dry process kilns can lead to substantial energy savings and reduced operational costs.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Wet process kilns generate higher CO2 emissions and consume more energy due to the need to evaporate large amounts of water, resulting in increased fuel consumption and greenhouse gas output. Dry process kilns operate more efficiently with significantly lower fuel requirements and reduced emissions, aligning better with sustainable cement production practices. Reduced water usage in dry process kilns also minimizes wastewater discharge, mitigating environmental contamination risks.
Product Quality and Consistency
Wet process kilns produce cement with high product quality and consistency due to thorough mixing of raw materials in slurry form, ensuring uniform chemical composition. Dry process kilns offer enhanced control over temperature and energy efficiency, delivering consistent clinker quality with lower moisture content. Your choice impacts final cement durability and performance in construction applications.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
Wet process kilns generally incur higher maintenance and operational costs due to increased energy consumption from evaporating water in the slurry and the need for frequent wear parts replacement caused by aggressive moisture conditions. Dry process kilns offer lower maintenance expenses as they handle dry raw materials, resulting in reduced thermal stress and less frequent component wear, which contributes to improved fuel efficiency. Choosing dry process kilns can lead to significant cost savings in fuel, labor, and equipment upkeep, optimizing long-term operational budgets.
Suitability for Raw Material Types
Wet process kilns are best suited for raw materials with high moisture content, such as clay or shale, allowing for easier mixing and homogenization. Dry process kilns excel with raw materials that contain low moisture levels, like limestone and sand, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing fuel consumption. Your choice depends on the composition and moisture of the raw materials in your cement production process.
Choosing the Right Kiln Process for Your Plant
Selecting the appropriate kiln process for your plant depends on factors such as raw material characteristics, energy consumption, and production capacity. Wet process kilns handle raw materials with high moisture content, requiring more fuel but offering better raw mix homogenization, while dry process kilns utilize drier materials, resulting in lower energy usage and faster production rates. Evaluating local resource availability and environmental regulations ensures the optimal kiln choice for efficient and sustainable cement manufacturing.
Wet process kiln vs Dry process kiln Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com