A flash dryer rapidly removes moisture from materials using hot air and short drying times, ideal for drying fine particles and powders quickly. In contrast, a rotary dryer uses a rotating drum to tumble larger, bulkier materials through hot air for more uniform drying over an extended period, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
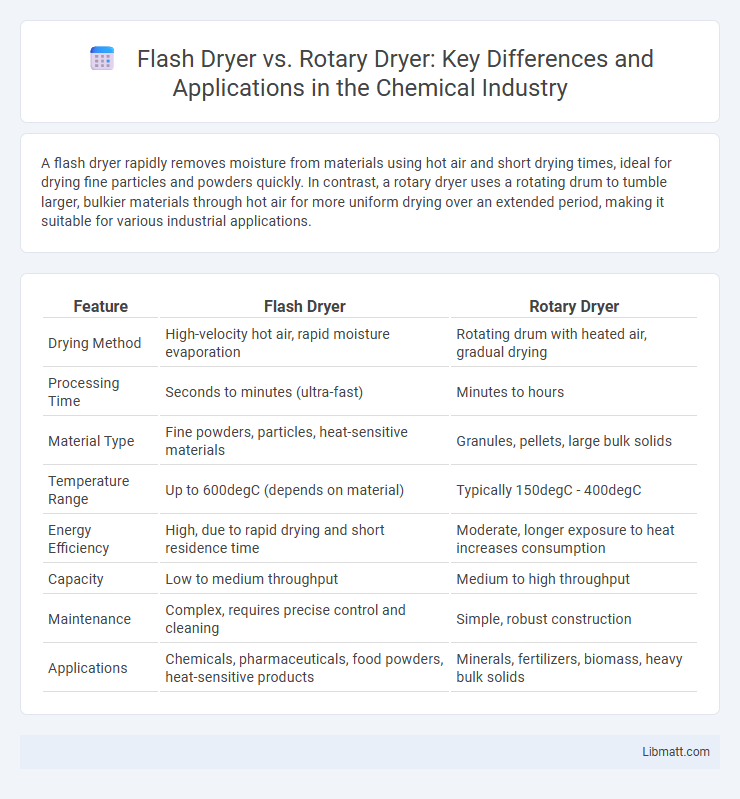
| Feature | Flash Dryer | Rotary Dryer |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | High-velocity hot air, rapid moisture evaporation | Rotating drum with heated air, gradual drying |
| Processing Time | Seconds to minutes (ultra-fast) | Minutes to hours |
| Material Type | Fine powders, particles, heat-sensitive materials | Granules, pellets, large bulk solids |
| Temperature Range | Up to 600degC (depends on material) | Typically 150degC - 400degC |
| Energy Efficiency | High, due to rapid drying and short residence time | Moderate, longer exposure to heat increases consumption |
| Capacity | Low to medium throughput | Medium to high throughput |
| Maintenance | Complex, requires precise control and cleaning | Simple, robust construction |
| Applications | Chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food powders, heat-sensitive products | Minerals, fertilizers, biomass, heavy bulk solids |
Introduction to Industrial Drying Technologies
Flash dryers rapidly remove moisture by exposing materials to hot gas streams, making them ideal for heat-sensitive or fine particles. Rotary dryers use a rotating drum to gently dry bulk solids, offering a durable and energy-efficient solution for large-scale industrial operations. Your choice depends on material characteristics, processing speed, and energy efficiency needs within industrial drying technologies.
Flash Dryer: Overview and Key Features
Flash dryers rapidly remove moisture from powdered or granular materials through a high-velocity hot air stream, ensuring efficient drying in seconds. These dryers feature a compact design, high thermal efficiency, and the ability to handle heat-sensitive materials with minimal particle degradation. Their fast drying times and precise temperature control make them ideal for industries like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing.
Rotary Dryer: Overview and Key Features
Rotary dryers are industrial equipment designed for efficient drying of bulk solids through continuous rotation and hot air circulation, making them ideal for materials like minerals, chemicals, and biomass. Key features include a robust rotating drum, adjustable temperature controls, and the ability to handle large capacity loads while ensuring uniform moisture removal. Your operation benefits from energy efficiency and adaptability to varied feed materials with the rotary dryer's proven performance in heavy-duty drying applications.
Working Principles: Flash Dryer vs Rotary Dryer
Flash dryers operate by rapidly drying materials using high-velocity hot air, which instantly evaporates moisture as the material is conveyed through the drying chamber. Rotary dryers function by tumbling wet material in a rotating drum, exposing it to hot air for a longer duration to progressively remove moisture through direct or indirect heat transfer. Your choice between flash dryer and rotary dryer depends on factors such as moisture content, particle size, and desired drying speed.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Flash dryers exhibit higher energy efficiency compared to rotary dryers due to their rapid drying process, which reduces heat exposure time and minimizes energy consumption. Rotary dryers require longer residence times and continuous heat input, often resulting in greater fuel usage and operational costs. Energy efficiency in flash dryers can be enhanced further by optimizing airflow and temperature control, making them more suitable for drying heat-sensitive materials.
Material Suitability and Applications
Flash dryers efficiently handle fine, heat-sensitive materials such as powders, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals, making them ideal for rapid drying of small particle sizes. Rotary dryers are versatile for bulk solids like minerals, aggregates, and biomass, offering uniform drying through continuous tumbling action suitable for coarse or granular materials. Industrial applications leverage flash dryers for quick moisture removal in delicate products, while rotary dryers excel in large-scale drying processes requiring robust handling of heterogeneous feedstocks.
Space and Installation Requirements
Flash dryers require significantly less space due to their compact and vertical design, making them ideal for facilities with limited floor area. Rotary dryers demand more extensive installation space because of their horizontal layout and larger rotating drum, often necessitating additional structural support. Your choice between the two should consider available space and installation complexity to optimize operational efficiency.
Operational and Maintenance Costs
Flash dryers typically incur lower operational and maintenance costs due to their simpler design and shorter drying times, which reduce energy consumption and wear on components. Rotary dryers require more frequent maintenance because of their larger size, moving parts, and the potential for mechanical issues such as drum wear and seal failures. Your choice between the two should consider the balance between maintenance labor and energy efficiency based on your specific drying requirements.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Flash dryers consume less energy and produce lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to rotary dryers due to their rapid drying process and shorter residence time. Rotary dryers often require higher fuel consumption and generate more airborne particulates, increasing environmental concerns. Choosing a flash dryer can reduce your facility's carbon footprint and minimize air pollution.
Choosing the Right Dryer: Factors to Consider
Selecting between a flash dryer and a rotary dryer depends on factors such as material characteristics, drying time requirements, and energy efficiency. Flash dryers excel in drying fine, moisture-sensitive particles quickly using high-velocity hot air, making them ideal for powders and granules. Rotary dryers suit bulk materials with high moisture content, offering uniform drying with longer retention time and greater capacity.
Flash dryer vs rotary dryer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com