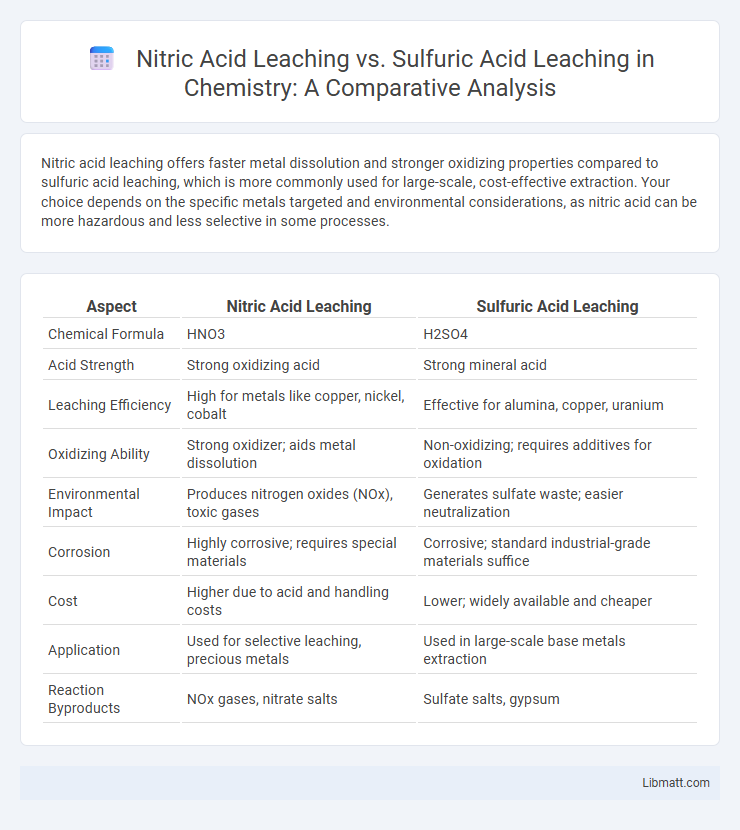
Nitric acid leaching offers faster metal dissolution and stronger oxidizing properties compared to sulfuric acid leaching, which is more commonly used for large-scale, cost-effective extraction. Your choice depends on the specific metals targeted and environmental considerations, as nitric acid can be more hazardous and less selective in some processes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nitric Acid Leaching | Sulfuric Acid Leaching |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | HNO3 | H2SO4 |
| Acid Strength | Strong oxidizing acid | Strong mineral acid |
| Leaching Efficiency | High for metals like copper, nickel, cobalt | Effective for alumina, copper, uranium |
| Oxidizing Ability | Strong oxidizer; aids metal dissolution | Non-oxidizing; requires additives for oxidation |
| Environmental Impact | Produces nitrogen oxides (NOx), toxic gases | Generates sulfate waste; easier neutralization |
| Corrosion | Highly corrosive; requires special materials | Corrosive; standard industrial-grade materials suffice |
| Cost | Higher due to acid and handling costs | Lower; widely available and cheaper |
| Application | Used for selective leaching, precious metals | Used in large-scale base metals extraction |
| Reaction Byproducts | NOx gases, nitrate salts | Sulfate salts, gypsum |
Introduction to Acid Leaching Processes
Nitric acid leaching involves using HNO3 to dissolve metals from ores, offering strong oxidizing properties that enhance metal recovery and impurity removal. Sulfuric acid leaching uses H2SO4, a cheaper and widely available acid that effectively dissolves metal sulfides and oxides under controlled conditions. The choice between nitric and sulfuric acid leaching depends on ore composition, desired metal extraction efficiency, and environmental considerations.
Overview of Nitric Acid Leaching
Nitric acid leaching is an efficient hydrometallurgical process used primarily for dissolving precious metals and base metals from ores, leveraging the strong oxidizing properties of nitric acid to facilitate metal extraction. Compared to sulfuric acid leaching, nitric acid offers enhanced oxidation potential, enabling effective dissolution of sulfide minerals and refractory ores rich in copper, gold, and silver. The process typically results in higher metal recovery rates but may involve dealing with nitrogen oxide gas emissions and higher reagent costs.
Overview of Sulfuric Acid Leaching
Sulfuric acid leaching is a widely used hydrometallurgical process for extracting metals like copper, uranium, and rare earth elements from ores, utilizing sulfuric acid as the leaching agent. This method offers high efficiency in dissolving metal oxides and sulfides, making it suitable for low-grade ores and minerals with complex compositions. Your choice of sulfuric acid leaching can enhance metal recovery rates while minimizing environmental impact compared to alternative methods such as nitric acid leaching.
Chemical Reactions and Mechanisms
Nitric acid leaching involves strong oxidizing reactions that convert metal sulfides into soluble metal nitrates through redox mechanisms, facilitating efficient extraction of metals like copper and cobalt. Sulfuric acid leaching primarily relies on proton-driven acid-base reactions to dissolve metal oxides and carbonates, forming soluble metal sulfates without significant oxidation. Your choice between these acids depends on the ore type and desired metal recovery, as nitric acid offers more aggressive oxidation while sulfuric acid provides selective dissolution with lower environmental impact.
Extraction Efficiency and Selectivity
Nitric acid leaching generally offers higher extraction efficiency for metals such as copper and nickel due to its strong oxidative properties, enabling better dissolution of complex ores. Sulfuric acid leaching shows superior selectivity, particularly in copper extraction from oxidized ores, minimizing the co-dissolution of impurities compared to nitric acid. Process conditions like pH, temperature, and ore type critically influence the efficiency and selectivity differences between the two leaching methods.
Operational Conditions and Parameters
Nitric acid leaching operates effectively under moderate temperatures of 50-80degC and typically requires acidic concentrations between 1 to 4 M, promoting strong oxidation and metal dissolution, especially for complex ores. Sulfuric acid leaching generally functions well at slightly higher temperatures of 70-90degC with acid concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 2 M, favoring selective metal recovery through its strong acidic environment and enhanced kinetics in sulfate-rich systems. The pH control, leaching time, and solid-to-liquid ratios critically influence the efficiency of both processes, with nitric acid leaching often demanding stricter control due to its oxidative nature and potential for nitrate ion interactions.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Nitric acid leaching poses significant environmental risks due to the formation of nitrogen oxides, which contribute to air pollution and require stringent emission controls. Sulfuric acid leaching generates sulfate-containing waste streams that can lead to soil and water acidification if not properly managed, demanding careful neutralization and disposal measures. Your choice between these leaching methods should account for facility capabilities to handle hazardous emissions and effluents to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and worker safety standards.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Nitric acid leaching generally incurs higher operational costs due to the increased price of nitric acid and the need for specialized handling and waste treatment facilities compared to sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid leaching offers greater economic viability, especially in large-scale operations, because of its lower reagent cost, widespread availability, and established industrial processes. Cost efficiencies from sulfuric acid use often translate into reduced overall expenses, making it the preferred choice in metal recovery applications such as nickel and cobalt extraction.
Applications in Metal Recovery and Processing
Nitric acid leaching is widely used for extracting precious metals such as gold and silver due to its strong oxidative properties that dissolve metal oxides efficiently. Sulfuric acid leaching is predominantly applied in the recovery of base metals like copper, nickel, and cobalt, especially from sulfide ores, owing to its cost-effectiveness and high selectivity. Both acids play crucial roles in hydrometallurgical processes, with nitric acid suited for complex ores requiring oxidative conditions and sulfuric acid favored for large-scale industrial metal recovery and refining.
Future Trends and Research Directions
Future trends in nitric acid leaching emphasize the development of environmentally friendly processes with enhanced metal recovery efficiency, particularly for precious and rare earth metals. Research is focusing on optimizing reaction parameters and integrating bioleaching techniques to reduce acid consumption and waste generation. In sulfuric acid leaching, advances aim at improving selectivity and kinetics through the use of catalysts and greener additives, alongside the exploration of closed-loop systems to minimize environmental impact.
Nitric acid leaching vs sulfuric acid leaching Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com