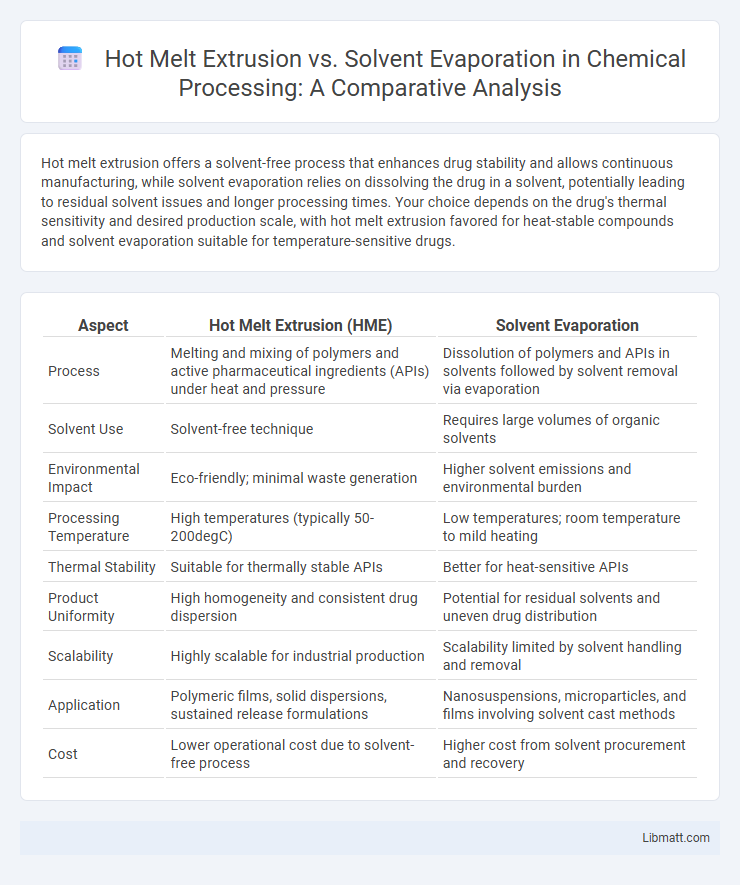
Hot melt extrusion offers a solvent-free process that enhances drug stability and allows continuous manufacturing, while solvent evaporation relies on dissolving the drug in a solvent, potentially leading to residual solvent issues and longer processing times. Your choice depends on the drug's thermal sensitivity and desired production scale, with hot melt extrusion favored for heat-stable compounds and solvent evaporation suitable for temperature-sensitive drugs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hot Melt Extrusion (HME) | Solvent Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Melting and mixing of polymers and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) under heat and pressure | Dissolution of polymers and APIs in solvents followed by solvent removal via evaporation |
| Solvent Use | Solvent-free technique | Requires large volumes of organic solvents |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; minimal waste generation | Higher solvent emissions and environmental burden |
| Processing Temperature | High temperatures (typically 50-200degC) | Low temperatures; room temperature to mild heating |
| Thermal Stability | Suitable for thermally stable APIs | Better for heat-sensitive APIs |
| Product Uniformity | High homogeneity and consistent drug dispersion | Potential for residual solvents and uneven drug distribution |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for industrial production | Scalability limited by solvent handling and removal |
| Application | Polymeric films, solid dispersions, sustained release formulations | Nanosuspensions, microparticles, and films involving solvent cast methods |
| Cost | Lower operational cost due to solvent-free process | Higher cost from solvent procurement and recovery |
Introduction to Drug Formulation Techniques
Hot melt extrusion and solvent evaporation are advanced drug formulation techniques used to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Hot melt extrusion involves the continuous processing of drug-polymer mixtures at elevated temperatures to create solid dispersions, offering improved stability and scalability. Solvent evaporation relies on dissolving drug and polymer in a volatile solvent followed by solvent removal, providing precise control over particle size but often facing challenges with residual solvents.
Overview of Hot Melt Extrusion
Hot melt extrusion (HME) is a solvent-free process that blends and shapes materials by applying heat and pressure, resulting in uniform dispersion of active pharmaceutical ingredients within a polymer matrix. This technique enhances the bioavailability and stability of poorly soluble drugs without the need for toxic solvents, making it environmentally friendly and scalable for industrial production. Your formulations benefit from continuous processing, precise control over drug release, and improved mechanical properties compared to solvent evaporation methods.
Principles of Solvent Evaporation Method
Solvent evaporation method involves dissolving the drug and polymer in a volatile organic solvent, followed by evaporation under controlled conditions to form a solid dispersion. This process ensures uniform drug distribution and enhanced bioavailability by removing the solvent, leaving behind a stable matrix. Your formulation benefits from precise solvent removal, which critically impacts the final product's quality and performance.
Comparative Advantages of Hot Melt Extrusion
Hot melt extrusion (HME) offers significant advantages over solvent evaporation by eliminating the need for organic solvents, enhancing environmental safety and reducing process complexity. HME enables continuous manufacturing with precise control over drug dispersion, improving bioavailability and stability of the pharmaceutical compounds. The technique also supports scale-up and consistent product quality, making it highly suitable for industrial applications in drug formulation.
Benefits and Limitations of Solvent Evaporation
Solvent evaporation offers precise control over drug particle size and improved homogeneity in pharmaceutical formulations, making it ideal for producing microspheres and nanoparticles. However, the method faces limitations such as potential residual solvent toxicity, lengthy drying times, and environmental concerns regarding solvent disposal. Compared to hot melt extrusion, solvent evaporation is less suitable for heat-sensitive drugs and may involve more complex processing steps.
Material Compatibility in Both Processes
Hot melt extrusion requires materials with thermal stability and melt processability, limiting compatibility to polymers and APIs that can withstand elevated temperatures without degradation. Solvent evaporation offers broader material compatibility, accommodating thermally sensitive drugs and polymers soluble in volatile solvents. Understanding the thermal and solubility properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients is critical for selecting the appropriate technique for formulation development.
Impact on Drug Bioavailability
Hot melt extrusion enhances drug bioavailability by improving the solubility and dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drugs through the formation of solid dispersions without using solvents. Solvent evaporation also increases bioavailability by producing amorphous drug forms, but residual solvents and incomplete evaporation can affect drug stability and release profiles. Your choice between these techniques should consider the drug's thermal stability and the desired release characteristics for optimal therapeutic effect.
Scale-Up and Manufacturing Considerations
Hot melt extrusion offers a continuous and scalable manufacturing process with fewer solvent-related hazards, enabling faster scale-up and consistent product quality in pharmaceutical production. Solvent evaporation methods require careful solvent handling, longer drying times, and pose regulatory challenges during scale-up due to residual solvent limits. Equipment selection, process control, and environmental compliance are critical factors influencing the choice between hot melt extrusion and solvent evaporation for commercial manufacturing.
Regulatory and Environmental Aspects
Hot melt extrusion (HME) offers significant regulatory advantages by eliminating the use of organic solvents, thereby reducing toxic residual solvent concerns and simplifying compliance with ICH Q3C guidelines. In contrast, solvent evaporation methods often involve volatile organic compounds (VOCs), increasing environmental impact and stringent regulatory scrutiny for solvent emissions and disposal. The solvent-free nature of HME aligns with greener manufacturing practices and supports regulatory trends favoring sustainable pharmaceutical production.
Future Trends in Drug Delivery Technologies
Hot melt extrusion (HME) is gaining traction in drug delivery for its solvent-free process and enhanced drug solubility, aligning with the shift towards sustainable manufacturing. Solvent evaporation, while effective for controlled release formulations, faces challenges due to solvent toxicity and regulatory constraints, prompting exploration of greener alternatives. Future trends emphasize integrating HME with advanced bioavailability enhancement techniques and continuous manufacturing to improve scalability and precision in pharmaceuticals.
Hot melt extrusion vs solvent evaporation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com