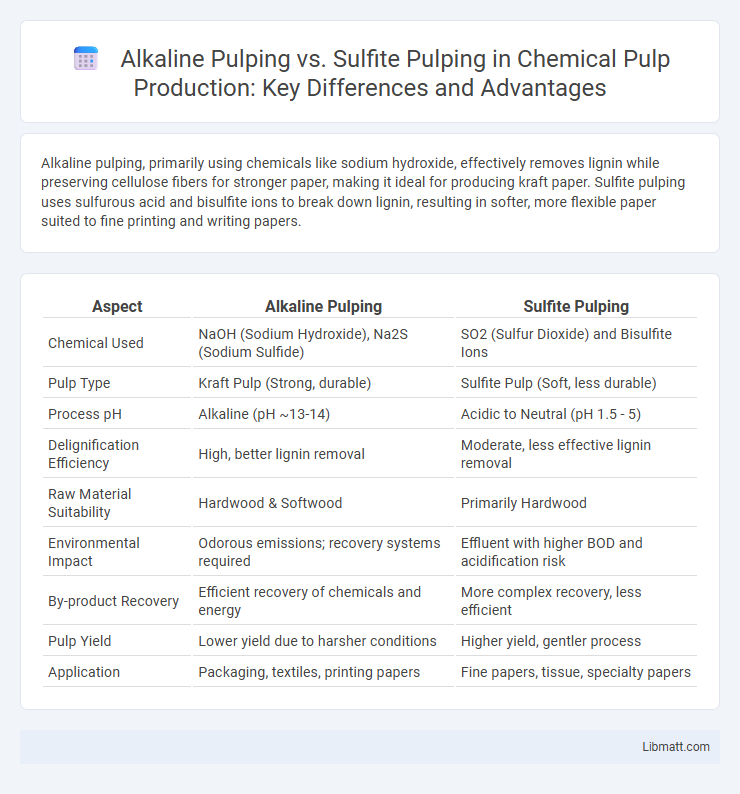
Alkaline pulping, primarily using chemicals like sodium hydroxide, effectively removes lignin while preserving cellulose fibers for stronger paper, making it ideal for producing kraft paper. Sulfite pulping uses sulfurous acid and bisulfite ions to break down lignin, resulting in softer, more flexible paper suited to fine printing and writing papers.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Alkaline Pulping | Sulfite Pulping |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Used | NaOH (Sodium Hydroxide), Na2S (Sodium Sulfide) | SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) and Bisulfite Ions |
| Pulp Type | Kraft Pulp (Strong, durable) | Sulfite Pulp (Soft, less durable) |
| Process pH | Alkaline (pH ~13-14) | Acidic to Neutral (pH 1.5 - 5) |
| Delignification Efficiency | High, better lignin removal | Moderate, less effective lignin removal |
| Raw Material Suitability | Hardwood & Softwood | Primarily Hardwood |
| Environmental Impact | Odorous emissions; recovery systems required | Effluent with higher BOD and acidification risk |
| By-product Recovery | Efficient recovery of chemicals and energy | More complex recovery, less efficient |
| Pulp Yield | Lower yield due to harsher conditions | Higher yield, gentler process |
| Application | Packaging, textiles, printing papers | Fine papers, tissue, specialty papers |
Introduction to Pulping Processes
Alkaline pulping utilizes sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide to break down lignin and separate cellulose fibers, producing strong, durable pulp primarily used for paper and packaging. Sulfite pulping employs sulfurous acid and bisulfite ions to dissolve lignin, resulting in pulp with higher brightness and smoothness favored for fine paper and specialty products. Both methods chemically treat wood chips but differ in chemistry, pulp characteristics, and environmental impact.
Overview of Alkaline Pulping
Alkaline pulping primarily uses sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide to break down lignin and separate cellulose fibers efficiently, making it the dominant method in the kraft process. This technique produces stronger pulp with higher yield and greater chemical recovery rates compared to sulfite pulping, which relies on acidic solutions. The alkaline environment allows for more selective lignin removal while preserving cellulose integrity, optimizing pulp quality for paper production.
Overview of Sulfite Pulping
Sulfite pulping involves cooking wood chips in a solution of sulfurous acid and bisulfite ions, breaking down lignin to separate cellulose fibers. This process is highly effective for producing high-quality, bright, and strong pulp used in fine papers and specialty products. Your choice between alkaline pulping and sulfite pulping depends on desired pulp properties and raw material compatibility.
Chemical Mechanisms in Alkaline Pulping
Alkaline pulping relies on the selective cleavage of lignin-carbohydrate bonds through the action of hydroxide ions (OH-) and hydrosulfide ions (HS-) in the cooking liquor, which disrupts the lignin structure and solubilizes it, preserving cellulose fibers. The process primarily involves nucleophilic attack on lignin's ether bonds, leading to fragmentation and dissolution without excessive degradation of cellulose. Understanding these chemical mechanisms enables you to optimize refining conditions for improved fiber quality in alkaline pulping.
Chemical Mechanisms in Sulfite Pulping
Sulfite pulping relies on the sulfonation of lignin, where sulfurous acid and bisulfite ions penetrate wood fibers, breaking down lignin's complex structure and converting it into water-soluble sulfonated fragments. This chemical mechanism allows for the effective separation of cellulose fibers while preserving their strength and flexibility. Understanding this process enables you to optimize pulping conditions for specific wood types in sulfite pulping operations.
Comparison of Pulp Yield and Quality
Alkaline pulping generally yields a higher pulp output and produces stronger fibers due to effective lignin removal, resulting in superior tensile strength and brightness compared to sulfite pulping. Sulfite pulping tends to generate a lower yield but offers pulp with finer fibers and better paper formation properties, particularly suitable for specialty papers. The choice between alkaline and sulfite pulping significantly influences pulp characteristics, where alkaline pulping favors durability and sulfite pulping supports smoothness and brightness.
Environmental Impact: Alkaline vs Sulfite Pulping
Alkaline pulping generates less acidic wastewater and produces lignin byproducts that can be efficiently recovered and reused, reducing environmental pollution compared to sulfite pulping. Sulfite pulping releases sulfur-containing compounds that contribute to water and air pollution, creating challenges for effluent treatment and odor control. The recovery systems in alkaline pulping are generally more energy-efficient, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced sustainability in paper production.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
Alkaline pulping, primarily using the kraft process, is favored in industrial applications for producing strong, durable paper products such as packaging materials and printing paper due to its efficient lignin removal and chemical recovery capabilities. Sulfite pulping is more suitable for producing fine, high-quality paper grades like tissue and book paper because it yields pulp with superior brightness and softness. The choice between alkaline and sulfite pulping depends on the desired end-product properties, production costs, and environmental considerations related to chemical handling and waste management.
Economic Considerations and Cost Efficiency
Alkaline pulping typically offers greater cost efficiency due to lower chemical consumption and simpler recovery systems compared to sulfite pulping. Sulfite processes involve more expensive chemicals and energy-intensive recovery, increasing overall production costs. Your choice between these methods should weigh the balance between raw material compatibility and long-term economic scalability.
Future Trends in Pulping Technologies
Future trends in pulping technologies highlight a shift towards more sustainable processes, with alkaline pulping gaining traction due to its higher yield and lower environmental impact compared to sulfite pulping. Innovations in enzymatic and bio-pulping methods aim to enhance the efficiency of alkaline pulping by reducing chemical usage and energy consumption. Research focuses on hybrid systems combining alkaline and sulfite techniques to optimize fiber quality while minimizing emissions and waste.
Alkaline pulping vs sulfite pulping Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com