O/W (oil-in-water) emulsions have oil droplets dispersed in a continuous water phase, making them lightweight and easily absorbed, ideal for hydration and non-greasy feel. W/O (water-in-oil) emulsions consist of water droplets dispersed in oil, providing stronger moisture barrier protection and richer texture suitable for dry or sensitive skin.
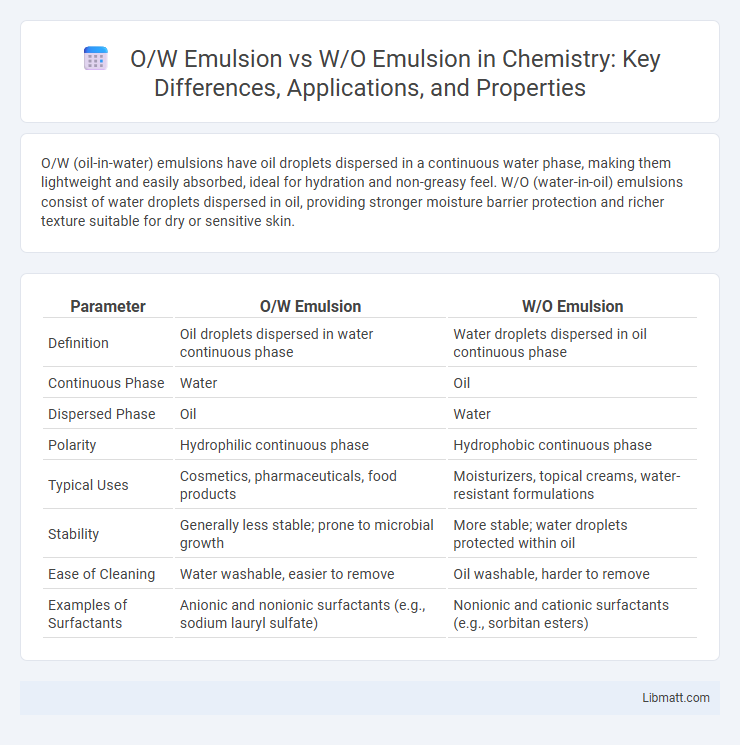
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | O/W Emulsion | W/O Emulsion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Oil droplets dispersed in water continuous phase | Water droplets dispersed in oil continuous phase |
| Continuous Phase | Water | Oil |
| Dispersed Phase | Oil | Water |
| Polarity | Hydrophilic continuous phase | Hydrophobic continuous phase |
| Typical Uses | Cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food products | Moisturizers, topical creams, water-resistant formulations |
| Stability | Generally less stable; prone to microbial growth | More stable; water droplets protected within oil |
| Ease of Cleaning | Water washable, easier to remove | Oil washable, harder to remove |
| Examples of Surfactants | Anionic and nonionic surfactants (e.g., sodium lauryl sulfate) | Nonionic and cationic surfactants (e.g., sorbitan esters) |
Introduction to Emulsion Types
O/W (oil-in-water) emulsion consists of oil droplets dispersed in a continuous water phase, commonly used in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals for its lightweight feel and easy rinsing. W/O (water-in-oil) emulsion features water droplets dispersed in an oil matrix, providing superior moisturizing properties and water resistance for skincare formulations. Understanding these emulsion types helps you select the right product based on desired texture, absorption, and durability.
What is an O/W (Oil-in-Water) Emulsion?
An O/W (Oil-in-Water) emulsion consists of oil droplets dispersed in a continuous water phase, commonly found in products like lotions and creams. This type of emulsion offers a lightweight, non-greasy texture, making it suitable for skincare formulations that emphasize hydration and easy absorption. You benefit from O/W emulsions when seeking moisturizers that provide effective oil delivery without leaving a heavy residue on the skin.
What is a W/O (Water-in-Oil) Emulsion?
A Water-in-Oil (W/O) emulsion consists of water droplets dispersed within a continuous oil phase, commonly used in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals for its moisturizing and barrier-enhancing properties. This emulsion type improves skin hydration by forming an occlusive layer that reduces transepidermal water loss, making it ideal for dry or sensitive skin formulations. W/O emulsions generally exhibit higher viscosity and stability against water dilution compared to Oil-in-Water (O/W) emulsions, influencing product texture and absorption rates.
Key Differences between O/W and W/O Emulsions
O/W emulsions consist of oil droplets dispersed in a continuous water phase, making them water-soluble and easily washable, while W/O emulsions contain water droplets dispersed in a continuous oil phase, providing enhanced moisture retention and water resistance. O/W emulsions typically feel lighter and are used in products like lotions and creams designed for quick absorption, whereas W/O emulsions offer better occlusive properties suitable for moisturizing dry or sensitive skin. Your choice between O/W and W/O emulsions depends on the desired texture, skin type, and product functionality.
Stability Factors in Emulsion Systems
Stability in O/W (oil-in-water) emulsions primarily depends on the type and concentration of surfactants, droplet size distribution, and the continuous water phase's viscosity, which inhibits coalescence and sedimentation. W/O (water-in-oil) emulsions rely heavily on the oil phase's viscosity and lipophilic emulsifiers to maintain droplet dispersion and prevent phase separation under stress conditions. Understanding these stability factors helps you tailor emulsifier selection and formulation parameters to achieve the desired emulsion performance and shelf-life.
Applications of O/W Emulsions
O/W emulsions, with oil droplets dispersed in a continuous water phase, are widely used in pharmaceutical creams, cosmetics, and food products due to their skin-friendly and non-greasy properties. They effectively deliver hydrophobic active ingredients while maintaining moisture, making them ideal for lotions, sunscreens, and salad dressings. The biocompatibility and easy washability of O/W emulsions enhance their application in dermatological formulations and personal care items.
Applications of W/O Emulsions
Water-in-oil (W/O) emulsions are widely used in cosmetic formulations such as rich moisturizers and sunscreen creams due to their superior occlusive properties that help retain skin hydration. These emulsions are also essential in pharmaceutical ointments and topical drug delivery systems, providing controlled release and enhanced absorption of active ingredients. Your skincare routine benefits from W/O emulsions by improving skin barrier function and delivering long-lasting moisture protection.
Methods for Identifying Emulsion Type
To identify whether an emulsion is oil-in-water (O/W) or water-in-oil (W/O), you can perform tests such as the dilution test, where adding water to an O/W emulsion results in easy mixing, whereas a W/O emulsion resists dilution. Another method is the conductivity test because O/W emulsions conduct electricity due to their continuous aqueous phase, while W/O emulsions show poor conductivity. You can also use the dye solubility test, where water-soluble dyes color O/W emulsions but not W/O emulsions, helping you clearly distinguish the type of emulsion.
Choosing the Right Emulsion for Your Product
Choosing the right emulsion for your product depends on the desired texture, stability, and application. O/W (oil-in-water) emulsions are lighter, more hydrating, and ideal for skincare products requiring easy absorption and a non-greasy feel. W/O (water-in-oil) emulsions offer superior moisture retention and barrier protection, making them suitable for products targeting dry or sensitive skin.
Future Trends in Emulsion Technology
Future trends in emulsion technology emphasize the development of advanced O/W (oil-in-water) and W/O (water-in-oil) emulsions with enhanced stability and functionality for applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries. Innovations include stimuli-responsive emulsions that alter properties under specific conditions, and nanoemulsions offering improved bioavailability and controlled release of active ingredients. Sustainable formulation methods utilizing biodegradable surfactants and green solvents are driving eco-friendly advancements in emulsion production.
O/W emulsion vs W/O emulsion Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com