A reaction calorimeter measures heat changes during chemical reactions under controlled conditions, providing real-time thermal data critical for process optimization. A bomb calorimeter determines the heat of combustion of a sample by burning it in a sealed container, offering precise measurements essential for energy content analysis.
Table of Comparison
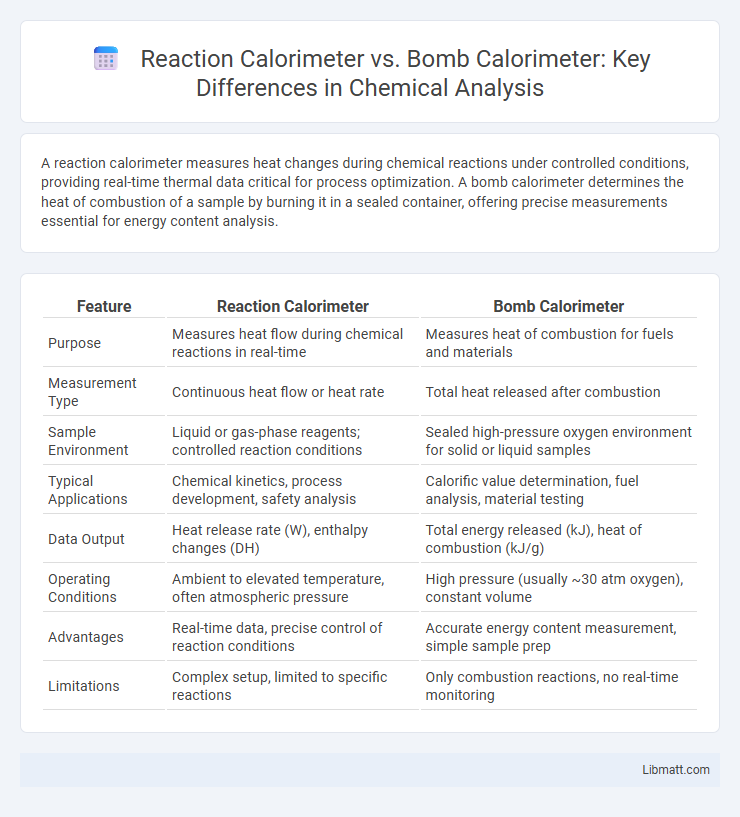
| Feature | Reaction Calorimeter | Bomb Calorimeter |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures heat flow during chemical reactions in real-time | Measures heat of combustion for fuels and materials |
| Measurement Type | Continuous heat flow or heat rate | Total heat released after combustion |
| Sample Environment | Liquid or gas-phase reagents; controlled reaction conditions | Sealed high-pressure oxygen environment for solid or liquid samples |
| Typical Applications | Chemical kinetics, process development, safety analysis | Calorific value determination, fuel analysis, material testing |
| Data Output | Heat release rate (W), enthalpy changes (DH) | Total energy released (kJ), heat of combustion (kJ/g) |
| Operating Conditions | Ambient to elevated temperature, often atmospheric pressure | High pressure (usually ~30 atm oxygen), constant volume |
| Advantages | Real-time data, precise control of reaction conditions | Accurate energy content measurement, simple sample prep |
| Limitations | Complex setup, limited to specific reactions | Only combustion reactions, no real-time monitoring |
Introduction to Calorimetry
Calorimetry measures heat changes during physical or chemical processes, essential for understanding reaction energetics. Reaction calorimeters monitor heat flow in real-time during ongoing reactions, providing dynamic thermal data for kinetics and process control. Bomb calorimeters determine the total heat of combustion in a sealed container, yielding precise calorific values primarily for fuels and materials.
Fundamentals of Reaction Calorimeters
Reaction calorimeters measure the heat flow or heat evolution during chemical reactions by monitoring temperature changes in a controlled environment, often utilizing heat exchange fluids or sensors directly in the reaction mixture. Unlike bomb calorimeters, which operate at constant volume and measure heat released from combustion within a sealed vessel, reaction calorimeters provide real-time data on reaction kinetics and heat transfer. This ongoing measurement capability allows for precise control and optimization of industrial processes by identifying exothermic or endothermic behavior during various reaction stages.
Understanding Bomb Calorimeters
Bomb calorimeters measure the heat of combustion by igniting a sample in a sealed, high-pressure container, providing precise data on energy release for chemical reactions. Reaction calorimeters, on the other hand, monitor heat flow during a reaction under controlled conditions, useful for studying reaction kinetics and thermodynamics. Your choice depends on whether you need detailed combustion energy or real-time reaction heat data.
Design Differences Between Reaction and Bomb Calorimeters
Reaction calorimeters feature a vessel coupled with sensors to monitor heat flow dynamically during chemical reactions, enabling real-time temperature and heat release measurements under controlled conditions. Bomb calorimeters consist of a sealed, robust steel container designed to withstand high pressure during combustion, with a surrounding water jacket to accurately measure heat released from explosive reactions. The design prioritizes safety and containment for high-energy samples in bomb calorimeters, whereas reaction calorimeters emphasize flexible reaction monitoring and precise thermal data acquisition.
Measurement Principles: Reaction vs Bomb Calorimeters
Reaction calorimeters measure heat flow during chemical reactions by continuously monitoring temperature changes and heat exchange with the surroundings, enabling real-time analysis of reaction kinetics. Bomb calorimeters determine the energy released by combusting a sample in a sealed, high-pressure container, measuring the resultant temperature rise in a surrounding water bath for precise combustion enthalpy data. Both instruments rely on temperature changes, but reaction calorimeters focus on dynamic reaction heat profiles, while bomb calorimeters provide static, total heat release measurements.
Applications in Industry and Research
Reaction calorimeters are essential in pharmaceutical and chemical industries for measuring heat flow during chemical reactions, enabling process optimization and scale-up. Bomb calorimeters are primarily used in materials science and energy sectors to determine the energy content of fuels and combustion properties with high precision. Your choice depends on whether you require dynamic reaction monitoring or precise energy content measurement of solid and liquid samples.
Sample Requirements and Preparation
Reaction calorimeters require smaller sample sizes and often allow in situ preparation, making them suitable for monitoring ongoing chemical processes and reactions under controlled conditions. Bomb calorimeters demand tightly sealed, non-volatile, and often homogeneous samples to ensure accurate combustion and heat measurement. Your choice depends on the nature of the sample and the precision needed for thermal analysis, with reaction calorimeters offering more flexibility in sample handling and preparation.
Data Accuracy and Precision Comparison
Reaction calorimeters offer high data accuracy by measuring heat flow in real time during chemical reactions, capturing dynamic thermal changes with precise temperature control. Bomb calorimeters provide exceptional precision in determining the heat of combustion for solid and liquid samples under constant volume conditions, yielding highly reproducible results. Your choice depends on whether you require continuous reaction monitoring or exact energy quantification for specific sample types.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Type
Reaction calorimeters offer precise control over reaction conditions and can measure heat flow in real time, making them ideal for studying dynamic chemical processes, though they may have limitations in handling highly exothermic or fast reactions. Bomb calorimeters provide accurate measurements of heat of combustion via constant-volume conditions, delivering reliable enthalpy data for solid and liquid fuels, but they are limited to combustion reactions and require substantial sample preparation. Each calorimeter type addresses specific experimental needs, with reaction calorimeters excelling in kinetic studies and bomb calorimeters in thermochemical analysis.
Choosing the Right Calorimeter for Your Needs
Selecting between a reaction calorimeter and a bomb calorimeter depends on the specific application and the nature of the chemical process being studied. Reaction calorimeters are ideal for monitoring heat flow in dynamic reactions, offering real-time data suitable for process optimization and safety assessments in industrial or research settings. Bomb calorimeters provide precise measurements of heat of combustion in a controlled, sealed environment, making them essential for applications requiring accurate energy content determination of fuels and materials.
Reaction calorimeter vs bomb calorimeter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com