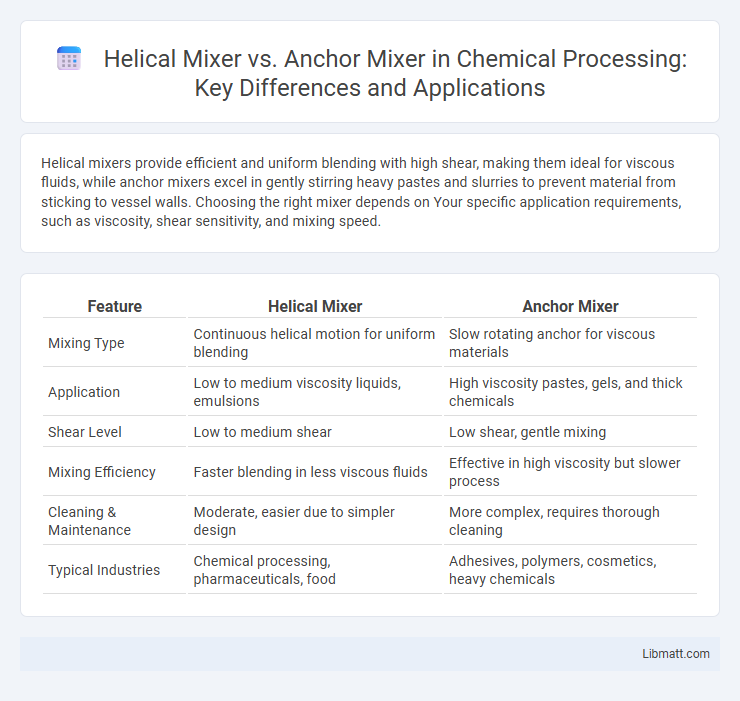
Helical mixers provide efficient and uniform blending with high shear, making them ideal for viscous fluids, while anchor mixers excel in gently stirring heavy pastes and slurries to prevent material from sticking to vessel walls. Choosing the right mixer depends on Your specific application requirements, such as viscosity, shear sensitivity, and mixing speed.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Helical Mixer | Anchor Mixer |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing Type | Continuous helical motion for uniform blending | Slow rotating anchor for viscous materials |
| Application | Low to medium viscosity liquids, emulsions | High viscosity pastes, gels, and thick chemicals |
| Shear Level | Low to medium shear | Low shear, gentle mixing |
| Mixing Efficiency | Faster blending in less viscous fluids | Effective in high viscosity but slower process |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Moderate, easier due to simpler design | More complex, requires thorough cleaning |
| Typical Industries | Chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food | Adhesives, polymers, cosmetics, heavy chemicals |
Introduction to Industrial Mixing Technologies
Helical mixers utilize spiral blades to generate axial flow, enhancing homogeneity in high-viscosity materials, making them ideal for thorough blending in chemical and food industries. Anchor mixers employ large, slow-moving paddles closely fitted to vessel walls to scrape and mix sticky or dense substances efficiently, commonly used in adhesives and pharmaceuticals. These industrial mixing technologies differ significantly in design and application, impacting mixing efficiency, shear force, and energy consumption in various production processes.
What is a Helical Mixer?
A helical mixer features a spiral-shaped mixing blade designed to create axial and radial flow for uniform blending in viscous materials. It excels in applications requiring gentle, efficient mixing of high-viscosity products like adhesives, paints, and food pastes. Compared to an anchor mixer, which uses a broad paddle for scraping vessel walls and handling thicker substances, helical mixers provide superior shear and homogeneity in semi-solid mixtures.
Understanding the Anchor Mixer Design
The anchor mixer design features a slow-moving anchor-shaped agitator that scrapes the vessel walls to ensure efficient heat transfer and thorough mixing of high-viscosity materials. Its mechanical seal and robust frame provide durability for heavy-duty applications, especially in industries like adhesives and food processing. Compared to helical mixers, anchor mixers excel in minimizing dead zones and promoting uniform material consistency in thick, viscous batches.
Key Differences Between Helical and Anchor Mixers
Helical mixers feature spiral blades that provide efficient axial and radial flow for thorough mixing, while anchor mixers use broad, flat blades that scrape vessel walls to handle high-viscosity materials. The helical design excels in consistent shear and rapid blending, whereas anchor mixers are ideal for slow-speed mixing and heat transfer in thick pastes. Understanding these key differences helps you select the optimal mixer based on material viscosity and mixing requirements.
Mixing Efficiency: Helical vs. Anchor
Helical mixers deliver superior mixing efficiency by creating a uniform flow pattern that ensures consistent blending and minimizes dead zones, especially in high-viscosity fluids. In contrast, anchor mixers provide effective heat transfer and prevent material buildup on vessel walls but often fall short in achieving the same homogeneity and speed in mixing as helical designs. Your choice between these mixers should consider the specific viscosity and mixing uniformity requirements of your process to optimize performance.
Suitable Applications for Helical Mixers
Helical mixers are ideal for handling viscous and non-Newtonian fluids, making them suitable for applications in adhesives, food processing, and pharmaceuticals where gentle yet thorough mixing is essential. These mixers provide efficient radial and axial flow patterns, ensuring uniform blending without damaging sensitive components. Your choice of a helical mixer can optimize consistency and quality in processes requiring careful shearing and low shear stress environments.
Ideal Use Cases for Anchor Mixers
Anchor mixers are ideal for blending high-viscosity materials, such as pastes, adhesives, and heavy creams, where thorough mixing without air incorporation is critical. Their slow-speed, high-torque design ensures consistent shear and temperature control, making them suitable for heat-sensitive products in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. Industries requiring gentle yet effective mixing of thick substances benefit significantly from the robust structure and efficient scraping action of anchor mixers.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Helical mixers consume significantly less energy than anchor mixers due to their efficient fluid dynamics and reduced friction during operation. Studies show that helical mixers can reduce energy consumption by up to 30% in viscous fluid mixing processes compared to traditional anchor mixers. Optimizing energy use in industrial mixing applications often favors helical designs for their superior mixing efficiency and lower power requirements.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Helical mixers generally require less maintenance due to their streamlined design and uniform wear patterns, resulting in longer operational lifespan compared to anchor mixers. Anchor mixers involve more moving parts and complex sealing systems, which can increase maintenance frequency and impact overall durability. Your choice should consider the specific maintenance capabilities and longevity expectations of your application to optimize performance and reduce downtime.
Choosing the Right Mixer for Your Process
Choosing the right mixer for your process depends heavily on the viscosity and shear sensitivity of your materials. Helical mixers excel in handling medium to high viscosity fluids with uniform shearing action, ensuring consistent blending without damaging sensitive components. Anchor mixers suit very high viscosity or pasty materials by providing gentle scraping and efficient heat transfer, making your choice critical for optimizing mixing efficiency and product quality.
Helical mixer vs anchor mixer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com