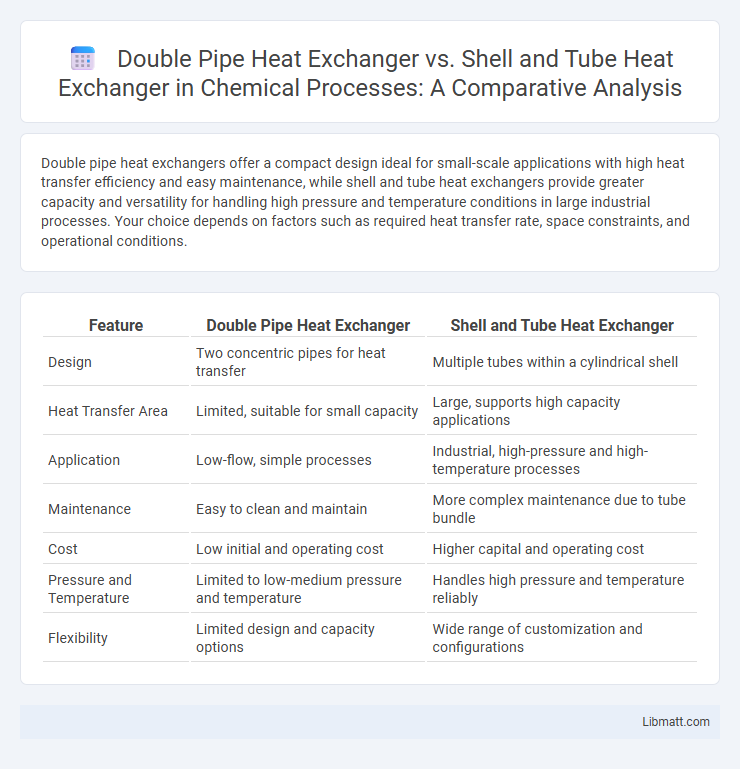
Double pipe heat exchangers offer a compact design ideal for small-scale applications with high heat transfer efficiency and easy maintenance, while shell and tube heat exchangers provide greater capacity and versatility for handling high pressure and temperature conditions in large industrial processes. Your choice depends on factors such as required heat transfer rate, space constraints, and operational conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Double Pipe Heat Exchanger | Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Two concentric pipes for heat transfer | Multiple tubes within a cylindrical shell |
| Heat Transfer Area | Limited, suitable for small capacity | Large, supports high capacity applications |
| Application | Low-flow, simple processes | Industrial, high-pressure and high-temperature processes |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and maintain | More complex maintenance due to tube bundle |
| Cost | Low initial and operating cost | Higher capital and operating cost |
| Pressure and Temperature | Limited to low-medium pressure and temperature | Handles high pressure and temperature reliably |
| Flexibility | Limited design and capacity options | Wide range of customization and configurations |
Introduction to Heat Exchangers
Double pipe heat exchangers consist of one pipe inside another, enabling efficient heat transfer between two fluids with a simple design ideal for smaller capacities and easy maintenance. Shell and tube heat exchangers feature multiple tubes enclosed within a cylindrical shell, offering higher heat transfer area and suitability for high-pressure, high-temperature industrial applications. Both types facilitate thermal energy exchange, with shell and tube designs providing greater flexibility and capacity for complex processes.
Overview of Double Pipe Heat Exchangers
Double pipe heat exchangers consist of one pipe enclosed within another, enabling efficient heat transfer between fluids flowing in counter-current or co-current configurations. They are typically used in applications requiring low to medium heat transfer rates, such as chemical processing and HVAC systems. Compared to shell and tube heat exchangers, double pipe designs offer simpler construction, easier maintenance, and suitability for handling high-pressure fluids in smaller volumes.
Overview of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of a series of tubes, one set carrying the hot fluid and the other the cold fluid, enclosed within a cylindrical shell to facilitate efficient heat transfer. They are widely used in industries such as chemical processing, power generation, and oil refining due to their robust design and ability to handle high pressures and temperatures. Compared to double pipe heat exchangers, shell and tube models offer greater surface area, enhanced heat transfer efficiency, and scalability for larger applications.
Design Differences: Double Pipe vs Shell and Tube
Double pipe heat exchangers feature a simple design with one pipe inside another, allowing counterflow or parallel flow heat transfer, ideal for small-scale applications and easier maintenance. Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of multiple tubes enclosed within a shell, enabling higher heat transfer area, handling of larger capacities, and better pressure resistance. Your choice between these designs depends on factors like fluid volume, pressure requirements, and space constraints.
Heat Transfer Efficiency Comparison
Double pipe heat exchangers offer higher heat transfer efficiency in applications involving small flow rates and significant temperature differences due to their straightforward design and enhanced turbulence. Shell and tube heat exchangers provide more surface area and better handling of high-pressure and high-volume flows, making them efficient for large-scale industrial processes. Your choice depends on whether surface area or flow volume efficiency aligns better with your heat transfer requirements.
Applications and Industry Suitability
Double pipe heat exchangers excel in small-scale applications requiring low to moderate heat transfer efficiency, commonly used in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food industries for heating or cooling of fluids with limited flow rates. Shell and tube heat exchangers, with their robust design and higher capacity, are ideal for heavy-duty operations in petrochemical, power generation, and oil refining industries, handling large volumes and high pressures. Their versatility and scalability make shell and tube exchangers suitable for high-temperature applications and complex process requirements across diverse industrial sectors.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Double pipe heat exchangers feature simpler designs with easy disassembly, allowing for straightforward cleaning and routine maintenance, especially suitable for handling viscous fluids or those prone to fouling. Shell and tube heat exchangers require more comprehensive maintenance due to their complex structure, including periodic tube bundle removal and chemical cleaning to manage scale buildup and corrosion. Effective maintenance schedules for both types enhance heat transfer efficiency and extend equipment lifespan, with shell and tube units demanding higher operational downtime during cleaning.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Double pipe heat exchangers generally have lower upfront costs and simpler installation requirements due to their compact, straightforward design, making them ideal for small-scale applications or limited spaces. Shell and tube heat exchangers typically involve higher material and labor costs because of their complex construction and need for specialized mounting or support structures. Installation of shell and tube units demands more space and skilled labor, whereas double pipe models offer easier maintenance and flexibility in configurations, impacting overall project budgets and timelines.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type
Double pipe heat exchangers offer advantages such as simple construction, easy cleaning, and suitability for small-scale applications with high pressure or temperature variations. However, their disadvantages include limited heat transfer area, lower efficiency, and larger footprint for high capacity compared to shell and tube heat exchangers. Shell and tube heat exchangers provide high heat transfer efficiency, versatility for various fluids and pressures, and compact design for large-scale industrial processes, but they require complex maintenance and higher initial cost than double pipe heat exchangers.
Choosing the Right Heat Exchanger for Your Needs
Selecting the right heat exchanger depends on factors such as heat transfer efficiency, space constraints, and maintenance requirements. Double pipe heat exchangers offer simplicity and are ideal for small-scale applications with easy cleaning needs, while shell and tube heat exchangers provide higher capacity and superior heat transfer for industrial processes. Evaluating thermal performance, operating pressure, and fluid compatibility is essential to determine the most suitable option for your specific thermal management challenges.
double pipe heat exchanger vs shell and tube heat exchanger Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com