Tensile membrane structures offer superior strength and flexibility, allowing for large, uninterrupted spans with sleek, modern aesthetics ideal for outdoor shading. Your choice between tensile membrane and fabric canopy should consider durability, design preferences, and the specific environmental conditions of your space.
Table of Comparison
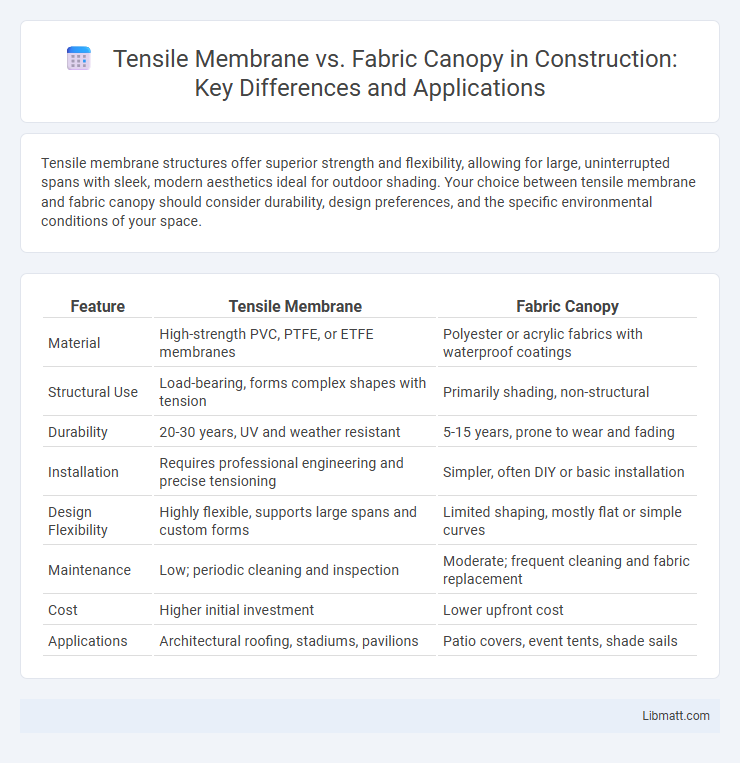
| Feature | Tensile Membrane | Fabric Canopy |
|---|---|---|
| Material | High-strength PVC, PTFE, or ETFE membranes | Polyester or acrylic fabrics with waterproof coatings |
| Structural Use | Load-bearing, forms complex shapes with tension | Primarily shading, non-structural |
| Durability | 20-30 years, UV and weather resistant | 5-15 years, prone to wear and fading |
| Installation | Requires professional engineering and precise tensioning | Simpler, often DIY or basic installation |
| Design Flexibility | Highly flexible, supports large spans and custom forms | Limited shaping, mostly flat or simple curves |
| Maintenance | Low; periodic cleaning and inspection | Moderate; frequent cleaning and fabric replacement |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Applications | Architectural roofing, stadiums, pavilions | Patio covers, event tents, shade sails |
Overview of Tensile Membranes and Fabric Canopies
Tensile membranes utilize high-strength materials such as PTFE-coated fiberglass or PVC-coated polyester, designed to withstand tension and create dynamic, curved architectural forms. Fabric canopies typically employ woven textiles like canvas or acrylic, offering flexible, lightweight shading solutions with a focus on ease of installation and cost-effectiveness. Both structures provide weather protection and aesthetic appeal, but tensile membranes excel in large-span applications due to their structural integrity and durability under varying environmental conditions.
Structural Design Differences
Tensile membranes rely on tensioned fabric stretched over a rigid framework, creating curved, aerodynamic shapes that efficiently distribute loads through continuous tension forces. Fabric canopies typically use simpler frameworks with loosely draped or fixed fabric that may rely more on compression and bending forces within the supporting structure. The tensile membrane's structural design emphasizes pre-stressed elements, whereas fabric canopies often involve minimal tension and are more dependent on their frame for stability and shape.
Material Composition and Properties
Tensile membranes are typically made from high-strength materials such as PTFE-coated fiberglass or PVC-coated polyester, offering superior tensile strength, durability, and weather resistance compared to standard fabric canopies. Fabric canopies usually utilize lighter materials like canvas, acrylic, or polyester, which provide flexibility and ease of installation but may lack the advanced UV resistance and load-bearing capabilities of tensile membranes. Material composition directly influences performance characteristics, with tensile membranes excelling in long-term structural stability and fabric canopies favored for cost-effectiveness and aesthetic versatility.
Installation Process Comparison
Tensile membrane installation requires precise engineering, custom fabrication, and skilled labor to tension the membrane onto a structural framework, ensuring durability and aerodynamic stability. Fabric canopy installation is typically faster and less complex, involving attaching pre-cut fabric panels to a support frame using simple fastening methods like ties or clips. The tensile membrane process demands specialized equipment and professional expertise, while fabric canopies allow for more flexible, cost-effective setups suitable for temporary or less demanding applications.
Durability and Longevity
Tensile membrane structures typically use high-strength materials like PTFE-coated fiberglass or PVC-coated polyester, which offer superior resistance to UV radiation, weathering, and tears, resulting in enhanced durability and extended lifespan of 20-30 years or more. Fabric canopies often employ materials such as acrylic, polyester, or vinyl, which may degrade faster under harsh environmental conditions, generally lasting 10-15 years depending on maintenance and exposure. The advanced engineering and material technology inherent in tensile membranes provide greater structural integrity and longevity, making them a preferred choice for long-term outdoor installations.
Aesthetic and Architectural Flexibility
Tensile membrane structures offer superior aesthetic appeal and architectural flexibility due to their ability to create bold, sweeping curves and dynamic shapes that fabric canopies often cannot achieve. Fabric canopies provide practical shading solutions but are typically limited to simpler, more traditional forms, which may restrict creative design opportunities. Your choice will influence the visual impact and versatility of the space, with tensile membranes allowing more innovative, sculptural installations.
Cost Considerations and Budgeting
Tensile membrane structures generally involve higher upfront costs due to specialized materials and complex installation processes, whereas fabric canopies offer a more budget-friendly option with simpler construction and standard materials. Maintenance expenses should also be factored in, as tensile membranes require professional cleaning and potential repairs over time, while fabric canopies may need more frequent replacements but simpler upkeep. Understanding Your project's size, durability requirements, and long-term financial plan will help determine which option aligns best with Your budget constraints.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Tensile membrane structures typically require low maintenance due to their durable, weather-resistant materials such as PTFE-coated fiberglass or PVC-coated polyester, which resist dirt and mildew. Fabric canopies, often made from materials like acrylic or vinyl, demand more frequent cleaning to prevent staining and mold buildup, especially in humid environments. Regular inspection and gentle cleaning with mild soaps are essential for both to prolong lifespan and maintain aesthetic appeal.
Climate and Weather Performance
Tensile membranes excel in extreme weather conditions due to their high tensile strength and flexibility, allowing them to withstand heavy winds, rain, and snow loads effectively. Fabric canopies typically offer good UV protection and ventilation but may require additional treatment or reinforcement to endure severe climates or prolonged exposure to harsh elements. Selecting between the two depends on your location's specific climate challenges, ensuring optimal durability and performance for your outdoor space.
Best Applications for Each System
Tensile membrane structures excel in large-span applications such as stadiums, airports, and exhibition halls due to their ability to cover vast areas with minimal support. Fabric canopies are best suited for smaller-scale uses like patios, walkways, and outdoor seating areas where flexibility and easy installation are priorities. The choice depends on the required scale, structural complexity, and aesthetic goals of the project.
Tensile membrane vs fabric canopy Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com