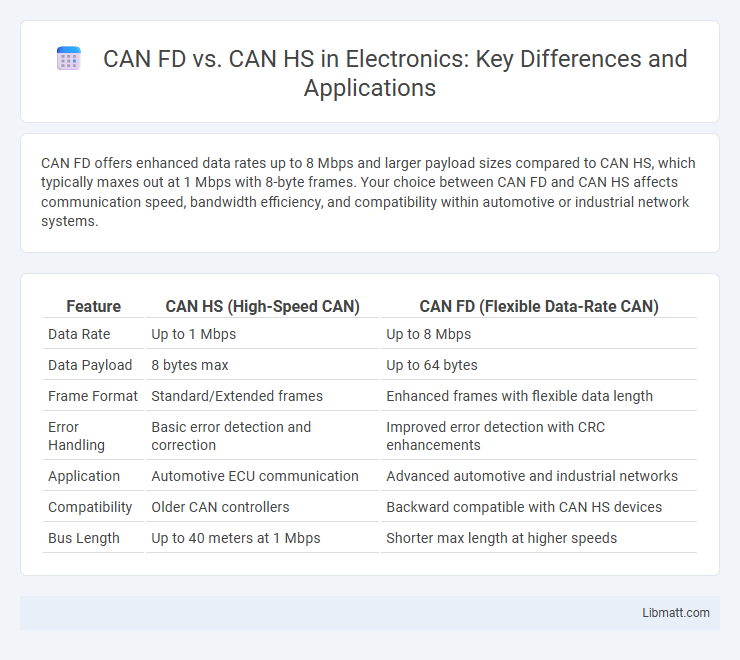
CAN FD offers enhanced data rates up to 8 Mbps and larger payload sizes compared to CAN HS, which typically maxes out at 1 Mbps with 8-byte frames. Your choice between CAN FD and CAN HS affects communication speed, bandwidth efficiency, and compatibility within automotive or industrial network systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | CAN HS (High-Speed CAN) | CAN FD (Flexible Data-Rate CAN) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Rate | Up to 1 Mbps | Up to 8 Mbps |
| Data Payload | 8 bytes max | Up to 64 bytes |
| Frame Format | Standard/Extended frames | Enhanced frames with flexible data length |
| Error Handling | Basic error detection and correction | Improved error detection with CRC enhancements |
| Application | Automotive ECU communication | Advanced automotive and industrial networks |
| Compatibility | Older CAN controllers | Backward compatible with CAN HS devices |
| Bus Length | Up to 40 meters at 1 Mbps | Shorter max length at higher speeds |
Introduction to CAN FD and CAN HS
CAN FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data-rate) enhances the classic CAN HS (High-Speed) protocol by supporting data rates up to 8 Mbps and payload sizes up to 64 bytes, compared to CAN HS's 1 Mbps and 8-byte limit. CAN FD improves network efficiency and flexibility in automotive and industrial applications by enabling faster data transmission and larger message frames. This advancement addresses the growing demand for higher bandwidth and more complex communication in modern electronic control units (ECUs).
Overview of CAN Protocol Evolution
CAN FD (Flexible Data-rate) represents the latest advancement in CAN protocol evolution, enhancing data payload capacity up to 64 bytes compared to the 8 bytes limit in CAN HS (High-Speed). This improvement allows Your automotive and industrial communication systems to handle more complex data efficiently while maintaining robust error detection capabilities. The shift from CAN HS to CAN FD reflects the industry's demand for higher bandwidth and faster transmission rates, promoting more versatile and scalable network performance.
Key Differences Between CAN FD and CAN HS
CAN FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data-rate) supports data rates up to 8 Mbps and allows payloads up to 64 bytes per frame, significantly surpassing CAN HS (High-Speed) which maxes out at 1 Mbps with an 8-byte payload. CAN FD improves efficiency by enabling variable data rates within a single frame, while CAN HS uses a fixed speed for all frames. Enhanced error detection and flexible data length in CAN FD provide greater robustness and bandwidth compared to the traditional, lower-capacity CAN HS.
Data Transfer Rates: CAN FD vs CAN HS
CAN FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data-Rate) supports data transfer rates up to 8 Mbps during the data phase, significantly higher than CAN HS (High-Speed), which typically maxes out at 1 Mbps. The improved throughput in CAN FD is achieved by allowing variable data lengths up to 64 bytes and faster bit rates in the data phase, optimizing bandwidth usage. CAN HS remains limited by a fixed 8-byte data length and lower speeds, making CAN FD ideal for applications requiring higher data payloads and faster communication.
Message Frame Structure Comparison
CAN FD and CAN HS differ significantly in message frame structure, with CAN FD supporting longer data fields of up to 64 bytes compared to CAN HS's maximum of 8 bytes. The extended data length in CAN FD allows for more efficient transmission of larger payloads without increasing protocol overhead. Your applications benefit from CAN FD's flexible frame design, enhancing data throughput and reducing communication latency in high-speed automotive and industrial networks.
Error Detection and Reliability
CAN FD offers enhanced error detection and reliability compared to CAN HS by supporting a flexible data rate and increased payload size, which improves fault tolerance during data transmission. The improved CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) mechanism in CAN FD provides stronger error checking, reducing the likelihood of undetected errors. CAN FD's ability to dynamically adjust bit timing also contributes to better signal integrity and communication robustness in complex automotive environments.
Network Compatibility and Interoperability
CAN FD (Flexible Data-rate) maintains backward compatibility with standard CAN HS (High-Speed) networks by using the same physical layer, enabling seamless integration and communication between devices on a shared bus. CAN FD extends data payloads from 8 to 64 bytes and increases bit rates during the data phase without disrupting network timing or protocol structure, thus preserving interoperability with existing CAN HS controllers. However, full utilization of CAN FD's enhanced features requires all nodes to support the FD protocol, while mixed networks can safely operate at standard CAN HS speeds to ensure compatibility.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
CAN FD (Flexible Data-Rate) is widely adopted in automotive and industrial automation sectors where higher data throughput and enhanced diagnostic capabilities are critical, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and smart factory machinery. CAN HS (High-Speed) remains prevalent in traditional automotive body control modules, engine management systems, and standard industrial equipment, supporting reliable communication with data rates up to 1 Mbps. The extended data length and faster transmission of CAN FD suit complex applications requiring real-time data exchange and larger payloads, whereas CAN HS excels in environments where simplicity and proven technology are prioritized.
Advantages and Limitations
CAN FD offers higher data rates up to 8 Mbps and larger payloads of up to 64 bytes, improving communication efficiency compared to CAN HS's 1 Mbps and 8-byte limit. CAN HS provides reliable high-speed communication with lower implementation complexity and compatibility with legacy systems. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize faster data transfer and scalability with CAN FD or simplicity and established infrastructure with CAN HS.
Future Trends in CAN Communication Systems
CAN FD (Flexible Data-rate) enhances traditional CAN HS (High-Speed) by supporting higher data rates up to 8 Mbps and larger payloads of up to 64 bytes, addressing increasing bandwidth demands in automotive and industrial networks. Future trends emphasize CAN FD's integration with automotive Ethernet and time-sensitive networking (TSN) to enable higher data throughput, improved synchronization, and enhanced real-time communication reliability. Ongoing advancements focus on combining CAN FD's robustness with emerging technologies to support autonomous driving, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and Industry 4.0 applications.
CAN FD vs CAN HS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com