LDO regulators provide low-noise, simple voltage regulation ideal for low-dropout applications but tend to have lower efficiency compared to buck converters, which offer high efficiency and can step down voltage from a higher level but generate more noise. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize power efficiency or noise-sensitive performance in your electronic design.
Table of Comparison
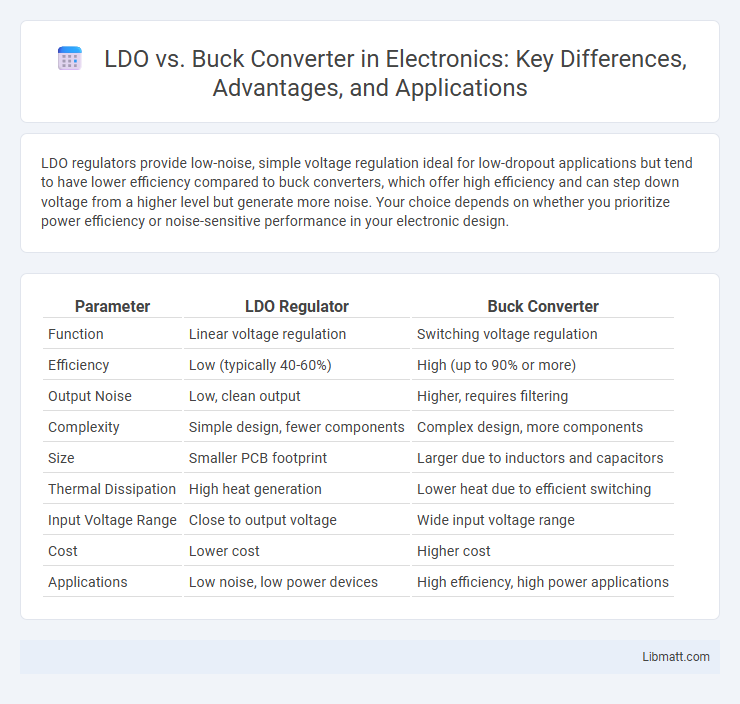
| Parameter | LDO Regulator | Buck Converter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Linear voltage regulation | Switching voltage regulation |
| Efficiency | Low (typically 40-60%) | High (up to 90% or more) |
| Output Noise | Low, clean output | Higher, requires filtering |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | Complex design, more components |
| Size | Smaller PCB footprint | Larger due to inductors and capacitors |
| Thermal Dissipation | High heat generation | Lower heat due to efficient switching |
| Input Voltage Range | Close to output voltage | Wide input voltage range |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Low noise, low power devices | High efficiency, high power applications |
Introduction to Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. LDO (Low Dropout) regulators offer simple, low-noise voltage regulation ideal for low-voltage difference applications and provide fast transient response with minimal output ripple. Buck converters deliver high efficiency by switching elements at high frequency, making them suitable for applications requiring significant voltage step-down with higher current demands.
Overview of LDO and Buck Converters
LDO (Low Dropout) regulators provide simple, low-noise voltage regulation with minimal external components, ideal for low power applications requiring clean output voltage. Buck converters, also known as step-down switching regulators, efficiently convert higher input voltages to lower output voltages through high-frequency switching and energy storage elements, making them suitable for high-current, energy-sensitive designs. Both regulators serve distinct roles in power management, with LDOs offering simplicity and low noise, while buck converters deliver higher efficiency and thermal performance.
Working Principles: LDO vs Buck Converter
An LDO (Low Dropout Regulator) regulates voltage by dissipating excess power as heat, using a linear control element to maintain a steady output voltage slightly below the input voltage, making it ideal for low noise and simple applications. In contrast, a Buck Converter is a switching regulator that efficiently steps down voltage through rapid switching and energy storage components like inductors and capacitors, significantly improving power efficiency in higher load scenarios. Your choice depends on balancing noise sensitivity with power efficiency requirements, as LDOs offer simplicity and low noise, while Buck Converters provide higher efficiency and better thermal management.
Efficiency Comparison: LDO vs Buck
Buck converters typically achieve efficiency levels between 80% to 95% by using switching elements to regulate voltage, making them ideal for applications with significant voltage drops. LDO regulators, on the other hand, offer simpler design and lower noise at the cost of efficiency, which can drop below 50% when input-to-output voltage difference is high. Choosing between LDO and buck depends on power efficiency requirements, input voltage range, and noise sensitivity in the specific application.
Noise Performance and Output Quality
LDO regulators excel in noise-sensitive applications due to their low output ripple and minimal electromagnetic interference, providing superior output quality for analog and RF circuits. Buck converters generate higher switching noise and ripple but offer greater efficiency for power-intensive devices. When your design demands ultra-clean power, an LDO is ideal, whereas a buck converter suits applications prioritizing efficiency over ultra-low noise.
Power Dissipation and Thermal Management
LDO (Low Dropout) regulators exhibit higher power dissipation compared to buck converters because they regulate voltage by linear resistance, converting excess voltage directly into heat. Buck converters achieve greater efficiency by switching at high frequencies and using inductors to maintain output voltage, significantly reducing thermal stress and power loss. Effective thermal management in LDOs requires larger heat sinks or thermal vias, whereas buck converters typically operate cooler and demand less complex cooling solutions.
Size and Design Complexity
LDO regulators feature simpler designs with fewer components, resulting in smaller size and easier integration on compact PCBs. Buck converters require inductors and more complex circuitry, increasing overall size and design complexity but offering higher efficiency for power management. Your choice depends on balancing space constraints and efficiency needs in your electronic design.
Application Suitability: Use Cases
LDO regulators are ideal for low-dropout voltage applications in noise-sensitive environments such as RF circuits, battery-powered devices, and low-power analog electronics. Buck converters excel in high-efficiency power conversion for applications requiring significant voltage step-down, including motor drives, LED lighting, and industrial power supplies. The choice depends on factors like load current, efficiency demands, and noise tolerance in the specific use case.
Cost Considerations and Availability
LDO regulators generally offer lower initial cost and simpler design, making them more economically viable for low-power and low-voltage-drop applications. Buck converters, while typically more expensive due to complex circuitry and external components, provide higher efficiency and better thermal performance, justifying their cost in high-current or battery-powered devices. Availability for both components is widespread, but buck converters may require sourcing specific inductor and MOSFET components, potentially affecting lead times and overall BOM cost compared to integrated LDO solutions.
Choosing Between LDO and Buck Converters
Choosing between an LDO and a buck converter depends on efficiency, voltage difference, and noise sensitivity. Buck converters offer higher efficiency for large voltage drops and high current loads, while LDOs provide simpler design with lower noise and better transient response for small voltage differences. Your application's power requirements and noise tolerance will determine the most suitable voltage regulation method.
LDO vs Buck converter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com