Thermistors offer high sensitivity and rapid response to temperature changes, ideal for applications requiring precise measurements over narrow temperature ranges. RTDs provide superior accuracy and stability across wider temperature spans, making them suitable for industrial environments where consistent, long-term monitoring of Your equipment's temperature is critical.
Table of Comparison
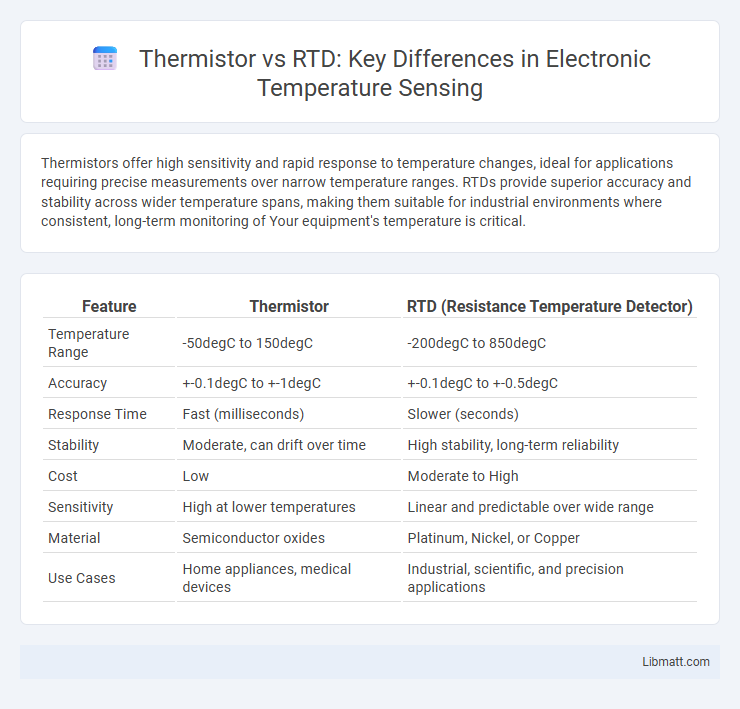
| Feature | Thermistor | RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | -200degC to 850degC |
| Accuracy | +-0.1degC to +-1degC | +-0.1degC to +-0.5degC |
| Response Time | Fast (milliseconds) | Slower (seconds) |
| Stability | Moderate, can drift over time | High stability, long-term reliability |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to High |
| Sensitivity | High at lower temperatures | Linear and predictable over wide range |
| Material | Semiconductor oxides | Platinum, Nickel, or Copper |
| Use Cases | Home appliances, medical devices | Industrial, scientific, and precision applications |
Introduction to Temperature Sensors
Thermistors and RTDs are precise temperature sensors widely used in industrial and scientific applications for accurate temperature measurement. Thermistors offer high sensitivity and fast response times, making them ideal for detecting small temperature changes, while RTDs provide superior accuracy and stability over a broader temperature range. Your choice between thermistor and RTD depends on factors like required accuracy, temperature range, and environmental conditions.
What is a Thermistor?
A thermistor is a temperature sensor made from semiconductor materials that exhibits a significant change in resistance with temperature fluctuations, typically classified as either NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) or PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient). Your choice of a thermistor is ideal for precise temperature measurements in a limited range due to its high sensitivity and fast response time. Unlike RTDs, thermistors provide greater accuracy in specific applications but operate effectively within narrower temperature intervals.
What is an RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector)?
An RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) is a precision temperature sensor that measures temperature by correlating the resistance of a metal, typically platinum, with temperature changes. Platinum RTDs, like the widely used Pt100, offer high accuracy, stability, and repeatability across a broad temperature range from -200degC to 850degC. RTDs are preferred in industrial applications for their linear response, long-term reliability, and suitability in environments requiring precise temperature monitoring.
Working Principles: Thermistor vs RTD
Thermistors operate based on the rapid change in electrical resistance of semiconductor materials with temperature, exhibiting either a negative or positive temperature coefficient. RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors) function by measuring the linear change in resistance of pure metals, typically platinum, as temperature varies. Your choice between a thermistor and an RTD depends on the required temperature range, accuracy, and response time, with thermistors excelling in sensitivity and RTDs offering superior stability and precision.
Accuracy and Precision: Comparing Thermistor and RTD
Thermistors offer high sensitivity and rapid response time but generally provide lower accuracy compared to RTDs, which deliver superior precision and repeatability over a wide temperature range. RTDs maintain stable and consistent measurements with minimal drift, making them ideal for applications demanding strict accuracy, whereas thermistors are better suited for non-critical temperature monitoring due to their nonlinear response. Understanding these differences helps you select the most appropriate sensor for your specific temperature measurement needs.
Temperature Range and Sensitivity
RTDs typically operate within a temperature range of -200degC to 850degC, offering high accuracy and excellent stability over time, while thermistors function primarily between -50degC and 150degC with superior sensitivity at lower temperatures. Thermistors provide rapid response and greater sensitivity to small temperature changes, making them ideal for precise measurements in limited temperature ranges. RTDs maintain linear characteristics over wider temperature spans, suiting applications requiring consistent accuracy across extreme environmental conditions.
Response Time and Stability
Thermistors offer faster response times due to their smaller size and higher sensitivity, making them ideal for applications requiring quick temperature changes detection. RTDs provide superior long-term stability and accuracy, benefiting from their metal construction that resists drift over time. While thermistors excel in dynamic environments, RTDs maintain consistent performance in precise and stable measurement scenarios.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Thermistors generally offer a lower cost solution compared to RTDs, making them ideal for budget-sensitive applications requiring moderate temperature accuracy. Installation of thermistors is simpler due to their smaller size and less stringent wiring requirements, reducing setup time and labor expenses. Your choice should consider long-term maintenance costs and the specific environmental conditions each sensor can handle, as RTDs tend to offer greater durability and stability in harsh settings.
Typical Applications of Thermistors and RTDs
Thermistors are commonly used in applications requiring high sensitivity and rapid response, such as digital thermometers, automotive temperature sensors, and battery management systems. RTDs are preferred for industrial processes and HVAC systems due to their accuracy, stability, and wide temperature range, making them ideal for monitoring equipment and environmental conditions. Your choice between thermistors and RTDs depends on the specific requirements for precision, temperature range, and response time in your application.
Which is Better: Thermistor or RTD?
RTDs offer higher accuracy and stability over a wider temperature range, making them ideal for precision industrial applications. Thermistors respond faster and provide greater sensitivity at lower temperatures, suitable for safety or medical devices. Your choice depends on the required temperature range, accuracy, and response time for your specific application.
Thermistor vs RTD Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com