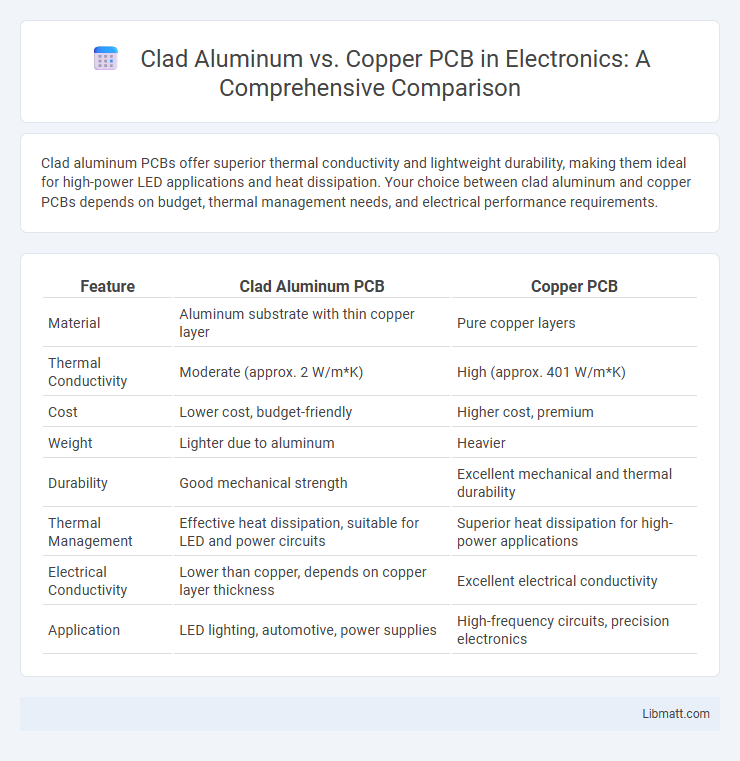
Clad aluminum PCBs offer superior thermal conductivity and lightweight durability, making them ideal for high-power LED applications and heat dissipation. Your choice between clad aluminum and copper PCBs depends on budget, thermal management needs, and electrical performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Clad Aluminum PCB | Copper PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum substrate with thin copper layer | Pure copper layers |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate (approx. 2 W/m*K) | High (approx. 401 W/m*K) |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost, premium |
| Weight | Lighter due to aluminum | Heavier |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength | Excellent mechanical and thermal durability |
| Thermal Management | Effective heat dissipation, suitable for LED and power circuits | Superior heat dissipation for high-power applications |
| Electrical Conductivity | Lower than copper, depends on copper layer thickness | Excellent electrical conductivity |
| Application | LED lighting, automotive, power supplies | High-frequency circuits, precision electronics |
Introduction to Clad Aluminum and Copper PCBs
Clad aluminum PCBs feature an aluminum base layer combined with a conductive copper foil, offering excellent thermal management and lightweight properties ideal for high-power applications. Copper PCBs consist entirely of copper layers laminated onto a substrate, providing superior electrical conductivity and flexibility for complex circuit designs. Selecting between clad aluminum and copper PCBs depends on balancing thermal performance and electrical efficiency tailored to specific electronic device requirements.
Key Material Properties: Aluminum vs Copper
Aluminum PCBs offer excellent thermal conductivity with lightweight and superior heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-power LED applications, whereas copper PCBs provide higher electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, suitable for complex circuitry requiring robust signal integrity. The thermal expansion coefficient of aluminum is higher than copper, which may affect durability under temperature fluctuations, but aluminum's cost-effectiveness supports budget-friendly manufacturing. Your choice between clad aluminum and copper PCB depends on balancing heat management needs against electrical performance and mechanical reliability.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Clad aluminum PCBs offer thermal conductivity ranging from 120 to 180 W/m*K, efficiently dissipating heat from high-power electronic components, while copper PCBs possess superior thermal conductivity of approximately 385 W/m*K, ensuring rapid heat transfer in demanding applications. Your choice between clad aluminum and copper PCBs depends on balancing cost and thermal performance needs, with copper providing optimal heat dissipation but at higher material and manufacturing expenses. For high-frequency or high-temperature environments, copper's excellence in thermal management enhances device reliability and longevity compared to clad aluminum alternatives.
Electrical Performance in PCB Applications
Clad aluminum PCBs offer improved thermal conductivity and lightweight properties compared to copper, making them suitable for power electronics and LED applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. Copper PCBs exhibit superior electrical conductivity and lower resistive losses, essential for high-frequency and signal integrity-critical circuits. The choice between clad aluminum and copper PCBs depends on balancing thermal management needs with electrical performance demands in specific PCB applications.
Cost Implications and Economic Considerations
Clad aluminum PCBs offer a cost-effective solution due to lower raw material expenses and reduced manufacturing complexity compared to copper PCBs. Copper PCBs, while more expensive upfront, provide superior electrical conductivity that can enhance performance in high-frequency applications, potentially lowering long-term operational costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including thermal management and application-specific requirements, is essential for making economically sound decisions between clad aluminum and copper PCBs.
Weight and Mechanical Strength Differences
Clad aluminum PCBs are significantly lighter than copper PCBs, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace and portable electronics. The mechanical strength of clad aluminum is enhanced by its aluminum base, providing excellent thermal conductivity and improved durability under mechanical stress compared to pure copper PCBs. Your choice between clad aluminum and copper PCBs should consider the balance between lightweight design and the mechanical robustness required for your specific project.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Clad aluminum PCBs use an aluminum base layer bonded with a thin copper foil through heat and pressure, ensuring efficient thermal conductivity and structural integrity during manufacturing. Copper PCBs involve copper layers laminated onto a fiberglass substrate, requiring precise etching and layering to achieve desired circuit patterns. Your choice impacts both thermal management and production complexity due to these distinct fabrication methods.
Application Suitability: Which PCB for Which Industry?
Clad aluminum PCBs are ideal for high-thermal applications such as LED lighting, power electronics, and automotive industries due to their excellent heat dissipation and lightweight properties. Copper PCBs offer superior electrical conductivity and are preferred in telecommunications, aerospace, and high-frequency circuit applications where signal integrity is critical. Your choice between clad aluminum and copper PCB depends on balancing thermal management needs against electrical performance requirements for your specific industry.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Clad aluminum PCBs offer superior environmental benefits due to aluminum's lower energy consumption during production and higher recyclability compared to copper. Aluminum's lighter weight reduces transportation emissions, and its corrosion-resistant properties extend PCB lifespan, minimizing electronic waste. Copper PCBs, while highly conductive, require more intensive mining and refining processes, resulting in greater environmental impact and resource depletion.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right PCB Material
Choosing the right PCB material depends on the application's thermal management and electrical conductivity requirements. Clad aluminum PCBs excel in heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-power LED and automotive electronics, while copper PCBs offer superior electrical conductivity and signal integrity for complex, high-frequency circuits. Balancing cost, performance, and durability guides the optimal selection between clad aluminum and copper PCBs in advanced electronic designs.
Clad Aluminum vs Copper PCB Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com