MOV (Metal Oxide Varistor) and TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) both protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes, but MOVs are better suited for high-energy transient suppression, while TVSs offer faster response times and precise clamping voltages for sensitive components. Understanding the differences helps you select the right device to enhance your circuit's reliability during electrical surges.
Table of Comparison
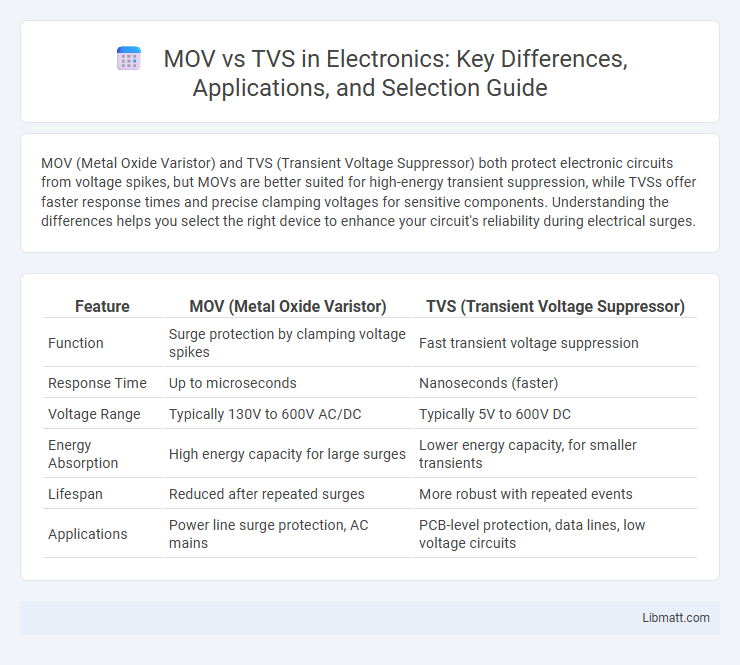
| Feature | MOV (Metal Oxide Varistor) | TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Surge protection by clamping voltage spikes | Fast transient voltage suppression |
| Response Time | Up to microseconds | Nanoseconds (faster) |
| Voltage Range | Typically 130V to 600V AC/DC | Typically 5V to 600V DC |
| Energy Absorption | High energy capacity for large surges | Lower energy capacity, for smaller transients |
| Lifespan | Reduced after repeated surges | More robust with repeated events |
| Applications | Power line surge protection, AC mains | PCB-level protection, data lines, low voltage circuits |
Introduction to MOV and TVS
Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) are voltage-dependent resistors primarily used for surge protection by clamping high voltage transients in electrical circuits. Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS) diodes are semiconductor devices designed to protect sensitive electronics from voltage spikes by rapidly shunting excess current to the ground. Both MOVs and TVS diodes serve critical roles in safeguarding electronic components from transient voltage damage but differ in response time, energy handling, and lifespan characteristics.
What is a Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV)?
A Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV) is an electronic component designed to protect circuits from voltage surges by clamping excessive transient voltages. It consists of zinc oxide grains sandwiched between metal electrodes, which enables it to conduct current only when voltage exceeds a specific threshold. MOVs are widely used in surge protectors to safeguard sensitive electronics by absorbing and dissipating energy from spikes caused by lightning strikes or switching operations.
What is a Transient Voltage Suppression Diode (TVS)?
A Transient Voltage Suppression Diode (TVS) is a semiconductor device designed to protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes by clamping transient voltages to safe levels. Unlike Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs), TVS diodes react within picoseconds to nanoseconds, providing fast response times critical for sensitive components. TVS diodes are commonly used in applications requiring precise voltage regulation and surge protection due to their reliable and repeatable voltage clamping characteristics.
Key Differences Between MOV and TVS
Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) and Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS) differ primarily in their response time and application. MOVs typically handle large surge currents with slower response times ideal for power line protection, while TVS diodes react almost instantaneously, making them suitable for sensitive electronic circuits. MOVs have a non-linear resistance that varies with voltage, whereas TVS devices clamp voltage by entering avalanche breakdown.
Working Principle of MOV
Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) operate by changing their resistance with applied voltage, protecting circuits from voltage surges by clamping excessive voltage to a safe level. When the voltage exceeds a certain threshold, the MOV's resistance drastically decreases, diverting the surge current away from sensitive components. Unlike TVS diodes, which rapidly respond to transient events by breakdown, MOVs provide a nonlinear response suited for ongoing surge suppression in your electronic circuits.
Working Principle of TVS
TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diodes protect electronic circuits by clamping voltage spikes and diverting transient currents through a low-impedance path during overvoltage conditions. Unlike MOVs (Metal Oxide Varistors) that operate based on variable resistance, TVS devices react instantly by entering avalanche breakdown without damage to maintain voltage within safe limits. This fast response time and precise clamping voltage make TVS diodes ideal for safeguarding sensitive semiconductor components from transient surges.
Applications of MOV
Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) are widely used in surge protection for electronic devices, power supplies, and industrial equipment due to their ability to absorb high transient voltages. They are commonly applied in power strips, circuit boards, and communication systems to safeguard against voltage spikes caused by lightning or switching events. Your electronic systems can benefit from MOVs by preventing damage and ensuring longer operational life.
Applications of TVS
TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diodes protect sensitive electronic circuits by clamping voltage spikes and absorbing transient surges in applications such as telecommunications, automotive electronics, and consumer devices. Their fast response time and low leakage current make TVS ideal for safeguarding microprocessors, data lines, and power supply inputs against electrostatic discharge (ESD) and lightning-induced surges. Unlike MOVs (Metal Oxide Varistors), TVS diodes maintain consistent clamping voltage and superior reliability in high-frequency and low-voltage environments.
MOV vs TVS: Performance Comparison
MOVs (Metal Oxide Varistors) excel in handling high energy surges with their ability to clamp voltage spikes efficiently, offering robust protection for power lines against transient events. TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressors) provide faster response times and precise voltage clamping, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from transient voltage spikes. Your choice between MOV and TVS should consider the specific application requirements, including response speed, energy capacity, and operating voltage.
Choosing Between MOV and TVS for Circuit Protection
MOV (Metal Oxide Varistor) and TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diodes serve different roles in circuit protection, with MOVs ideal for clamping high-energy surges like lightning strikes due to their nonlinear resistance properties, while TVS diodes provide fast response times for transient voltage spikes. Your choice depends on the application's surge energy level, response speed requirements, and frequency of transient events, as MOVs handle higher energy but respond slower, whereas TVS diodes offer precise, rapid clamping of low to medium energy spikes. Selecting the right device ensures optimal protection, preventing damage to sensitive electronics by balancing energy absorption capacity and response time.
MOV vs TVS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com