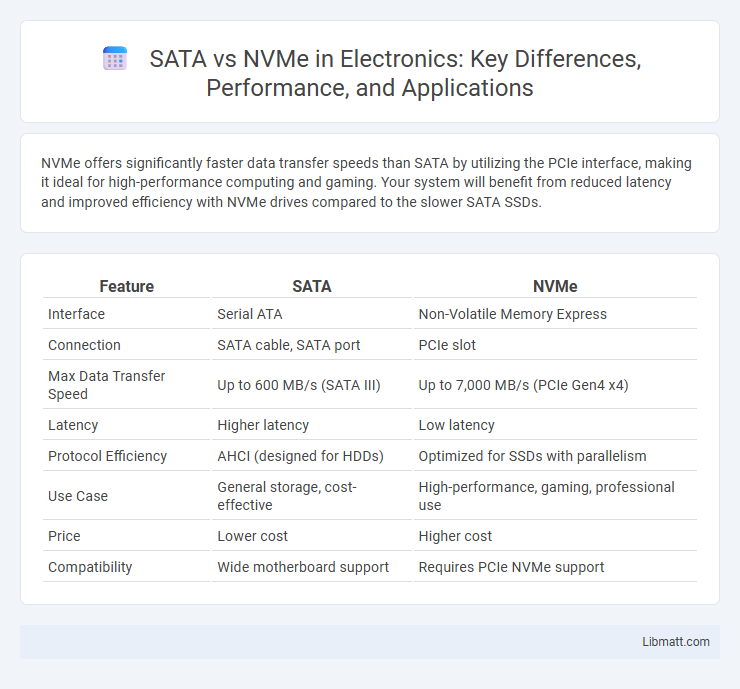
NVMe offers significantly faster data transfer speeds than SATA by utilizing the PCIe interface, making it ideal for high-performance computing and gaming. Your system will benefit from reduced latency and improved efficiency with NVMe drives compared to the slower SATA SSDs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SATA | NVMe |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Serial ATA | Non-Volatile Memory Express |
| Connection | SATA cable, SATA port | PCIe slot |
| Max Data Transfer Speed | Up to 600 MB/s (SATA III) | Up to 7,000 MB/s (PCIe Gen4 x4) |
| Latency | Higher latency | Low latency |
| Protocol Efficiency | AHCI (designed for HDDs) | Optimized for SSDs with parallelism |
| Use Case | General storage, cost-effective | High-performance, gaming, professional use |
| Price | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Compatibility | Wide motherboard support | Requires PCIe NVMe support |
Introduction to SATA and NVMe
SATA (Serial ATA) is a traditional interface designed primarily for connecting hard drives and SSDs, offering maximum data transfer speeds up to 6 Gbps. NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a modern protocol developed specifically for SSDs, utilizing the PCIe bus to achieve significantly higher throughput and lower latency compared to SATA. NVMe drives support parallel data processing with multiple queues, optimizing performance for intensive computing tasks and gaming.
What Is SATA?
SATA (Serial ATA) is a widely used interface for connecting storage devices like hard drives and SSDs to a computer's motherboard, offering data transfer speeds typically up to 6 Gbps. This technology relies on a cable connection and is compatible with older hardware, making it a practical choice for many users upgrading their storage. Understanding how SATA works can help you determine if it's the right fit for your storage needs compared to faster alternatives like NVMe.
What Is NVMe?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a high-performance storage protocol designed specifically for SSDs to maximize data transfer speeds and reduce latency by connecting directly to the PCIe bus. Unlike SATA, which has speed limitations up to 600 MB/s, NVMe can achieve speeds exceeding 3500 MB/s, improving your system's overall responsiveness and efficiency. Using NVMe drives significantly enhances tasks involving large file transfers, gaming, and professional workloads requiring rapid data access.
Key Technical Differences
SATA interfaces offer maximum data transfer speeds up to 600 MB/s, while NVMe technology leverages the PCIe bus, achieving speeds exceeding 3,500 MB/s for significantly faster performance. SATA drives use the AHCI protocol designed for older spinning hard drives, whereas NVMe utilizes a streamlined protocol specifically optimized for solid-state drives, resulting in lower latency and higher input/output operations per second (IOPS). When selecting storage, your choice impacts system responsiveness and load times, with NVMe providing superior technical advantages for demanding applications.
Performance Comparison: SATA vs NVMe
NVMe drives deliver significantly faster data transfer speeds than SATA, reaching up to 3500 MB/s compared to SATA's maximum of 600 MB/s. NVMe leverages PCIe lanes for a direct connection to the CPU, reducing latency and increasing IOPS capabilities beyond 500,000, whereas SATA's AHCI protocol limits it to around 100,000 IOPS. This performance gap makes NVMe ideal for high-demand applications such as gaming, video editing, and large-scale data processing.
Storage Device Compatibility
SATA interfaces support a wide range of storage devices, including traditional HDDs and many SSDs, making them highly compatible with older and most current systems. NVMe drives require M.2 or U.2 slots compatible with PCIe lanes, limiting their use to newer motherboards and laptops. Compatibility of NVMe storage is often restricted by BIOS support and physical slot availability, whereas SATA's universal interface ensures broader device and system compatibility across diverse hardware configurations.
Use Cases for SATA Drives
SATA drives are ideal for everyday computing tasks such as web browsing, office applications, and basic data storage due to their cost-effectiveness and compatibility with most systems. They provide reliable performance for bulk storage needs or secondary drives where high-speed data transfer is not critical, making them suitable for media libraries and backup solutions. Your choice of SATA drives supports consistent, affordable performance without the need for advanced hardware required by NVMe SSDs.
Use Cases for NVMe Drives
NVMe drives excel in scenarios demanding high-speed data transfer and low latency, such as gaming, video editing, and large-scale data analytics. Their direct connection to the PCIe bus allows rapid access to storage, significantly boosting performance for intensive applications and multitasking environments. If your workflow requires swift responsiveness and fast load times, choosing NVMe drives enhances overall system efficiency.
Cost Differences and Value
SATA SSDs offer a more affordable entry point with significantly lower costs per gigabyte compared to NVMe drives, making them suitable for budget-conscious users seeking improved performance over traditional hard drives. NVMe SSDs command higher prices due to their advanced PCIe interface, delivering superior speed and lower latency that justifies the premium for demanding applications and professional workloads. The value proposition depends on use case, where SATA drives excel in cost-efficiency for general storage, while NVMe provides greater performance benefits that can enhance productivity in data-intensive tasks.
Choosing the Right Storage: SATA or NVMe?
When choosing the right storage for your system, NVMe drives offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to traditional SATA SSDs, making them ideal for high-performance tasks such as gaming, video editing, and large data transfers. SATA SSDs, while slower, provide a cost-effective solution with wide compatibility for everyday computing and budget-conscious users. Consider NVMe for speed-critical applications and SATA for reliability and affordability in standard workloads.
SATA vs NVMe Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com