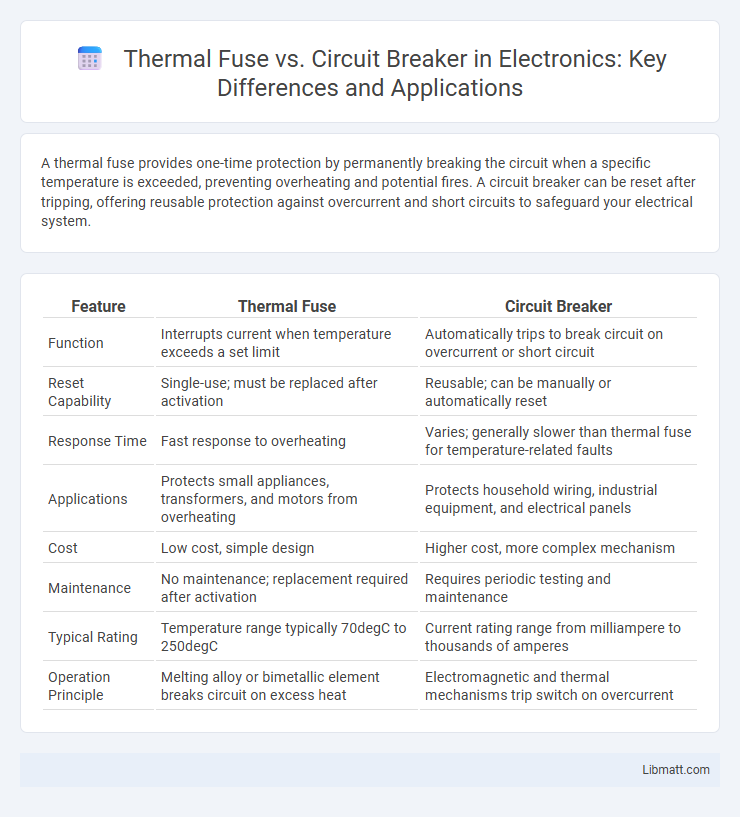
A thermal fuse provides one-time protection by permanently breaking the circuit when a specific temperature is exceeded, preventing overheating and potential fires. A circuit breaker can be reset after tripping, offering reusable protection against overcurrent and short circuits to safeguard your electrical system.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Thermal Fuse | Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Interrupts current when temperature exceeds a set limit | Automatically trips to break circuit on overcurrent or short circuit |
| Reset Capability | Single-use; must be replaced after activation | Reusable; can be manually or automatically reset |
| Response Time | Fast response to overheating | Varies; generally slower than thermal fuse for temperature-related faults |
| Applications | Protects small appliances, transformers, and motors from overheating | Protects household wiring, industrial equipment, and electrical panels |
| Cost | Low cost, simple design | Higher cost, more complex mechanism |
| Maintenance | No maintenance; replacement required after activation | Requires periodic testing and maintenance |
| Typical Rating | Temperature range typically 70degC to 250degC | Current rating range from milliampere to thousands of amperes |
| Operation Principle | Melting alloy or bimetallic element breaks circuit on excess heat | Electromagnetic and thermal mechanisms trip switch on overcurrent |
Introduction to Thermal Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Thermal fuses and circuit breakers are essential safety devices designed to protect electrical circuits from overheating and overcurrent conditions, respectively. A thermal fuse interrupts the circuit permanently when the temperature exceeds a specific threshold, ensuring protection against fire hazards caused by excessive heat. In contrast, circuit breakers can be reset after tripping due to an overcurrent, providing reusable protection for your electrical systems.
How Thermal Fuses Work
Thermal fuses operate by breaking an electrical circuit when a predetermined temperature is exceeded, using a heat-sensitive element that melts to interrupt current flow. This rapid response prevents overheating and potential fire hazards in electrical devices. Unlike circuit breakers, thermal fuses are single-use safety components that must be replaced after activation.
How Circuit Breakers Work
Circuit breakers protect electrical circuits by automatically interrupting the flow of current when an overload or short circuit occurs, preventing damage and fire hazards. Inside a circuit breaker, a bimetallic strip or electromagnet senses excess current and triggers the internal switch to trip, breaking the circuit. Understanding how circuit breakers work helps you safeguard your electrical system with reliable, reusable protection compared to single-use thermal fuses.
Key Differences Between Thermal Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Thermal fuses are single-use safety devices that interrupt electrical circuits when a specific temperature is exceeded, providing protection against overheating by permanently breaking the circuit. Circuit breakers are reusable switches that automatically interrupt electrical flow in response to overcurrent or short circuits, offering resettable protection for electrical systems. Unlike circuit breakers, thermal fuses cannot be reset and require replacement after activation, making them suitable for compact appliances and circuit breakers ideal for complex electrical installations.
Applications of Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses are commonly used in household appliances like coffee makers, hair dryers, and refrigerators to prevent overheating by interrupting the electrical circuit when a specific temperature is exceeded. Unlike circuit breakers that protect entire circuits and can be reset, thermal fuses provide a one-time safety cutoff in compact, sensitive devices for precise temperature control. Your electronics rely on thermal fuses to ensure safe operation by effectively mitigating fire hazards in temperature-sensitive applications.
Applications of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are essential for protecting electrical circuits in residential, commercial, and industrial applications by automatically interrupting current flow during overloads or short circuits. They are commonly used in power distribution systems, motor control centers, and electrical panels to prevent damage and ensure safety. Unlike thermal fuses, circuit breakers can be reset after tripping, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent testing and maintenance.
Advantages of Using Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses offer precise protection by permanently disconnecting electrical circuits when temperatures exceed safe limits, preventing overheating and potential fires. They are highly reliable for single-use applications, providing fast response times without the need for manual resetting like circuit breakers. Your electrical devices benefit from compact design and cost-effectiveness, making thermal fuses ideal for safeguarding sensitive components.
Benefits of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers offer rapid response in protecting electrical circuits by automatically interrupting current flow during overloads or short circuits, minimizing fire risks and equipment damage. Unlike thermal fuses, circuit breakers are reusable, allowing easy resetting without replacement, which enhances cost-efficiency and system reliability. Your electrical safety is significantly improved with circuit breakers due to their precise detection and quick disconnection capabilities.
Limitations and Drawbacks
Thermal fuses have limitations such as being single-use devices that require replacement after activation, which can lead to downtime and increased maintenance costs. Circuit breakers offer reusability but may experience mechanical wear over time, reducing their reliability and requiring regular testing. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize permanent damage prevention with thermal fuses or the convenience of resettable protection provided by circuit breakers.
Choosing the Right Protection Device
Choosing the right protection device between a thermal fuse and a circuit breaker depends on your specific application and safety requirements. Thermal fuses provide one-time protection by permanently breaking the circuit when overheating occurs, ideal for preventing fire hazards in small appliances. Circuit breakers offer reusable protection by automatically interrupting current flow during overloads or short circuits, suitable for residential and industrial electrical systems.
Thermal fuse vs Circuit breaker Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com