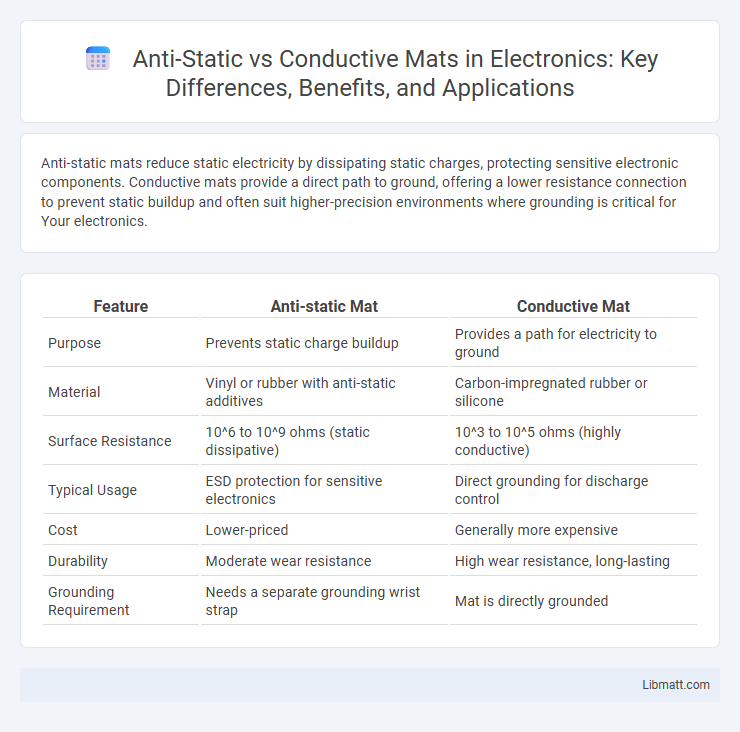
Anti-static mats reduce static electricity by dissipating static charges, protecting sensitive electronic components. Conductive mats provide a direct path to ground, offering a lower resistance connection to prevent static buildup and often suit higher-precision environments where grounding is critical for Your electronics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-static Mat | Conductive Mat |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents static charge buildup | Provides a path for electricity to ground |
| Material | Vinyl or rubber with anti-static additives | Carbon-impregnated rubber or silicone |
| Surface Resistance | 10^6 to 10^9 ohms (static dissipative) | 10^3 to 10^5 ohms (highly conductive) |
| Typical Usage | ESD protection for sensitive electronics | Direct grounding for discharge control |
| Cost | Lower-priced | Generally more expensive |
| Durability | Moderate wear resistance | High wear resistance, long-lasting |
| Grounding Requirement | Needs a separate grounding wrist strap | Mat is directly grounded |
Introduction to Anti-static and Conductive Mats
Anti-static mats are designed to dissipate static electricity safely to prevent damage to sensitive electronic components, typically made from materials like vinyl with static-dissipative properties. Conductive mats provide a path for electrical charges to ground by using highly conductive materials such as carbon or metal fibers embedded within the mat, offering superior conductivity for environments needing rapid static discharge. Both mats are essential in electronics manufacturing and assembly, serving different grounding and static control needs based on conductivity requirements.
Understanding Static Electricity in Work Environments
Static electricity in work environments can damage sensitive electronic components and disrupt manufacturing processes. Anti-static mats dissipate static charges by providing a controlled surface resistance, while conductive mats offer a low-resistance path to ground for rapid charge neutralization. Choosing the right mat depends on Your specific static control needs and the sensitivity of the electronic devices handled.
What Is an Anti-static Mat?
An anti-static mat is designed to safely dissipate static electricity from your body or equipment, preventing electrostatic discharge (ESD) that can damage sensitive electronic components. These mats are typically made from materials with controlled resistance levels, allowing static charges to drain away slowly and safely. Unlike conductive mats, anti-static mats strike a balance between insulation and conductivity to protect your devices while you work.
How Does a Conductive Mat Work?
A conductive mat works by providing a path for static electricity to safely dissipate from your body to the ground, preventing electrostatic discharge (ESD) that can damage sensitive electronic components. Designed with conductive materials like carbon or metal fibers, the mat maintains a low resistance level, ensuring efficient grounding. Using a conductive mat in your workspace helps protect your devices while you handle or assemble electronics.
Key Differences: Anti-static vs Conductive Mats
Anti-static mats neutralize static electricity to prevent damage to sensitive electronic components by dissipating charges safely, while conductive mats provide a low-resistance path to ground to ensure rapid discharge of static buildup. The key difference lies in their electrical resistance: anti-static mats have a higher resistance range (typically 10^6 to 10^9 ohms) to control static discharge, whereas conductive mats have much lower resistance (below 10^5 ohms) for immediate grounding. Choosing the right mat for your workspace depends on the sensitivity of your equipment and the required level of static control.
Applications for Anti-static Mats
Anti-static mats are primarily used in electronic manufacturing and repair environments where preventing electrostatic discharge (ESD) is crucial for protecting sensitive components. These mats dissipate static charges safely to ground, ensuring your work area remains ESD-safe. Unlike conductive mats that provide a direct path for electrical currents, anti-static mats are designed to neutralize and control static buildup, making them ideal for assembling and handling electronic devices.
Common Uses for Conductive Mats
Conductive mats are commonly used in industrial environments where electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection is critical, such as electronics manufacturing, assembly lines, and repair stations. These mats provide a controlled path for static electricity to ground, preventing damage to sensitive electronic components. Additionally, conductive mats are essential in cleanrooms and laboratories to maintain ESD safety standards and ensure product integrity.
Choosing the Right Mat for Your Workspace
Selecting the right mat for your workspace depends on your specific static control needs and the environment's sensitivity to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Anti-static mats reduce static build-up by dissipating charges slowly, ideal for areas with minimal static hazards, while conductive mats provide a rapid discharge path to ground, essential for highly sensitive electronics assembly or repair. Your choice should align with the required level of ESD protection and grounding capabilities to ensure optimal safety and performance.
Maintenance and Lifespan of ESD Mats
Anti-static mats require regular cleaning with specific ESD-safe cleaners to maintain their dissipation properties and prevent dust buildup that can degrade performance. Conductive mats, while generally more durable due to their lower surface resistance, also demand routine inspection for cracks and wear to ensure consistent grounding effectiveness. Proper maintenance directly influences the lifespan of both ESD mats, typically extending their functional use beyond several years depending on environmental conditions and usage frequency.
Safety Standards and Compliance Considerations
Anti-static mats comply with IEC 61340-5-1 standards, ensuring they safely dissipate static charges without grounding, reducing the risk of electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage in sensitive electronic environments. Conductive mats must meet MIL-STD-1686 or ANSI/ESD S20.20 standards, offering low electrical resistance for effective grounding to prevent static buildup. Selecting mats that adhere to these safety standards guarantees compliance with industry regulations and enhances workplace safety in ESD-protected areas.
Anti-static vs Conductive Mat Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com