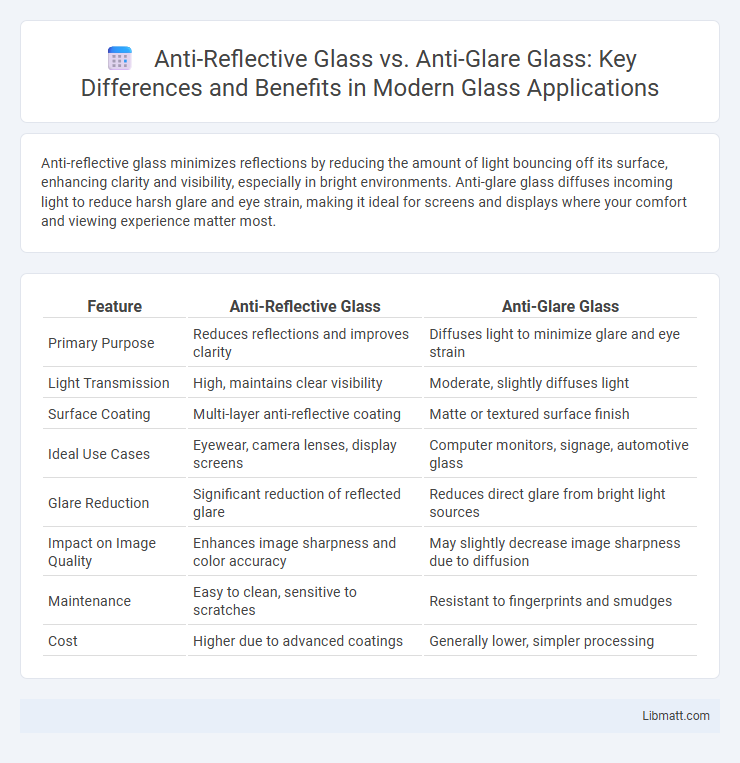
Anti-reflective glass minimizes reflections by reducing the amount of light bouncing off its surface, enhancing clarity and visibility, especially in bright environments. Anti-glare glass diffuses incoming light to reduce harsh glare and eye strain, making it ideal for screens and displays where your comfort and viewing experience matter most.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Reflective Glass | Anti-Glare Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Reduces reflections and improves clarity | Diffuses light to minimize glare and eye strain |
| Light Transmission | High, maintains clear visibility | Moderate, slightly diffuses light |
| Surface Coating | Multi-layer anti-reflective coating | Matte or textured surface finish |
| Ideal Use Cases | Eyewear, camera lenses, display screens | Computer monitors, signage, automotive glass |
| Glare Reduction | Significant reduction of reflected glare | Reduces direct glare from bright light sources |
| Impact on Image Quality | Enhances image sharpness and color accuracy | May slightly decrease image sharpness due to diffusion |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, sensitive to scratches | Resistant to fingerprints and smudges |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced coatings | Generally lower, simpler processing |
Understanding Anti-Reflective Glass
Anti-reflective glass features a nanostructured coating designed to minimize light reflection by enhancing light transmission through the surface, improving visual clarity and reducing eye strain. This type of glass is commonly used in optical devices, camera lenses, and high-end displays to provide sharper images with increased contrast and less glare compared to standard glass. Unlike anti-glare glass, which diffuses light to reduce glare primarily on screens, anti-reflective glass directly combats reflections for clearer viewing without sacrificing brightness.
What Is Anti-Glare Glass?
Anti-glare glass features a matte or textured surface that diffuses light, reducing reflections and minimizing eye strain in bright environments. Its primary function is to scatter incoming light, improving visibility and comfort on screens or windows by preventing harsh glare. You benefit from enhanced clarity without the distracting mirror-like reflections typical of standard glass surfaces.
Key Differences Between Anti-Reflective and Anti-Glare Glass
Anti-reflective glass reduces reflections by using thin-film coatings that enhance light transmission and improve clarity, making it ideal for displays and eyewear where clear vision is crucial. Anti-glare glass diffuses incoming light through a textured surface, minimizing glare and reducing eye strain in bright environments, often used in computer screens and televisions. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right glass type to optimize visual comfort and performance based on your specific needs.
How Anti-Reflective Glass Works
Anti-reflective glass reduces reflected light by using multiple ultra-thin coatings that create destructive interference for reflected wavelengths, allowing more light to pass through the glass. These coatings are engineered with precise thicknesses and refractive indices to minimize reflections and improve visibility, especially in high-glare environments. This technology enhances clarity and contrast by suppressing distracting reflections that typically obstruct the view on standard glass surfaces.
How Anti-Glare Glass Functions
Anti-glare glass reduces screen reflections by diffusing light through a matte coating that scatters incoming light, minimizing glare and enhancing visibility in bright environments. This textured surface prevents sharp reflections, improving contrast and reducing eye strain for prolonged screen use. Unlike anti-reflective glass, which uses multilayer coatings to cancel reflected light waves, anti-glare glass achieves glare reduction primarily through light diffusion.
Applications of Anti-Reflective Glass
Anti-reflective glass is widely used in applications requiring enhanced visibility and reduced glare, such as in eyeglasses, camera lenses, smartphone screens, and solar panels, improving light transmission and user experience. It is essential in architectural glass for windows and display cases, minimizing reflections and allowing clearer views of interiors or displayed items. This technology benefits optical instruments and automotive glass by enhancing clarity and reducing eye strain in various lighting conditions.
Applications of Anti-Glare Glass
Anti-glare glass is widely used in electronic displays, such as computer monitors, smartphones, and televisions, to minimize eye strain and improve visibility under various lighting conditions. Its application extends to automotive windshields and architectural windows, where it reduces reflections and enhances safety by providing clearer vision. This type of glass effectively enhances user experience in environments with high ambient light, making it essential for both consumer electronics and building design.
Pros and Cons of Anti-Reflective Glass
Anti-reflective (AR) glass significantly reduces glare and reflections by using thin-film coatings that enhance light transmission, improving screen clarity and visual comfort in bright environments. It offers superior clarity compared to anti-glare glass, which uses surface etching or matte finishes that can diffuse light but often reduce sharpness and vibrancy. However, AR glass can be more expensive and may require delicate cleaning to maintain its coating, whereas anti-glare glass is generally more durable and less prone to showing fingerprints or smudges.
Pros and Cons of Anti-Glare Glass
Anti-glare glass reduces reflections and glare by diffusing light through a matte finish, enhancing screen visibility in bright environments. Your main advantage is improved comfort and reduced eye strain, especially for digital displays and outdoor usage, but it may slightly blur images and diminish sharpness compared to anti-reflective glass. The trade-off involves prioritizing glare reduction over image clarity, making anti-glare glass ideal when visibility under harsh lighting is crucial.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Anti-reflective glass minimizes surface reflections by using multiple layers of coatings to enhance clarity and reduce glare, making it ideal for displays, eyewear, and photographic lenses where visual sharpness is critical. Anti-glare glass employs a matte finish or etched surface to diffuse light, reducing harsh reflections and eye strain in environments with strong ambient light, such as computer screens and office lighting. Selecting between anti-reflective and anti-glare glass depends on your prioritization of clarity versus diffuse light reduction for optimal visual comfort and performance.
anti-reflective glass vs anti-glare glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com