Hard automation uses fixed machinery designed for high-volume, repetitive tasks with minimal flexibility, ideal for mass production environments. Soft automation relies on programmable equipment and robotics, allowing Your processes to adapt easily to changes in product design or production volume.
Table of Comparison
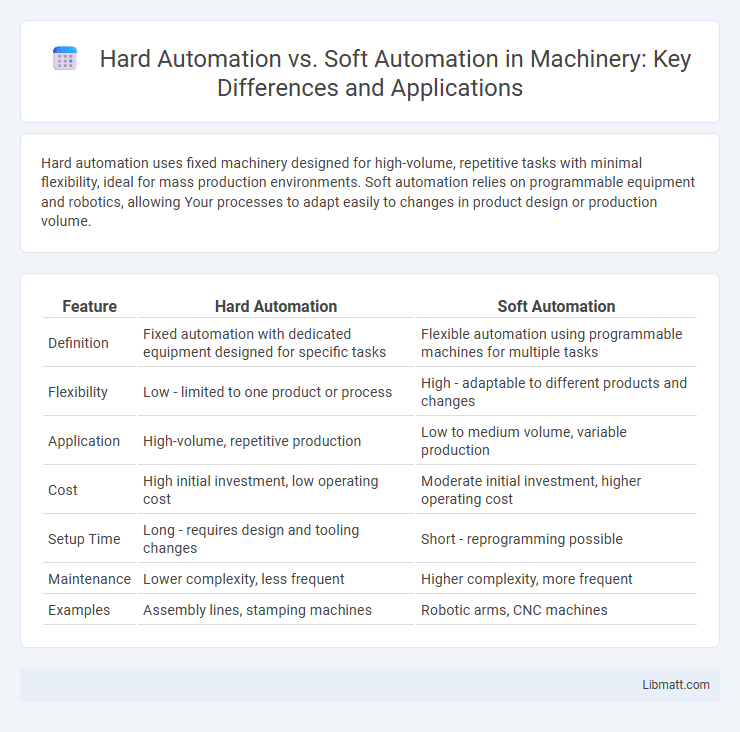
| Feature | Hard Automation | Soft Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed automation with dedicated equipment designed for specific tasks | Flexible automation using programmable machines for multiple tasks |
| Flexibility | Low - limited to one product or process | High - adaptable to different products and changes |
| Application | High-volume, repetitive production | Low to medium volume, variable production |
| Cost | High initial investment, low operating cost | Moderate initial investment, higher operating cost |
| Setup Time | Long - requires design and tooling changes | Short - reprogramming possible |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity, less frequent | Higher complexity, more frequent |
| Examples | Assembly lines, stamping machines | Robotic arms, CNC machines |
Introduction to Hard Automation and Soft Automation
Hard automation involves fixed, specialized equipment designed for high-volume production with minimal flexibility, ideal for repetitive tasks in industries such as automotive manufacturing. Soft automation utilizes programmable controllers and adaptable software systems, enabling rapid reconfiguration for varied product lines and lower-volume production. Both approaches significantly impact manufacturing efficiency, with hard automation emphasizing speed and cost-effectiveness and soft automation prioritizing flexibility and customization.
Defining Hard Automation
Hard automation involves the use of fixed, specialized machinery designed for high-volume production with minimal flexibility. It relies on rigid control systems and mechanical devices tailored to perform repetitive tasks efficiently, making it ideal for mass manufacturing environments. This type of automation reduces variable costs through economies of scale but lacks adaptability to product changes or variations.
Defining Soft Automation
Soft automation refers to the use of programmable controllers, sensors, and software to perform flexible, adaptable tasks in manufacturing and production systems. Unlike hard automation, which relies on fixed mechanical or electrical devices designed for specific repetitive operations, soft automation allows for easier reprogramming and customization to accommodate varying product designs or process changes. This flexibility improves efficiency and reduces downtime when switching between different tasks or products.
Key Differences Between Hard and Soft Automation
Hard automation uses fixed mechanical devices designed for high-volume, repetitive tasks with minimal flexibility, often implemented in automotive and electronics manufacturing. Soft automation relies on programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and industrial robots, allowing easy reprogramming for varied production processes and reduced downtime. The key differences lie in flexibility, cost of changeover, and suitability for customized versus mass production environments.
Applications of Hard Automation
Hard automation is primarily applied in high-volume manufacturing environments such as automotive assembly lines, where repetitive and precise tasks require fixed sequences. You will find it extensively used in processes like metal stamping, plastic injection molding, and packaging operations due to its ability to deliver consistent output with minimal variation. Its design excels in industries demanding high-speed production and low unit costs.
Applications of Soft Automation
Soft automation finds extensive applications in industries requiring flexibility and customization, including electronics manufacturing, food processing, and pharmaceutical production. It enables rapid reprogramming and adjustment of processes, making it ideal for batch production and small to medium-sized enterprises. Robotics integrated with AI in soft automation enhances quality control, reduces downtime, and improves throughput in complex assembly tasks.
Advantages of Hard Automation
Hard automation offers unparalleled efficiency in high-volume, repetitive production tasks by using fixed sequences and specialized machinery, resulting in consistent product quality and reduced labor costs. It excels in industries such as automotive manufacturing and electronics assembly where speed and precision are critical. Your operations benefit from lower per-unit costs and minimal variability, making hard automation ideal for mass production environments.
Advantages of Soft Automation
Soft automation offers greater flexibility and adaptability compared to hard automation, enabling easier reprogramming for various tasks without extensive physical changes. It reduces downtime and maintenance costs by allowing quick updates to software and control systems. Your operations benefit from enhanced scalability and improved integration with intelligent technologies such as AI and machine learning.
Choosing Between Hard and Soft Automation
Choosing between hard and soft automation depends on the specific manufacturing needs and production volume. Hard automation suits high-volume, repetitive tasks with fixed sequences, offering efficiency and low unit costs, while soft automation provides flexibility for variable product designs and shorter production runs through programmable machinery. Evaluating factors like production complexity, customization requirements, and investment costs guides the optimal choice for automation strategy.
Future Trends in Industrial Automation
Hard automation relies on fixed, rigid machinery designed for repetitive, high-volume tasks, while soft automation utilizes programmable robots and flexible systems adaptable to varying production needs. Future trends in industrial automation emphasize the integration of AI-driven soft automation, enabling smarter, more efficient processes capable of real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance. Your manufacturing operations can greatly benefit from adopting hybrid automation solutions that combine the durability of hard automation with the versatility of soft automation to stay competitive in evolving markets.
Hard automation vs soft automation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com