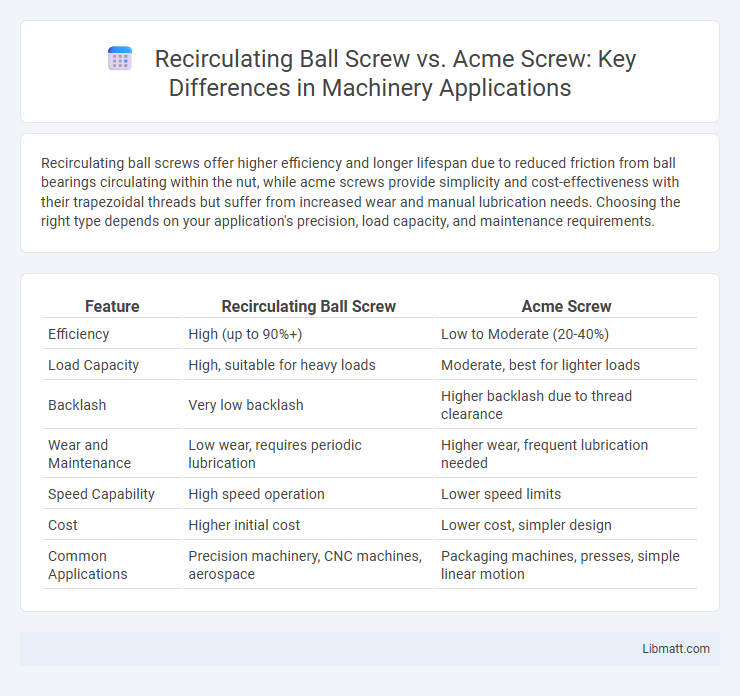
Recirculating ball screws offer higher efficiency and longer lifespan due to reduced friction from ball bearings circulating within the nut, while acme screws provide simplicity and cost-effectiveness with their trapezoidal threads but suffer from increased wear and manual lubrication needs. Choosing the right type depends on your application's precision, load capacity, and maintenance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recirculating Ball Screw | Acme Screw |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High (up to 90%+) | Low to Moderate (20-40%) |
| Load Capacity | High, suitable for heavy loads | Moderate, best for lighter loads |
| Backlash | Very low backlash | Higher backlash due to thread clearance |
| Wear and Maintenance | Low wear, requires periodic lubrication | Higher wear, frequent lubrication needed |
| Speed Capability | High speed operation | Lower speed limits |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, simpler design |
| Common Applications | Precision machinery, CNC machines, aerospace | Packaging machines, presses, simple linear motion |
Introduction: Recirculating Ball Screw vs Acme Screw
Recirculating ball screws provide higher efficiency and precision due to their rolling element design, significantly reducing friction compared to acme screws, which operate on sliding contact. Acme screws are cost-effective and simpler in design but tend to wear faster and require more maintenance under heavy loads. Your choice between recirculating ball screws and acme screws depends on the need for accuracy, load capacity, and operational longevity in specific machinery applications.
Understanding Recirculating Ball Screws
Recirculating ball screws convert rotational motion to linear motion with high efficiency and low friction by using ball bearings that roll between the screw shaft and the nut, significantly reducing wear and enabling precise, smooth movement. Compared to Acme screws, which rely on sliding friction and have lower efficiency, recirculating ball screws offer superior load capacity, higher accuracy, and longer service life in applications demanding rapid, repetitive motion. Their design minimizes backlash and heat generation, making them ideal for CNC machines, robotics, and aerospace systems requiring consistent, high-performance linear actuation.
What Are Acme Screws?
Acme screws feature trapezoidal thread profiles designed for power transmission and linear motion applications, offering high load-carrying capacity and ease of manufacturing. They excel in low to moderate speed operations due to their sliding friction, which requires proper lubrication to minimize wear and improve longevity. Your choice between acme and recirculating ball screws depends on factors like load capacity, efficiency, and precision requirements.
Key Differences: Ball Screws vs Acme Screws
Ball screws feature recirculating ball bearings that reduce friction and provide higher efficiency, precision, and load capacity compared to Acme screws with trapezoidal threads. Acme screws typically offer simpler manufacturing and lower cost but exhibit increased wear and lower efficiency due to sliding friction. Your choice depends on the application's need for accuracy, durability, and smooth motion performance.
Efficiency Comparison
Recirculating ball screws typically achieve efficiencies of 90-95%, significantly higher than acme screws, which generally range from 20-25%. The higher efficiency of ball screws is due to rolling contact between the screw and the nut, reducing friction and wear. Acme screws operate under sliding contact, resulting in more energy loss and lower overall mechanical efficiency.
Load Capacity and Durability
Recirculating ball screws offer significantly higher load capacity due to their rolling element design that reduces friction and wear, enabling smoother motion and greater efficiency under heavy loads. Acme screws, characterized by sliding contact between the nut and screw threads, generally have lower load capacity and experience more wear, leading to reduced durability in high-demand applications. The superior design of recirculating ball screws results in extended service life and better performance in precision machinery where load and durability are critical factors.
Precision and Backlash Control
Recirculating ball screws offer superior precision and minimal backlash due to their rolling element design, which reduces friction and wear compared to acme screws. Acme screws typically exhibit higher backlash because of their sliding contact, leading to less accurate positioning in high-precision applications. Engineers prioritize ball screws for applications requiring tight tolerances and smooth motion control, especially in CNC machines and robotics.
Maintenance Requirements
Recirculating ball screws require regular lubrication and occasional inspection to ensure smooth operation and prevent wear, but generally offer longer service life with less frequent maintenance compared to acme screws. Acme screws tend to experience higher friction and wear, necessitating more frequent lubrication and tighter monitoring of backlash and thread wear. Selecting a recirculating ball screw can reduce your maintenance efforts and improve machine uptime through its efficient load handling and lower friction design.
Cost Analysis: Ball Screw vs Acme Screw
Recirculating ball screws generally have a higher upfront cost compared to acme screws due to their precision manufacturing and superior efficiency. However, ball screws offer lower maintenance expenses and longer lifespan, which can reduce overall costs in high-demand or precision applications. Your choice should factor in initial budget constraints versus long-term operational savings and performance needs.
Best Applications for Each Screw Type
Recirculating ball screws excel in high-precision applications requiring smooth motion and high load capacity, such as CNC machines, robotics, and aerospace equipment, due to their low friction and high efficiency. Acme screws are best suited for applications demanding heavy load capacity and durability under harsh conditions, including presses, jacks, and clamps, because of their robust design and self-locking ability. Selecting between recirculating ball screws and acme screws depends on factors like required precision, load, speed, and environmental conditions for optimal performance.
Recirculating ball screw vs acme screw Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com