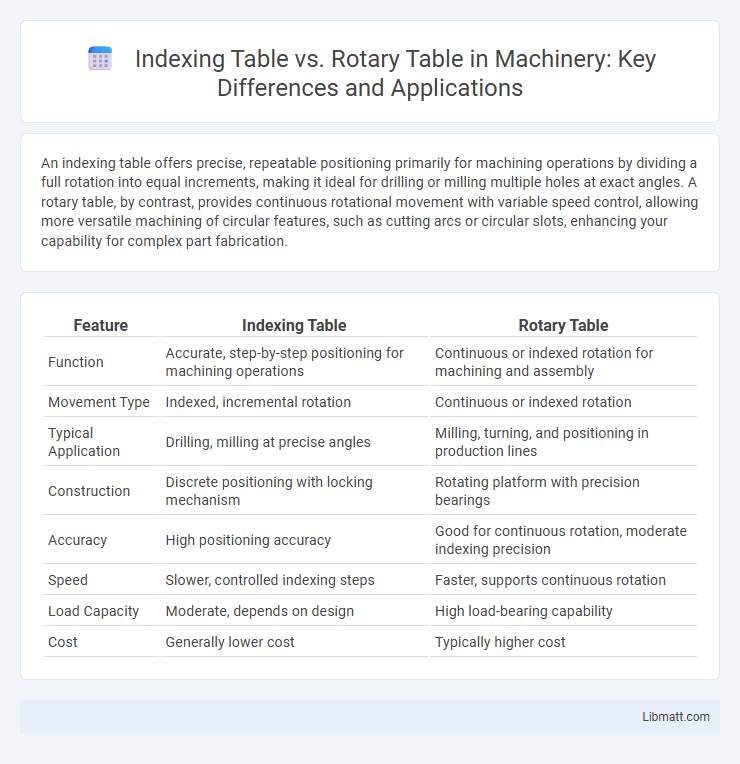
An indexing table offers precise, repeatable positioning primarily for machining operations by dividing a full rotation into equal increments, making it ideal for drilling or milling multiple holes at exact angles. A rotary table, by contrast, provides continuous rotational movement with variable speed control, allowing more versatile machining of circular features, such as cutting arcs or circular slots, enhancing your capability for complex part fabrication.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Indexing Table | Rotary Table |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Accurate, step-by-step positioning for machining operations | Continuous or indexed rotation for machining and assembly |
| Movement Type | Indexed, incremental rotation | Continuous or indexed rotation |
| Typical Application | Drilling, milling at precise angles | Milling, turning, and positioning in production lines |
| Construction | Discrete positioning with locking mechanism | Rotating platform with precision bearings |
| Accuracy | High positioning accuracy | Good for continuous rotation, moderate indexing precision |
| Speed | Slower, controlled indexing steps | Faster, supports continuous rotation |
| Load Capacity | Moderate, depends on design | High load-bearing capability |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
Introduction to Indexing Tables and Rotary Tables
Indexing tables and rotary tables are precision workholding devices used in machining to position a workpiece at accurate intervals for operations like milling and drilling. Indexing tables provide fixed angular positions using mechanical stops or detents, making them ideal for repetitive tasks requiring precision. Rotary tables offer continuous rotation and fine adjustment, allowing your machining projects to achieve complex angles and smooth circular cuts with high accuracy.
Key Differences Between Indexing and Rotary Tables
Indexing tables provide precise, incremental rotation for machining operations, typically dividing a full rotation into fixed angles, whereas rotary tables enable continuous 360-degree rotation for more versatile movement. The key difference lies in their control mechanisms: indexing tables use mechanical stops or digital encoders to lock positions firmly, while rotary tables often incorporate motorized drives for smooth rotation. Your choice depends on whether your machining requires fixed-angle repeatability or fluid rotational motion for complex cuts.
Construction and Design Features
Indexing tables feature a fixed base with a rotating top plate designed for precise angular positioning using mechanical or hydraulic systems, often equipped with detents or cam mechanisms for accurate indexing. Rotary tables exhibit a robust, cylindrical construction with integrated motor-driven rotation, allowing continuous 360-degree movement and greater load capacity, commonly used in CNC machining for complex multi-axis operations. Your choice depends on whether precise stop positions (indexing table) or smooth, controlled rotation (rotary table) better suits your machining requirements.
Operating Principles Explained
Indexing tables operate by dividing a full rotation into precise, fixed increments using mechanical or electronic means, enabling repeatable positioning for machining or assembly. Rotary tables provide smooth, continuous rotation, often driven by motors or manual cranks, allowing your workpiece to be positioned at any angle within a 360-degree range. The choice between these tables depends on whether accurate, discrete indexing or versatile, uninterrupted rotation is required for your application.
Applications in Manufacturing and Machining
Indexing tables provide precise angular positioning for operations such as gear cutting, drilling, and milling, making them ideal for repetitive tasks requiring high accuracy. Rotary tables enable continuous rotation, facilitating complex machining processes like circular milling, contouring, and multi-axis machining in CNC systems. Both devices enhance manufacturing efficiency but with distinct functional strengths suited to specific machining applications.
Accuracy and Precision Comparison
Indexing tables offer high accuracy and repeatability for simple, incremental positioning tasks with fixed-angle stops, typically achieving angular positioning accuracy within +-10 arcseconds. Rotary tables provide continuous rotation with finer precision and smoother motion control, often reaching positioning accuracy as precise as +-5 arcseconds or better, suitable for complex machining and inspection processes. Selecting between indexing and rotary tables depends on the required precision level, motion type, and application complexity.
Automation and Control Capabilities
Indexing tables offer basic automation with precise, repeatable positioning often controlled by simple mechanical or stepper motor systems, ideal for straightforward tasks requiring limited adjustment. Rotary tables provide advanced automation and control capabilities, integrating servo motors and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for smooth, continuous rotation and complex multi-axis coordination. Your choice depends on the level of control needed: indexing tables excel in incremental positioning, while rotary tables deliver dynamic, high-precision movement for automated manufacturing processes.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
Indexing tables require regular lubrication and periodic inspection of gears and bearings to maintain accuracy and prevent wear, while rotary tables typically demand more frequent sealing checks and calibration to ensure smooth rotation under heavy loads. Durability of indexing tables depends on the quality of the locking mechanism and the robustness of the indexing gears, whereas rotary tables rely heavily on the precision of the worm gear and the strength of the base to withstand continuous rotational stress. Both types benefit from routine maintenance schedules, but rotary tables generally exhibit higher durability in continuous-operation environments due to their design optimized for smooth, repeated rotation.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Indexing tables generally have lower initial costs and simpler construction, making them more cost-effective for applications requiring precise, incremental positioning. Rotary tables, while more expensive due to their continuous rotation capabilities and advanced features, offer higher productivity and versatility, enhancing ROI in processes involving complex, multi-axis machining. Evaluating production volume and operational requirements is crucial to balance upfront investment with long-term financial benefits for both indexing and rotary tables.
Choosing the Right Table for Your Workshop
Choosing between an indexing table and a rotary table depends on your workshop's precision and functionality needs. Indexing tables provide accurate, fixed-angle positioning ideal for repetitive machining tasks, while rotary tables offer continuous rotation for complex contouring and circular cuts. Evaluate your projects' requirements carefully to select the table that enhances your machining efficiency and accuracy.
Indexing table vs rotary table Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com