Closed die forging produces precise, complex shapes by forging metal within a set of contoured dies, ensuring consistent dimensional accuracy and superior surface finish. Open die forging allows for more flexibility in shaping large metal billets through repeated hammering or pressing between flat or simple contoured dies, ideal for custom or large-scale components where exact dimensions are less critical.
Table of Comparison
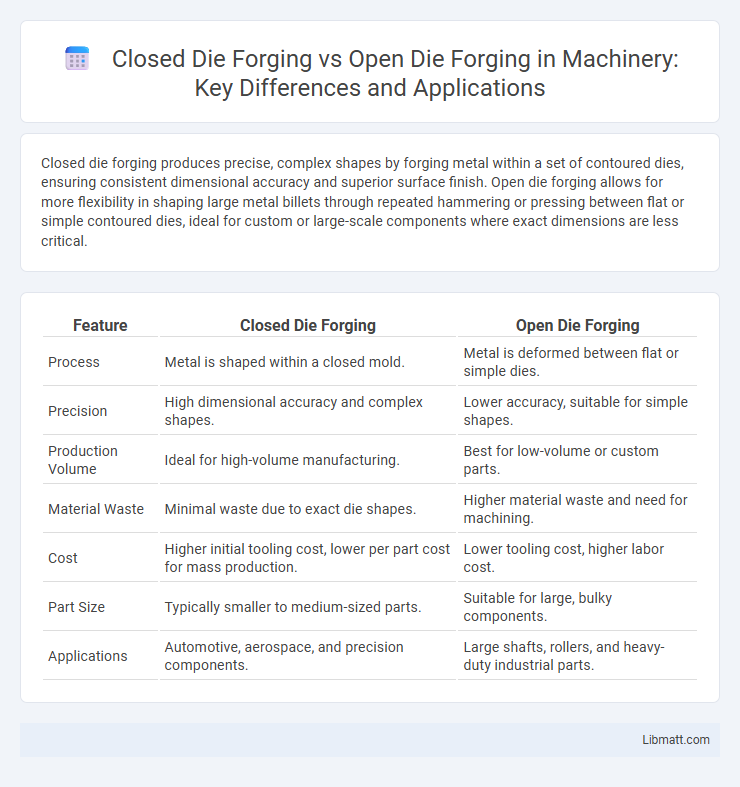
| Feature | Closed Die Forging | Open Die Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Metal is shaped within a closed mold. | Metal is deformed between flat or simple dies. |
| Precision | High dimensional accuracy and complex shapes. | Lower accuracy, suitable for simple shapes. |
| Production Volume | Ideal for high-volume manufacturing. | Best for low-volume or custom parts. |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste due to exact die shapes. | Higher material waste and need for machining. |
| Cost | Higher initial tooling cost, lower per part cost for mass production. | Lower tooling cost, higher labor cost. |
| Part Size | Typically smaller to medium-sized parts. | Suitable for large, bulky components. |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, and precision components. | Large shafts, rollers, and heavy-duty industrial parts. |
Introduction to Forging Processes
Closed die forging involves shaping metal within a set of confined dies, producing precise, complex components with high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface finishes. Open die forging, in contrast, uses flat or simply contoured dies that allow metal to deform freely between the tooling, ideal for large, simple shapes requiring improved mechanical properties. These forging methods differ significantly in tooling, operational control, and the range of achievable geometries, influencing their applications across automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery industries.
What is Closed Die Forging?
Closed die forging, also known as impression die forging, involves shaping metal within a set of pre-machined dies that enclose the workpiece completely, enabling precise and complex geometries. This process allows for higher dimensional accuracy, improved surface finish, and reduced material waste compared to open die forging. Commonly used for manufacturing high-strength components in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, closed die forging enhances mechanical properties through controlled deformation and grain flow.
What is Open Die Forging?
Open die forging is a metal shaping process where the workpiece is compressed between flat or simple contoured dies without enclosing it completely, allowing the material to flow freely. This technique is ideal for producing large, custom parts with varying sizes and shapes, offering flexibility and excellent metallurgical properties. The process often involves repeated hammering or pressing to achieve the desired form while maintaining structural integrity.
Key Differences Between Closed and Open Die Forging
Closed die forging involves shaping metal within a set of dies that fully enclose the workpiece, resulting in precise dimensions and complex geometries ideal for high-volume production. Open die forging deforms metal between flat or simple contoured dies without fully enclosing it, allowing for larger, less complex parts with excellent mechanical properties and grain structure. Your choice depends on factors like part complexity, production volume, and dimensional accuracy requirements.
Material Suitability for Each Forging Method
Closed die forging is ideal for high-strength alloys and complex shapes requiring precise dimensions, as it confines the material within a set of dies, allowing intricate details and consistent mechanical properties. Open die forging suits larger, simpler shapes and materials like carbon steel or titanium, permitting greater deformation and directional grain flow, which enhances toughness and fatigue resistance. Choose closed die forging for intricate components demanding accuracy, while open die forging is better for heavy, robust parts where flexibility in size and shape is essential.
Advantages of Closed Die Forging
Closed die forging offers superior dimensional accuracy and consistency compared to open die forging, resulting in less material waste and reduced machining costs. The process enables the production of complex shapes with enhanced mechanical properties due to directional grain flow and reduced porosity. High production rates and repeatability make closed die forging ideal for large-scale manufacturing of standardized, high-strength components.
Advantages of Open Die Forging
Open die forging offers superior flexibility in producing large, custom-shaped metal components with minimal material waste, unlike closed die forging which requires specific dies for each shape. It allows for better control over grain flow and mechanical properties, enhancing the strength and durability of the forged parts. This method enables the forging of oversized parts that are difficult or impossible to produce with closed die forging, making it ideal for heavy industrial applications.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Method
Closed die forging offers precise shapes and intricate details but is limited by higher tooling costs and less flexibility for large or custom parts. Open die forging provides greater adaptability for large components and varying sizes but challenges include lower dimensional accuracy and longer production times. Your choice depends on balancing cost, precision, and volume requirements.
Applications: Closed Die vs Open Die Forging
Closed die forging is commonly used in high-volume manufacturing of complex, precise components such as automotive gears, aerospace parts, and hand tools due to its ability to produce intricate shapes with tight tolerances. Open die forging is preferred for large, simple parts like shafts, discs, and flanges where dimensional precision is less critical, often utilized in heavy industries and power generation. The choice between closed die and open die forging depends on factors like part complexity, volume, and required mechanical properties.
Choosing the Right Forging Process for Your Needs
Closed die forging offers precise shaping and close dimensional tolerances, making it ideal for high-volume production of complex parts like automotive components or aerospace fittings. Open die forging provides greater flexibility for larger, simpler shapes such as shafts and discs, with lower tooling costs and customization options suited for low-volume or custom applications. Selecting between closed die and open die forging depends on factors including part complexity, production volume, material type, and desired mechanical properties.
Closed die forging vs open die forging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com