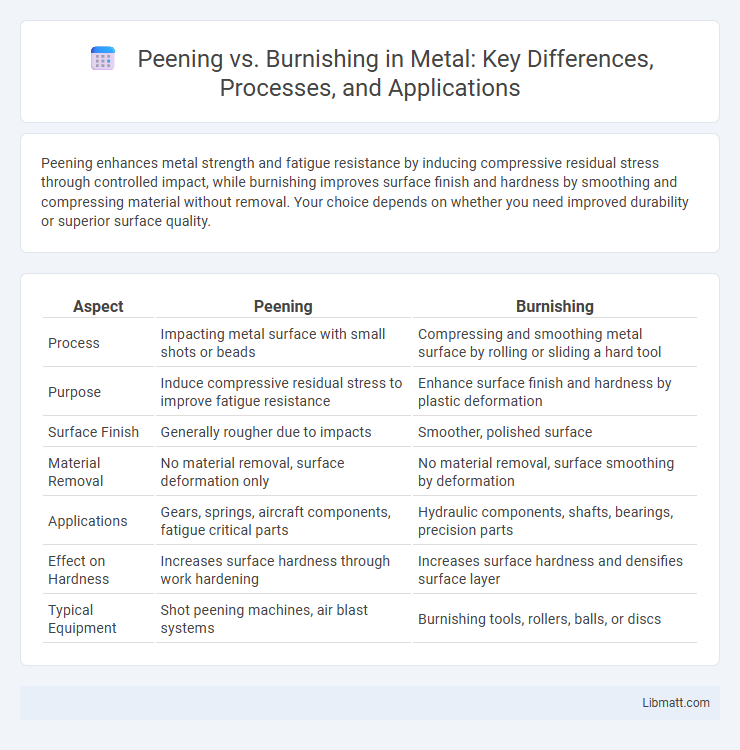
Peening enhances metal strength and fatigue resistance by inducing compressive residual stress through controlled impact, while burnishing improves surface finish and hardness by smoothing and compressing material without removal. Your choice depends on whether you need improved durability or superior surface quality.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Peening | Burnishing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Impacting metal surface with small shots or beads | Compressing and smoothing metal surface by rolling or sliding a hard tool |
| Purpose | Induce compressive residual stress to improve fatigue resistance | Enhance surface finish and hardness by plastic deformation |
| Surface Finish | Generally rougher due to impacts | Smoother, polished surface |
| Material Removal | No material removal, surface deformation only | No material removal, surface smoothing by deformation |
| Applications | Gears, springs, aircraft components, fatigue critical parts | Hydraulic components, shafts, bearings, precision parts |
| Effect on Hardness | Increases surface hardness through work hardening | Increases surface hardness and densifies surface layer |
| Typical Equipment | Shot peening machines, air blast systems | Burnishing tools, rollers, balls, or discs |
Introduction to Surface Enhancement Techniques
Peening and burnishing are surface enhancement techniques used to improve material properties such as hardness, fatigue resistance, and wear resistance. Peening involves bombarding the surface with small spherical media to induce compressive stresses, while burnishing smooths and hardens the surface by plastic deformation using a polished tool. Your choice between peening and burnishing depends on the required surface finish and mechanical performance for the specific application.
What is Peening?
Peening is a mechanical surface treatment process used to improve the fatigue strength and stress resistance of metals by inducing compressive residual stresses through controlled impact, typically via shot, laser, or ultrasonic methods. This technique enhances surface hardness and reduces the risk of crack initiation, making it ideal for automotive, aerospace, and structural components. Understanding how peening can strengthen Your parts helps optimize durability and extend service life in demanding applications.
What is Burnishing?
Burnishing is a surface finishing process that improves material hardness and surface smoothness by plastically deforming the workpiece's outer layer using a hardened tool or roller. This cold-working method enhances fatigue strength, reduces friction, and increases corrosion resistance without removing material. Commonly applied in metalworking and manufacturing industries, burnishing achieves superior surface integrity and dimensional accuracy.
Key Differences Between Peening and Burnishing
Peening involves mechanically impacting a metal surface with small spherical media to induce compressive stresses and improve fatigue strength, while burnishing utilizes a smooth, hard tool to plastically deform and smooth the surface, enhancing finish and hardness. Peening creates micro-indentations that increase surface roughness and residual stress, whereas burnishing produces a polished surface with reduced roughness and improved dimensional accuracy. The primary difference lies in peening's use of impact for stress modification versus burnishing's cold working for surface refinement.
Processes Involved in Peening
Peening involves processes such as shot peening and laser peening, where small spherical media or laser pulses create controlled surface compressive stresses to enhance material fatigue strength. This technique improves metal durability by inducing beneficial residual stresses that counteract tensile stresses and prevent crack formation. Your metal components can experience increased lifespan and resistance to wear through precise application of peening processes.
Processes Involved in Burnishing
Burnishing involves smoothing metal surfaces by plastic deformation using a hard, smooth tool that applies pressure, which enhances surface finish and increases fatigue strength. The process often includes cold working techniques such as roller or ball burnishing, where the tool moves over the material to compress and fill surface imperfections, thereby improving hardness and reducing roughness. Your components benefit from burnishing through improved wear resistance and extended service life, making it an essential finishing technique in precision manufacturing.
Comparative Benefits of Peening and Burnishing
Peening enhances material fatigue strength by inducing compressive residual stress through controlled impact, while burnishing improves surface finish and hardness by plastic deformation without material removal. Peening is ideal for components subjected to cyclic loading, such as gears and springs, whereas burnishing is preferred for precision components requiring smooth surfaces like hydraulic cylinders and pistons. Both techniques extend component lifespan, but selection depends on specific performance requirements and surface integrity goals.
Applications and Industries Using Peening vs Burnishing
Peening is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries to enhance fatigue resistance and stress relief in metal components such as gears and turbine blades. Burnishing finds primary applications in precision manufacturing sectors like automotive engine parts, medical devices, and molds, where surface smoothness and dimensional accuracy are critical. Your choice between peening and burnishing will depend on whether you need improved mechanical strength or superior surface finish for your specific industrial application.
Choosing the Right Technique: Factors to Consider
Selecting between peening and burnishing depends on material type, desired surface finish, and stress distribution requirements. Peening effectively induces compressive residual stresses to improve fatigue resistance in metals, while burnishing enhances surface smoothness and hardness through plastic deformation without altering geometry. Consider component application, mechanical properties, and tolerance constraints to determine the optimal surface treatment technique.
Future Trends in Surface Finishing Technologies
Emerging trends in surface finishing technologies emphasize the integration of advanced peening and burnishing methods to enhance material properties such as fatigue resistance and surface hardness. Innovations in laser peening and ultrasonic burnishing enable precise control over residual stress profiles and surface topography, promoting extended component lifespan in aerospace and automotive industries. Increased adoption of automated and AI-driven equipment is anticipated to optimize process parameters, ensuring consistent quality and sustainability in manufacturing workflows.
Peening vs burnishing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com