Spring steel offers superior flexibility and durability due to its high yield strength, making it ideal for applications like springs and high-stress tools, while carbon steel provides better hardness and wear resistance for cutting tools and structural components. Understanding the distinct properties of spring steel versus carbon steel helps you select the best material tailored to your specific engineering needs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Spring Steel | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|---|
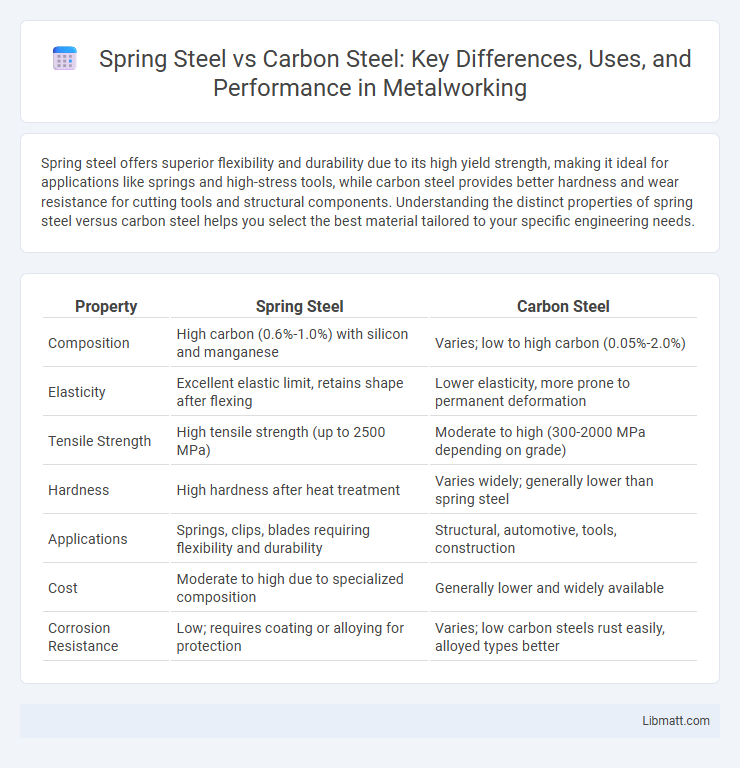
| Composition | High carbon (0.6%-1.0%) with silicon and manganese | Varies; low to high carbon (0.05%-2.0%) |
| Elasticity | Excellent elastic limit, retains shape after flexing | Lower elasticity, more prone to permanent deformation |
| Tensile Strength | High tensile strength (up to 2500 MPa) | Moderate to high (300-2000 MPa depending on grade) |
| Hardness | High hardness after heat treatment | Varies widely; generally lower than spring steel |
| Applications | Springs, clips, blades requiring flexibility and durability | Structural, automotive, tools, construction |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to specialized composition | Generally lower and widely available |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low; requires coating or alloying for protection | Varies; low carbon steels rust easily, alloyed types better |
Introduction to Spring Steel and Carbon Steel
Spring steel is a high-carbon steel alloy known for its exceptional elasticity and ability to return to its original shape after significant bending or twisting, making it ideal for manufacturing springs, clips, and flexible components. Carbon steel, containing varying carbon content up to approximately 2.1%, is prized for its strength, hardness, and versatility in construction, machinery, and automotive parts, with properties that can be adjusted through heat treatment. The primary distinction lies in spring steel's superior fatigue resistance and flexibility compared to the more rigid and generally less elastic carbon steel grades.
Chemical Composition Differences
Spring steel contains higher levels of carbon, typically ranging from 0.5% to 1.0%, which gives it enhanced elasticity and tensile strength compared to standard carbon steel. Carbon steel usually has lower carbon content, between 0.2% and 0.5%, making it less flexible but easier to weld and shape. Understanding these chemical composition differences helps you choose the right material for applications requiring either durability or formability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Spring steel exhibits superior elasticity and fatigue resistance compared to carbon steel, making it ideal for applications requiring repeated stress and deformation. Carbon steel, while generally stronger in tensile strength, lacks the same level of flexibility and resilience under cyclic loading. Your choice depends on whether durability under continuous strain or maximum strength is the priority for your mechanical application.
Strength and Hardness
Spring steel exhibits higher strength and exceptional hardness due to its alloy composition and heat treatment processes, making it ideal for applications requiring elasticity and fatigue resistance. Carbon steel varies widely in strength and hardness depending on carbon content, with higher carbon levels offering increased hardness but reduced ductility. Your choice between spring steel and carbon steel should consider the balance between strength, hardness, and flexibility needed for your specific application.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Spring steel exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity compared to carbon steel due to its unique alloy composition and heat treatment process, allowing it to withstand significant bending and return to its original shape without permanent deformation. Carbon steel, while strong and durable, tends to be more rigid and less elastic, making it less suitable for applications requiring repeated flexing or shock absorption. Choosing spring steel for your project ensures enhanced performance where flexibility and resilience are critical.
Common Applications of Spring Steel
Spring steel is extensively used in manufacturing high-stress components such as automotive suspension springs, industrial machinery springs, and precision tools requiring high fatigue resistance. Its excellent elasticity and tensile strength make it ideal for retaining clips, knives, and clamps where repeated flexing occurs. Compared to carbon steel, spring steel offers superior performance in dynamic applications demanding durability and resilience under cyclic loading.
Typical Uses of Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is widely used in construction, automotive manufacturing, and machinery due to its strength and affordability. It is ideal for producing structural beams, automotive frames, and heavy-duty tools that require durability and resistance to wear. Your projects benefit from carbon steel's versatility in applications where high tensile strength and toughness are essential.
Processing and Heat Treatment
Spring steel undergoes specialized heat treatments such as quenching and tempering to achieve high elasticity and tensile strength, ensuring it can withstand repeated stress without deforming. Carbon steel is typically processed through controlled cooling and annealing to optimize hardness and ductility, but it lacks the resilience required for dynamic loading found in spring applications. Your choice between these alloys should consider their distinct heat treatment profiles, as spring steel's enhanced elasticity is critical for applications demanding consistent performance over multiple cycles.
Cost and Availability
Spring steel typically costs more than carbon steel due to its specialized alloy composition and heat treatment processes that enhance its flexibility and durability. Carbon steel is widely available and more affordable, making it a popular choice for general-purpose applications where high strength and resilience are not critical. Your project budget and performance requirements will largely determine whether the higher expense of spring steel is justified over the more accessible carbon steel.
Choosing the Right Steel for Your Project
Choosing the right steel for your project depends on the specific requirements such as strength, flexibility, and wear resistance. Spring steel offers exceptional elasticity and is ideal for applications where resilience and repeated stress tolerance are crucial, while carbon steel provides higher hardness and is suited for structural uses demanding durability and impact resistance. Understanding these material properties ensures you select the optimal steel type to enhance performance and longevity.
spring steel vs carbon steel Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com