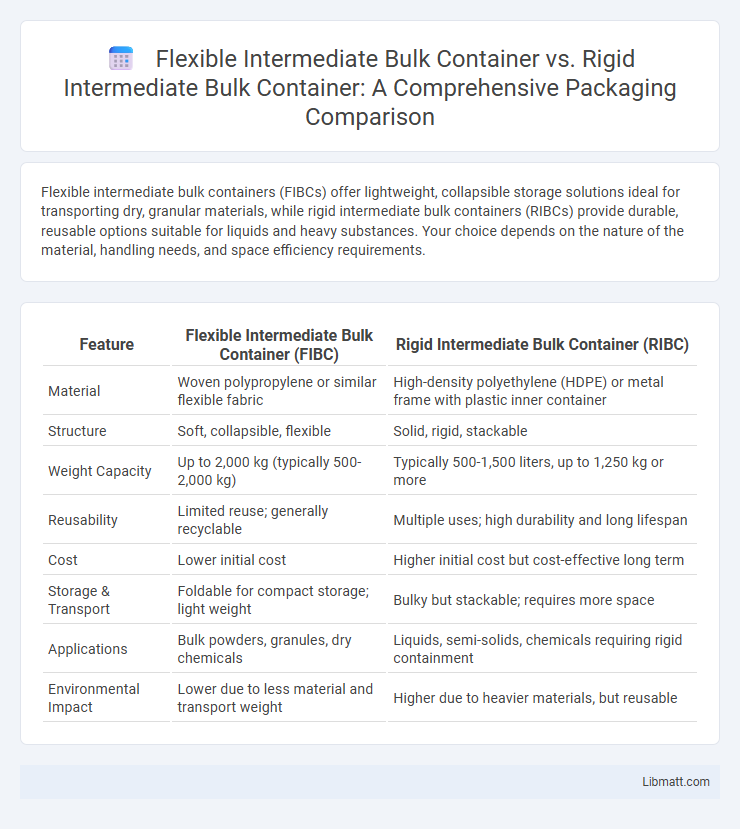
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) offer lightweight, collapsible storage solutions ideal for transporting dry, granular materials, while rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs) provide durable, reusable options suitable for liquids and heavy substances. Your choice depends on the nature of the material, handling needs, and space efficiency requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flexible Intermediate Bulk Container (FIBC) | Rigid Intermediate Bulk Container (RIBC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Woven polypropylene or similar flexible fabric | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or metal frame with plastic inner container |
| Structure | Soft, collapsible, flexible | Solid, rigid, stackable |
| Weight Capacity | Up to 2,000 kg (typically 500-2,000 kg) | Typically 500-1,500 liters, up to 1,250 kg or more |
| Reusability | Limited reuse; generally recyclable | Multiple uses; high durability and long lifespan |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but cost-effective long term |
| Storage & Transport | Foldable for compact storage; light weight | Bulky but stackable; requires more space |
| Applications | Bulk powders, granules, dry chemicals | Liquids, semi-solids, chemicals requiring rigid containment |
| Environmental Impact | Lower due to less material and transport weight | Higher due to heavier materials, but reusable |
Introduction to Flexible and Rigid Intermediate Bulk Containers
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) offer lightweight, collapsible solutions primarily made from woven polypropylene fabric, ideal for storing and transporting granular or powdered materials. Rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs), constructed from durable plastic or metal, provide robust structural support suited for liquids and heavy-duty applications requiring containment and protection. Your choice between FIBCs and RIBCs depends on the specific material properties, handling requirements, and storage conditions to optimize efficiency and safety.
Key Differences Between Flexible and Rigid IBCs
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) are made from woven polypropylene fabric, offering lightweight, collapsible storage ideal for dry bulk materials, while rigid intermediate bulk containers (Rigid IBCs) use durable plastic or metal shells for solid, reusable liquid and solid transport. FIBCs provide cost-effective, space-saving solutions with limited protection against moisture, whereas rigid IBCs ensure superior durability, chemical resistance, and stackability for heavy-duty applications. The choice between flexible and rigid IBCs depends on factors like material type, storage conditions, handling requirements, and transportation needs.
Material Composition and Design Features
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) are made from woven polypropylene fabric, offering lightweight, collapsible designs that facilitate easy handling and storage, while rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs) consist of hard plastic or metal frames combined with internal plastic liners for enhanced durability and stability. FIBCs incorporate breathable materials and flexible structures ideal for bulk solids, whereas RIBCs feature stackable, robust frameworks suited for liquid or sensitive materials requiring protection against impact. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize ease of transport and storage or maximum containment strength and reusability in demanding industrial applications.
Capacity and Size Variations
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) typically range from 500 to 2,000 liters and offer customizable sizes to fit various bulk material needs. Rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs) usually hold between 600 and 1,250 liters, with fixed dimensions designed for durability and stackability. Your choice depends on the required capacity and available storage space, as FIBCs provide more adaptability, while RIBCs offer consistent size and shape for optimized handling.
Handling and Transportation Efficiency
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) offer superior handling and transportation efficiency due to their lightweight construction and ability to collapse when empty, maximizing space utilization during return trips or storage. Rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs) provide enhanced structural integrity, allowing easier stacking and protection of contents during transit, which reduces damage and loss. Your choice depends on balancing the need for space-saving flexibility with the requirement for durability and stability in handling and transportation.
Storage Space Optimization
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) optimize storage space by collapsing when empty, allowing for compact stacking and efficient use of warehouse areas. Rigid intermediate bulk containers (IBCs) maintain their shape regardless of contents, requiring consistent space even when not in use, which can limit storage density. Choosing FIBCs can significantly enhance storage space optimization in facilities with variable inventory turnover and limited floor space.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) typically have a lower environmental impact due to their lightweight design, which reduces transportation emissions and requires fewer raw materials compared to rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs). While RIBCs offer durability and reusability, their heavier construction often leads to higher energy consumption during production and transport, increasing their carbon footprint. For your sustainability goals, choosing FIBCs can improve resource efficiency and decrease waste, especially when using recyclable or biodegradable fabrics.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) generally offer lower initial costs compared to rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs) due to their lightweight materials and simpler manufacturing processes, making them ideal for budget-conscious operations. However, RIBCs provide longer-term value through their durability and reusability, which can reduce replacement frequency and maintenance expenses over time. Evaluating your budget must include both upfront cost differences and potential savings from extended usability to optimize your overall cost efficiency.
Application Suitability for Different Industries
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) are ideal for industries requiring lightweight, reusable, and cost-effective solutions, such as agriculture, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals, due to their adaptability and ease of transport. Rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs) offer superior durability and protection, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications in sectors like automotive, food processing, and hazardous materials handling. Your choice between FIBC and RIBC should align with your industry's specific storage, transportation, and material safety requirements.
Safety, Durability, and Regulatory Compliance
Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) offer enhanced safety through features like static discharge protection and ease of handling, reducing spill risks during transport. Rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs) provide superior durability with robust materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) that resist impact and chemical corrosion, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Both FIBCs and RIBCs comply with regulatory standards such as UN certifications and FDA compliance, but RIBCs often meet stricter guidelines for reuse and hazardous materials transport.
Flexible intermediate bulk container vs rigid intermediate bulk container Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com