Nested packaging maximizes space efficiency by placing smaller items inside larger containers, reducing overall volume and material use, while segregated packaging keeps items separate to prevent cross-contamination or damage. Choosing the right method depends on Your product's safety, storage, and transportation requirements.
Table of Comparison
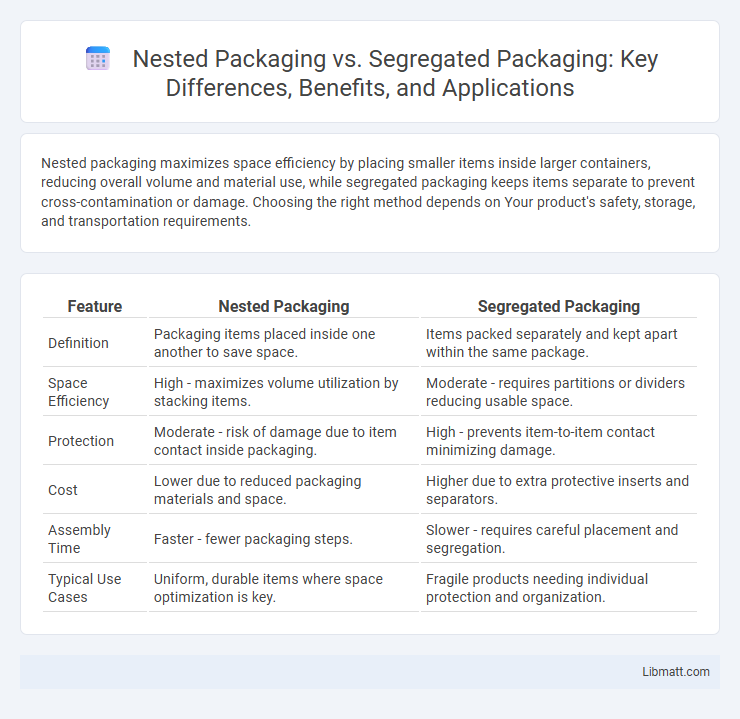
| Feature | Nested Packaging | Segregated Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Packaging items placed inside one another to save space. | Items packed separately and kept apart within the same package. |
| Space Efficiency | High - maximizes volume utilization by stacking items. | Moderate - requires partitions or dividers reducing usable space. |
| Protection | Moderate - risk of damage due to item contact inside packaging. | High - prevents item-to-item contact minimizing damage. |
| Cost | Lower due to reduced packaging materials and space. | Higher due to extra protective inserts and separators. |
| Assembly Time | Faster - fewer packaging steps. | Slower - requires careful placement and segregation. |
| Typical Use Cases | Uniform, durable items where space optimization is key. | Fragile products needing individual protection and organization. |
Introduction to Nested and Segregated Packaging
Nested packaging involves placing smaller packages or components within larger containers to maximize space efficiency and protect items during transit, commonly used in electronics and fragile goods industries. Segregated packaging separates products into distinct compartments or sections to prevent cross-contamination and simplify inventory management, often applied in pharmaceuticals and food sectors. Both methods enhance product safety and logistics efficiency by addressing specific handling and storage requirements.
Defining Nested Packaging
Nested packaging refers to arranging smaller packages within a larger container in a way that maximizes space efficiency by interlocking or stacking items closely together. This method reduces voids and protects delicate products during transit, enhancing overall packaging stability. Your choice between nested and segregated packaging impacts storage optimization and damage prevention based on product fragility and handling requirements.
Defining Segregated Packaging
Segregated packaging involves grouping different items into separate compartments or containers to avoid contact, reducing contamination risks and ensuring product integrity. This method is commonly used in pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries where cross-contamination must be minimized. Your choice between nested and segregated packaging depends on factors like product compatibility and regulatory requirements.
Key Differences Between Nested and Segregated Packaging
Nested packaging arranges items by fitting them closely together within a single container, maximizing space efficiency and reducing material usage. Segregated packaging separates products into distinct compartments or individual containers to prevent cross-contamination and simplify inventory management. The key difference lies in space optimization with nesting versus product isolation with segregation, impacting logistics and handling processes.
Advantages of Nested Packaging
Nested packaging offers significant advantages by maximizing space efficiency through the stacking of similar items within one another, reducing material costs and transportation expenses. It provides enhanced product protection by minimizing movement during transit, which lowers the risk of damage and improves shelf presentation. Your inventory management benefits from streamlined handling and storage, leading to faster packing and unpacking processes.
Advantages of Segregated Packaging
Segregated packaging reduces cross-contamination risks by keeping different products or components isolated, enhancing product safety and quality. It simplifies inventory management and product identification, leading to faster processing and reduced errors in handling. This method also allows for customized packaging solutions tailored to specific product requirements, improving overall operational efficiency.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Nested packaging is commonly used in the electronics and medical device industries where space efficiency and protection of delicate components are critical, ensuring compact storage and reducing material waste. Segregated packaging finds its applications in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, where contamination prevention and compliance with strict hygiene standards are paramount, facilitating safe handling of diverse products. Your choice between nested or segregated packaging should consider the specific requirements of product protection, regulatory compliance, and industry standards to optimize operational efficiency.
Cost Implications: Nested vs Segregated
Nested packaging reduces material usage and shipping volume, lowering overall transportation and storage costs compared to segregated packaging. Segregated packaging often requires additional cushioning and separate containers, increasing packaging expenses and handling labor. Companies prioritizing cost efficiency typically favor nested packaging for its streamlined logistics and minimized resource consumption.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Nested packaging minimizes material usage by fitting products within each other, significantly reducing waste and lowering carbon footprints during transportation. Segregated packaging, while offering better product protection, often requires additional materials that contribute to higher resource consumption and landfill waste. You can improve your sustainability efforts by choosing nested packaging solutions that optimize space and minimize environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Packaging Solution
Choosing the right packaging solution depends on your product's protection needs and space efficiency requirements. Nested packaging minimizes material use by fitting products within each other, ideal for compact storage and shipping. Segregated packaging provides dedicated compartments, enhancing organization and preventing damage during transit for delicate or diverse items.
Nested packaging vs segregated packaging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com