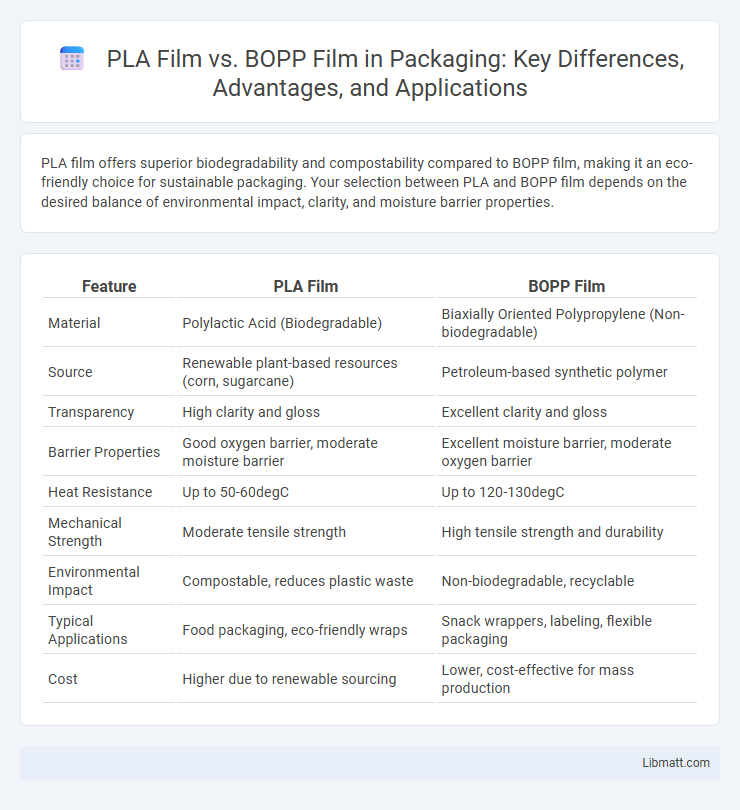
PLA film offers superior biodegradability and compostability compared to BOPP film, making it an eco-friendly choice for sustainable packaging. Your selection between PLA and BOPP film depends on the desired balance of environmental impact, clarity, and moisture barrier properties.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | PLA Film | BOPP Film |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polylactic Acid (Biodegradable) | Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene (Non-biodegradable) |
| Source | Renewable plant-based resources (corn, sugarcane) | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Transparency | High clarity and gloss | Excellent clarity and gloss |
| Barrier Properties | Good oxygen barrier, moderate moisture barrier | Excellent moisture barrier, moderate oxygen barrier |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 50-60degC | Up to 120-130degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength and durability |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable, reduces plastic waste | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Typical Applications | Food packaging, eco-friendly wraps | Snack wrappers, labeling, flexible packaging |
| Cost | Higher due to renewable sourcing | Lower, cost-effective for mass production |
Introduction to PLA Film and BOPP Film
PLA film, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers excellent biodegradability and compostability, making it ideal for sustainable packaging solutions. BOPP film, produced from polypropylene through biaxial orientation, provides superior clarity, moisture resistance, and mechanical strength, commonly used in food and consumer goods packaging. Both films cater to different market demands, with PLA emphasizing eco-friendliness and BOPP focusing on durability and versatility.
Chemical Composition and Material Origins
PLA film is derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, composed primarily of polylactic acid, a biodegradable polyester. BOPP film, or biaxially oriented polypropylene film, is synthesized from polypropylene resin, a thermoplastic polymer derived from fossil fuels like petroleum or natural gas. The biodegradable nature of PLA contrasts with the petrochemical origin and high crystallinity of BOPP, influencing their environmental impact and performance in packaging applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
PLA film is produced through the polymerization of lactic acid derived from renewable resources like corn starch, followed by extrusion and casting processes that yield a biodegradable and compostable film. In contrast, BOPP film is manufactured from polypropylene resin using a biaxial orientation process, which involves extrusion, reheating, and stretching the film in both machine and transverse directions to enhance mechanical strength and clarity. The PLA manufacturing process emphasizes sustainability and compostability, while BOPP film production focuses on high durability, moisture resistance, and optical properties suitable for packaging applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
PLA film exhibits excellent clarity and stiffness with moderate tensile strength, making it suitable for packaging that demands biodegradability and rigidity. BOPP film offers superior tensile strength, excellent moisture resistance, and high flexibility, providing durability for a wide range of applications. Your choice between PLA and BOPP film depends on the balance between mechanical robustness and environmental considerations.
Optical Clarity and Printability
PLA film offers superior optical clarity with its high transparency and gloss, making it ideal for applications requiring vibrant and sharp visual presentation. BOPP film provides excellent printability due to its smooth surface and compatibility with various printing technologies, enabling high-quality and durable prints. Both films serve distinct purposes: PLA excels in clarity for premium packaging, while BOPP is preferred for versatile, high-resolution printing.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
PLA film, made from renewable resources like corn starch, offers superior biodegradability compared to BOPP film, which is derived from non-renewable petroleum-based polypropylene. Your choice of PLA film can significantly reduce long-term environmental impact by breaking down naturally under industrial composting conditions, whereas BOPP film persists in landfills for decades due to its resistance to biodegradation. Opting for PLA film supports sustainability goals by minimizing plastic pollution and reliance on fossil fuels.
Common Applications in Packaging
PLA film is widely used for eco-friendly food packaging, disposable utensils, and compostable bags due to its biodegradability and clear appearance. BOPP film is preferred for packaging snacks, confectionery, and labels because of its excellent moisture resistance, high tensile strength, and glossy finish. Your choice between PLA and BOPP depends on whether sustainability or barrier performance is the priority for your packaging needs.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
PLA film generally has a higher production cost due to its biodegradable nature and reliance on renewable resources, whereas BOPP film benefits from economies of scale in petrochemical-based manufacturing, resulting in lower prices. Market availability for BOPP film is significantly broader, with widespread global production and established supply chains, making it more accessible for packaging applications. PLA film's market presence is growing, driven by demand for sustainable alternatives, but it remains limited compared to the extensive distribution of BOPP film.
Performance in Food Packaging
PLA film offers excellent biodegradability and compostability, making it an eco-friendly choice for food packaging with moderate barrier properties against moisture and oxygen. BOPP film provides superior tensile strength, clarity, and moisture resistance, ensuring long shelf life and maintaining food freshness. Both films are widely used, with PLA favored for sustainable packaging and BOPP preferred for high-performance sealing and barrier requirements.
Future Trends and Innovations
Future trends in PLA film focus on enhanced biodegradability and compostability, driven by increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable packaging. Innovations in BOPP film include improved barrier properties and integration with antimicrobial coatings to extend product shelf life in food packaging. Both materials are advancing through bio-based additives and nanotechnology to optimize performance while reducing ecological impact.
PLA film vs BOPP film Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com