Hot stamping uses heat and pressure to transfer metallic or pigmented foil onto a surface, creating vibrant and durable designs ideal for packaging and stationery. Cold foiling applies adhesive and then presses foil against it without heat, offering faster production and suitability for heat-sensitive materials, enhancing Your product's visual appeal with a smooth, reflective finish.
Table of Comparison
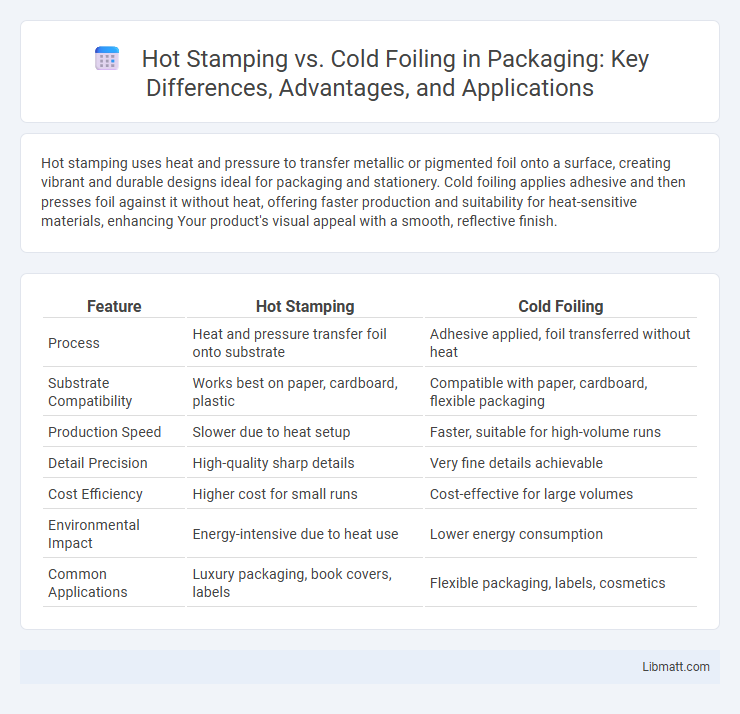
| Feature | Hot Stamping | Cold Foiling |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heat and pressure transfer foil onto substrate | Adhesive applied, foil transferred without heat |
| Substrate Compatibility | Works best on paper, cardboard, plastic | Compatible with paper, cardboard, flexible packaging |
| Production Speed | Slower due to heat setup | Faster, suitable for high-volume runs |
| Detail Precision | High-quality sharp details | Very fine details achievable |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost for small runs | Cost-effective for large volumes |
| Environmental Impact | Energy-intensive due to heat use | Lower energy consumption |
| Common Applications | Luxury packaging, book covers, labels | Flexible packaging, labels, cosmetics |
Introduction to Hot Stamping and Cold Foiling
Hot stamping is a traditional decorative printing technique that uses heat, pressure, and metallic foil to transfer shiny designs onto various substrates, offering vibrant colors and textured effects. Cold foiling employs a UV adhesive printed onto the substrate before applying foil without heat, enabling finer details and faster production on paper and flexible packaging. Both methods enhance visual appeal but differ in process, cost, and material compatibility, influencing their use in luxury branding and high-volume packaging.
How Hot Stamping Works
Hot stamping uses heat, pressure, and foil to create a metallic or pigmented design on surfaces like paper or plastic. A heated engraved die presses the foil onto the substrate, transferring the foil's thin layer in the desired shape. This process produces vibrant, durable finishes ideal for enhancing your packaging or branding materials with premium visual effects.
The Cold Foiling Process Explained
Cold foiling is a print finishing technique that applies metallic foil to paper using a UV coating instead of heat, allowing for vibrant, high-quality metallic effects on a broader range of substrates. The process involves printing a UV-curable adhesive pattern on the substrate, pressing the foil onto the adhesive with a rubber blanket, and curing it instantly with UV light, resulting in sharp and detailed foil application. This method contrasts with hot stamping, which requires heat and pressure, making cold foiling more efficient and versatile for intricate designs and thin materials.
Key Differences Between Hot Stamping and Cold Foiling
Hot stamping uses heat and pressure to transfer foil or pigment onto a surface, creating a durable and embossed effect, while cold foiling employs a UV adhesive and foil transfer without heat, resulting in a flatter, more intricate finish. Hot stamping excels in durability and tactile appeal, ideal for high-end packaging, whereas cold foiling offers faster production times and vibrant color options suitable for complex designs. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the best technique for your project's aesthetic and functional requirements.
Material Compatibility for Each Technique
Hot stamping excels with natural and coated papers, synthetic films, and leather, providing vibrant metallic or pigmented finishes that bond well under heat and pressure. Cold foiling suits delicate substrates like thin papers, synthetics, and shrink films, using UV adhesives that maintain material integrity without heat exposure. Your choice depends on the substrate type and desired finish durability, with hot stamping favored for robust materials and cold foiling for sensitive, flexible surfaces.
Visual Effects and Design Versatility
Hot stamping delivers vibrant, metallic finishes with deep embossing that enhances tactile engagement and visual richness. Cold foiling allows for intricate, precise designs on thinner materials, offering a wider palette of foil colors and complex patterns without heat damage. Your choice depends on the desired visual effect and material compatibility for optimal design versatility.
Production Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Hot stamping offers faster production speeds due to its direct heat transfer process, enabling rapid application on various substrates with minimal setup time. Cold foiling, while producing intricate designs with high precision, typically requires longer press runs and more frequent adjustments, impacting overall efficiency. Your choice depends on whether quick turnaround or detailed foil effects are the priority for your project.
Cost Considerations: Hot Stamping vs Cold Foiling
Hot stamping typically involves higher setup costs due to the need for metal dies but offers lower per-unit expenses, making it cost-effective for long print runs. Cold foiling requires less initial investment since it uses digital printing processes, but the per-unit cost can increase with larger quantities. Your choice depends on project volume and budget flexibility, as hot stamping favors large-scale production while cold foiling suits shorter runs with intricate designs.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hot stamping consumes more energy due to the high temperatures required for foil transfer, resulting in a larger carbon footprint compared to cold foiling, which uses UV or LED curing with lower energy consumption. Cold foiling produces less waste as it allows better control over foil application, reducing excess material and improving recyclability of substrates. Both processes involve metallic foils that can pose recycling challenges, but cold foiling's lower temperature process often supports more sustainable production workflows.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Hot stamping uses heat and pressure to transfer metallic foil onto materials, offering durability and a high-quality finish ideal for premium packaging and branding projects. Cold foiling applies foil with UV adhesive and curing, providing faster production times and the ability to print detailed multicolor designs, making it suitable for large runs with complex graphics. Selecting the right method depends on factors like project scale, material compatibility, design complexity, and budget constraints, ensuring optimal visual impact and cost-efficiency.
Hot stamping vs cold foiling Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com