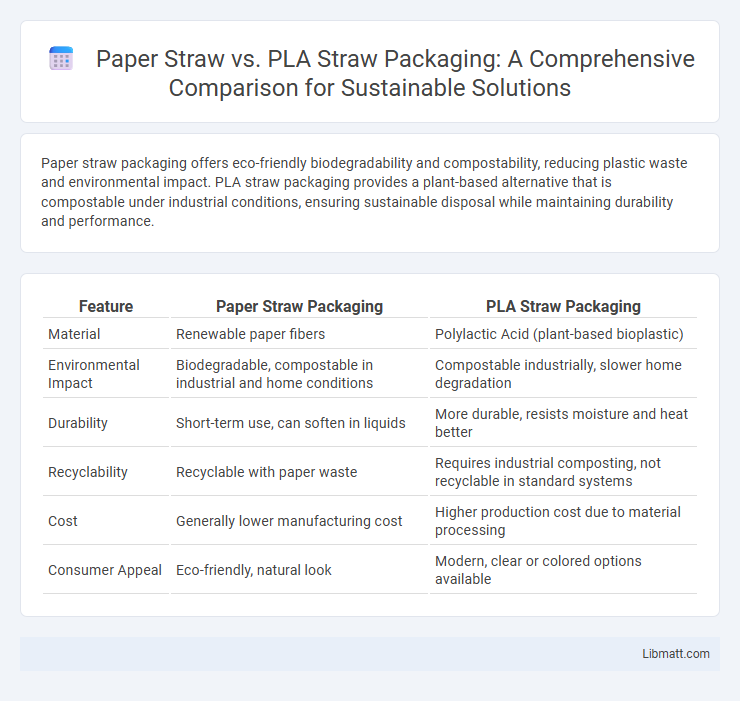
Paper straw packaging offers eco-friendly biodegradability and compostability, reducing plastic waste and environmental impact. PLA straw packaging provides a plant-based alternative that is compostable under industrial conditions, ensuring sustainable disposal while maintaining durability and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Paper Straw Packaging | PLA Straw Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Renewable paper fibers | Polylactic Acid (plant-based bioplastic) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable in industrial and home conditions | Compostable industrially, slower home degradation |
| Durability | Short-term use, can soften in liquids | More durable, resists moisture and heat better |
| Recyclability | Recyclable with paper waste | Requires industrial composting, not recyclable in standard systems |
| Cost | Generally lower manufacturing cost | Higher production cost due to material processing |
| Consumer Appeal | Eco-friendly, natural look | Modern, clear or colored options available |
Introduction to Sustainable Straw Packaging
Paper straws and PLA (polylactic acid) straws offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastic straws, addressing growing environmental concerns. Paper straws are biodegradable and compostable, made from renewable resources like cellulose fibers, while PLA straws derive from fermented plant starch, primarily corn, and biodegrade under industrial composting conditions. Both options reduce plastic pollution and support sustainable packaging initiatives in foodservice industries.
Environmental Impact: Paper vs PLA Straws
Paper straws are biodegradable and compostable, breaking down naturally within weeks and reducing landfill waste significantly. PLA straws, made from polylactic acid, require industrial composting facilities for complete degradation and may persist longer in natural environments if improperly disposed. Lifecycle analyses indicate paper straws generally have a lower carbon footprint and are preferable in ecosystems lacking advanced waste processing infrastructure.
Biodegradability and Compostability Comparison
Paper straws break down naturally in a few weeks, making them highly biodegradable and widely accepted in composting facilities. PLA straws, made from polylactic acid derived from renewable resources like corn starch, require industrial composting conditions with high heat to fully decompose and may persist in home compost bins. Choosing your straw packaging depends on whether your aim is quick biodegradability in natural environments or compatibility with industrial composting infrastructure.
Manufacturing Process and Resource Consumption
Paper straws are produced through a rolling and gluing process using cellulose fibers derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, requiring less energy and water compared to PLA straws. PLA (Polylactic Acid) straws are manufactured through a chemical conversion of fermented plant starch, such as corn or sugarcane, involving higher resource consumption including significant water use and fossil fuel inputs for polymerization and extrusion. The paper straw manufacturing process tends to have a lower carbon footprint and biodegrades faster, whereas PLA straws rely on industrial composting conditions and often involve more intensive agricultural inputs.
Consumer Safety and Health Considerations
Paper straws are biodegradable and free from harmful chemicals, reducing the risk of exposure to toxins during use, while PLA (polylactic acid) straws, made from fermented plant starch, are compostable but may release microplastics if not properly processed. Both materials avoid the health concerns associated with traditional plastic straws, such as BPA and phthalates. Consumer safety prioritizes choosing certified non-toxic, allergen-free options to minimize potential health risks linked to material composition and degradation products.
Performance: Durability and User Experience
Paper straws provide moderate durability but tend to soften and lose structural integrity after prolonged contact with liquids, impacting user experience during extended use. PLA (polylactic acid) straws offer superior durability and maintain rigidity longer in beverages, enhancing usability and comfort. Both options are biodegradable, but PLA straws also provide a smoother texture and reduced risk of disintegration compared to paper straws.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Paper straws generally cost between $0.02 and $0.05 per unit, making them more affordable than PLA (polylactic acid) straws, which range from $0.05 to $0.10 per straw due to higher material and manufacturing expenses. Market availability for paper straws is widespread across foodservice suppliers and retail outlets, while PLA straws are less commonly stocked, primarily found in specialized eco-friendly product lines. Both materials benefit from increasing demand in sustainable packaging, but paper straws dominate in low-cost bulk procurement and broader accessibility.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Paper straws must comply with FDA food contact regulations and often carry certifications like FSC or SFI for sustainable sourcing, ensuring environmental and health safety. PLA straws require compliance with FDA guidelines for bioplastics and may hold certifications such as ASTM D6400 or EN 13432, indicating they are compostable under industrial conditions. Both packaging types benefit from meeting regional standards like EU's EN 13432 or US FDA 21 CFR Part 177 to guarantee safe, eco-friendly consumer use.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Material
Paper straw packaging faces challenges with durability and moisture resistance, often becoming soggy or losing integrity when exposed to liquids over time. PLA straw packaging, derived from polylactic acid, offers better water resistance but encounters limitations related to higher production costs and dependence on industrial composting facilities for proper degradation. Your choice between these materials should consider the balance between environmental impact, performance needs, and waste management infrastructure availability.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Straw Packaging
Future trends in eco-friendly straw packaging emphasize the shift towards sustainable materials like paper and PLA (polylactic acid), both offering biodegradable solutions that reduce plastic pollution. Paper straws are gaining popularity due to their rapid biodegradability and renewable resource base, while PLA straws, derived from cornstarch, provide a compostable alternative with a plastic-like feel. Innovations in manufacturing processes and increasing consumer demand for environmentally responsible options will drive improvements in durability and cost-effectiveness, making your choice more sustainable in the long run.
Paper straw vs PLA straw packaging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com