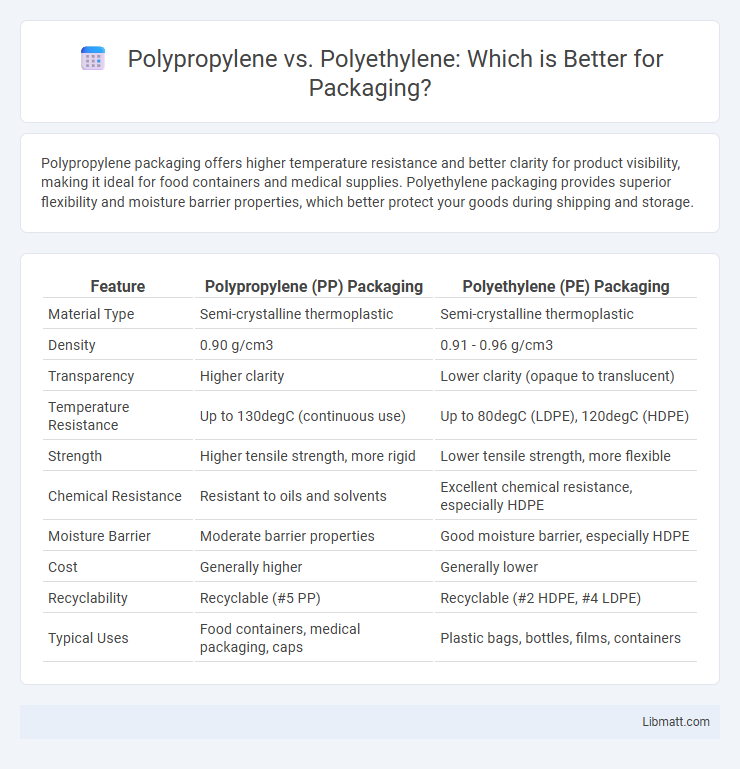
Polypropylene packaging offers higher temperature resistance and better clarity for product visibility, making it ideal for food containers and medical supplies. Polyethylene packaging provides superior flexibility and moisture barrier properties, which better protect your goods during shipping and storage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polypropylene (PP) Packaging | Polyethylene (PE) Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Semi-crystalline thermoplastic | Semi-crystalline thermoplastic |
| Density | 0.90 g/cm3 | 0.91 - 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Transparency | Higher clarity | Lower clarity (opaque to translucent) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 130degC (continuous use) | Up to 80degC (LDPE), 120degC (HDPE) |
| Strength | Higher tensile strength, more rigid | Lower tensile strength, more flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and solvents | Excellent chemical resistance, especially HDPE |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate barrier properties | Good moisture barrier, especially HDPE |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Recyclability | Recyclable (#5 PP) | Recyclable (#2 HDPE, #4 LDPE) |
| Typical Uses | Food containers, medical packaging, caps | Plastic bags, bottles, films, containers |
Introduction to Polypropylene vs Polyethylene Packaging
Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) are two of the most widely used polymers in packaging applications due to their distinct properties and cost-effectiveness. Polypropylene offers higher rigidity, melting point around 160-170degC, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for containers, caps, and films requiring thermal stability. Polyethylene, available in various densities such as LDPE, HDPE, and LLDPE, provides superior flexibility, moisture barrier properties, and impact resistance, commonly applied in bags, bottles, and stretch films.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polypropylene (PP) features a methyl group attached to every other carbon atom in its polymer chain, offering higher rigidity and a melting point around 160degC, which makes it suitable for heat-resistant packaging. Polyethylene (PE), with a simpler structure of repeating ethylene units, exhibits varied density forms like LDPE and HDPE, providing flexibility, chemical resistance, and a melting range between 105-135degC. Your choice between PP and PE packaging depends on required durability, temperature resistance, and product safety needs.
Manufacturing Processes and Applications
Polypropylene packaging is produced through polymerization of propylene monomers using Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysts, resulting in a material with higher melting point and rigidity, ideal for thermoforming and injection molding applications. Polyethylene, made via polymerization of ethylene using high-pressure or low-pressure processes, offers versatility with its various densities (LDPE, HDPE) suited for flexible films, bags, and containers due to its toughness and chemical resistance. Your choice between polypropylene and polyethylene packaging should consider the manufacturing method's impact on material properties and the specific application requirements, such as heat resistance and flexibility.
Strength and Durability Differences
Polypropylene packaging offers higher tensile strength and better resistance to fatigue compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for products requiring long-term durability. Polyethylene, particularly high-density variants, provides excellent impact resistance and flexibility, suited for applications needing toughness and stretchability. Your choice between polypropylene and polyethylene packaging should consider these strength and durability factors to ensure optimal protection and performance.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polypropylene (PP) packaging offers superior moisture barrier properties compared to polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for products sensitive to humidity. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), provides better chemical resistance and is more effective against solvents and acids. Both materials support diverse packaging needs, but choosing between PP and PE depends on specific moisture and chemical exposure requirements.
Flexibility and Clarity: Visual and Physical Attributes
Polypropylene packaging offers superior clarity with a glossy finish, making it ideal for showcasing product visuals clearly, while polyethylene tends to be more opaque with a matte appearance. In terms of flexibility, polyethylene is more pliable and resistant to stress cracking, suitable for applications requiring stretch and durability. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize visual appeal with rigidity or enhanced flexibility and toughness.
Cost Considerations and Economic Impact
Polypropylene packaging generally offers a lower production cost compared to polyethylene due to its higher melting point, allowing for energy-efficient processing and reduced material waste. Polyethylene, particularly LDPE, is often preferred for flexible packaging applications because of its cost-effectiveness in large-scale manufacturing despite slightly higher raw material prices. The economic impact of choosing polypropylene or polyethylene packaging depends on application requirements, with polypropylene providing better durability and reusability, ultimately influencing total cost of ownership and supply chain efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) packaging offers higher chemical resistance and can be recycled through established processes, but its recycling rates remain lower compared to polyethylene (PE), particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), which benefits from widespread collection and recycling infrastructure. Polyethylene packaging, especially HDPE, is more commonly recycled into new products, contributing to reduced landfill waste and lower carbon emissions over its lifecycle. Both materials are derived from fossil fuels, yet advances in bio-based versions and improved recycling technologies aim to mitigate their environmental footprint.
Typical Packaging Uses for Each Material
Polypropylene packaging excels in applications requiring high clarity and durability, such as food containers, medical device packaging, and flexible pouches due to its moisture resistance and heat tolerance. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE), is widely used for plastic bags, shrink wraps, and milk jugs because of its flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Your choice between these materials depends on the specific packaging needs, including barrier properties, strength, and environmental exposure.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Packaging Needs
Polypropylene and polyethylene are widely used plastics in packaging, each offering distinct benefits based on your requirements. Polypropylene is known for its higher rigidity, clarity, and resistance to heat, making it ideal for packaging items that require a sturdy and transparent container. Polyethylene, available in low-density (LDPE) and high-density (HDPE) forms, excels in flexibility, moisture resistance, and impact durability, which suits packaging needs where protection from moisture and shock is essential.
Polypropylene vs polyethylene packaging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com