EPS packaging offers lightweight, excellent insulation, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for protecting delicate items during shipping. Molded pulp is an eco-friendly alternative made from recycled paper, providing sustainable cushioning with biodegradability and compostability benefits that appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Table of Comparison
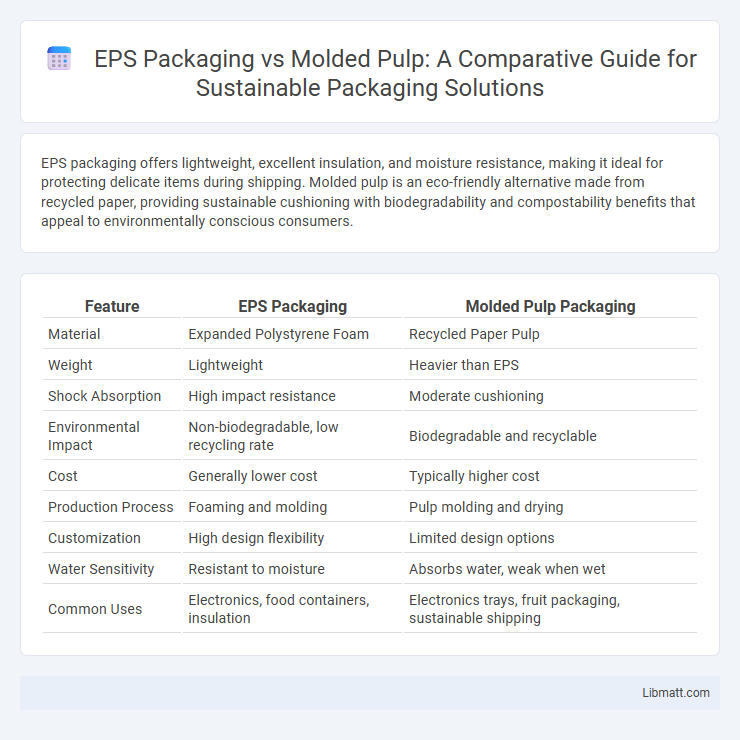
| Feature | EPS Packaging | Molded Pulp Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Expanded Polystyrene Foam | Recycled Paper Pulp |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than EPS |
| Shock Absorption | High impact resistance | Moderate cushioning |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, low recycling rate | Biodegradable and recyclable |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
| Production Process | Foaming and molding | Pulp molding and drying |
| Customization | High design flexibility | Limited design options |
| Water Sensitivity | Resistant to moisture | Absorbs water, weak when wet |
| Common Uses | Electronics, food containers, insulation | Electronics trays, fruit packaging, sustainable shipping |
Introduction to EPS Packaging and Molded Pulp
EPS packaging, made from expanded polystyrene, offers lightweight protection with excellent cushioning properties, making it ideal for electronic goods and fragile items. Molded pulp, composed of recycled paper fibers, provides an eco-friendly alternative that excels in biodegradability and sustainable packaging solutions. Both materials serve distinct sectors; EPS prioritizes impact resistance while molded pulp emphasizes environmental benefits.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
EPS packaging consists of expanded polystyrene beads that are heated and molded into lightweight, rigid foam shapes, offering excellent cushioning and moisture resistance. Molded pulp is made from recycled paper fibers that are pulped, shaped, and dried into biodegradable, eco-friendly packaging products. Understanding the material composition and manufacturing processes helps you select packaging that balances durability, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness for your needs.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Recycling
EPS packaging, made from expanded polystyrene, has limited biodegradability and poses significant environmental challenges due to its persistence in ecosystems and difficulty in recycling. Molded pulp packaging is biodegradable and compostable, breaking down naturally without releasing harmful substances, making it a more eco-friendly option. Choosing molded pulp can reduce your environmental footprint by promoting sustainable waste management through easier recycling and natural decomposition.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
EPS packaging offers superior cost efficiency due to low material and manufacturing expenses, making it ideal for high-volume production runs. Molded pulp, though often more expensive upfront, provides economic advantages through sustainability incentives and reduced environmental penalties. Companies analyzing packaging options must weigh initial investment against lifecycle costs, considering potential savings from regulatory compliance and consumer preference shifts toward eco-friendly materials.
Protection and Performance Capabilities
EPS packaging offers superior impact resistance and cushioning due to its lightweight, closed-cell foam structure that absorbs shocks effectively, making it ideal for fragile electronics and delicate items. Molded pulp provides adequate protection through its rigid, molded fiber composition, offering excellent crush resistance and environmental sustainability but typically less impact absorption compared to EPS. EPS outperforms molded pulp in moisture resistance and consistent performance under varying environmental conditions, ensuring reliable protection during long-distance shipping and storage.
Customization and Design Flexibility
EPS packaging offers superior customization and design flexibility, allowing intricate shapes and precise dimensions tailored to your product's needs. Molded pulp packaging provides eco-friendly options but is generally limited in fine detail and complex design compared to EPS. Choose EPS when detailed, lightweight, and protective custom forms are essential for optimal product presentation and safety.
Weight and Transportation Implications
EPS packaging weighs significantly less than molded pulp, reducing shipping costs and enabling more efficient transportation. Molded pulp's heavier weight can increase fuel consumption and carbon emissions during transit. Your choice of packaging directly impacts logistics expenses and environmental footprint.
Applications Across Industries
EPS packaging is widely used in electronics, food service, and medical industries due to its excellent cushioning and insulation properties. Molded pulp packaging is preferred in automotive, consumer goods, and agricultural sectors for its eco-friendly nature and ability to protect fragile items. Your choice depends on balancing durability, sustainability, and industry-specific requirements.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
EPS packaging meets stringent regulatory compliance and safety standards, including FDA approval for food contact and adherence to EPA guidelines for recyclability. Molded pulp packaging complies with ASTM standards for impact resistance and biodegradability, making it a sustainable choice for environmentally conscious businesses. Your selection should consider specific safety certifications and regulatory requirements relevant to your industry to ensure optimal compliance.
Future Trends and Innovations in Sustainable Packaging
Future trends in EPS packaging emphasize enhanced recyclability and the integration of bio-based EPS materials to reduce environmental impact. Molded pulp packaging innovations focus on improving durability and moisture resistance using advanced fiber treatments and hybrid composites. Both packaging types increasingly adopt circular economy principles, aiming for zero-waste solutions and lower carbon footprints in sustainable packaging development.
EPS packaging vs molded pulp Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com