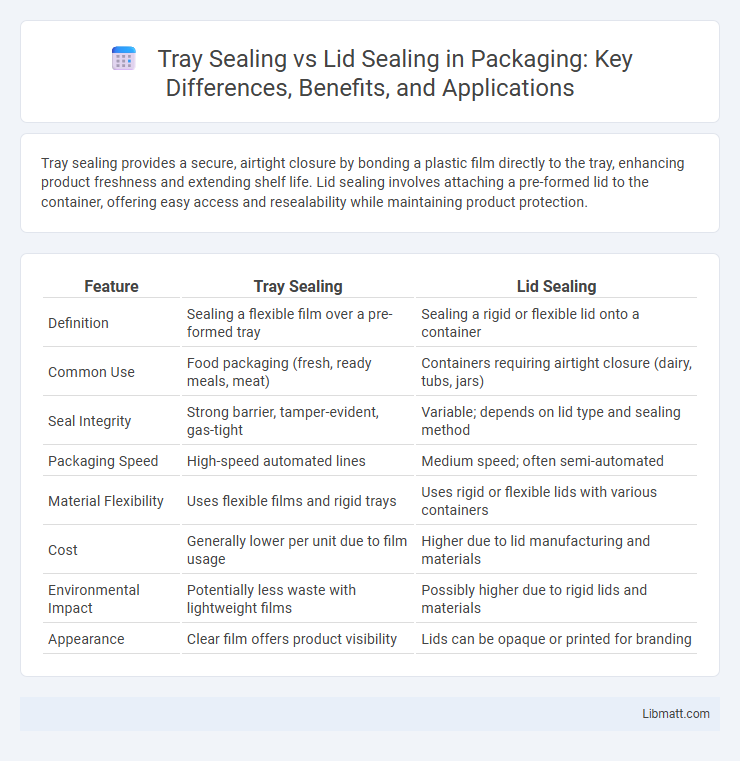
Tray sealing provides a secure, airtight closure by bonding a plastic film directly to the tray, enhancing product freshness and extending shelf life. Lid sealing involves attaching a pre-formed lid to the container, offering easy access and resealability while maintaining product protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tray Sealing | Lid Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sealing a flexible film over a pre-formed tray | Sealing a rigid or flexible lid onto a container |
| Common Use | Food packaging (fresh, ready meals, meat) | Containers requiring airtight closure (dairy, tubs, jars) |
| Seal Integrity | Strong barrier, tamper-evident, gas-tight | Variable; depends on lid type and sealing method |
| Packaging Speed | High-speed automated lines | Medium speed; often semi-automated |
| Material Flexibility | Uses flexible films and rigid trays | Uses rigid or flexible lids with various containers |
| Cost | Generally lower per unit due to film usage | Higher due to lid manufacturing and materials |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially less waste with lightweight films | Possibly higher due to rigid lids and materials |
| Appearance | Clear film offers product visibility | Lids can be opaque or printed for branding |
Introduction to Tray Sealing and Lid Sealing
Tray sealing involves the application of a flexible film over a pre-formed tray, creating a secure, airtight package commonly used in food and pharmaceutical industries to extend shelf life. Lid sealing, on the other hand, uses rigid lids to cover containers, providing a more durable closure often preferred for ready-to-eat meals and products requiring resealability. Your choice between tray sealing and lid sealing depends on factors such as product sensitivity, packaging aesthetics, and the need for durability or resealability.
How Tray Sealing Works
Tray sealing involves placing food or products into a pre-formed tray, then sealing it airtight with a plastic film using heat and pressure to create a secure barrier. This process preserves freshness by preventing contamination, extending shelf life, and allows for easy packaging of various food items like ready meals and fresh produce. Your product remains visible and protected, making tray sealing ideal for retail environments requiring both durability and presentation.
Understanding Lid Sealing Methods
Lid sealing methods include heat sealing, induction sealing, and ultrasonic sealing, each providing unique benefits for product safety and tamper evidence. Tray sealing typically involves bonding a film over a tray to protect food freshness, whereas lid sealing focuses on securing a pre-formed lid to a container, offering enhanced leak resistance. Understanding these lid sealing methods helps you choose the optimal packaging solution to maintain product integrity and extend shelf life.
Key Differences Between Tray and Lid Sealing
Tray sealing involves sealing the entire rim of a container with a film, providing an airtight and tamper-evident package ideal for fresh food preservation. Lid sealing attaches a pre-formed lid to a container, often offering easier opening and reclosing options suitable for ready-to-eat meals. Your choice between tray sealing and lid sealing should consider factors such as product type, shelf life requirements, and consumer convenience preferences.
Packaging Material Compatibility
Tray sealing provides compatibility with flexible films, ensuring a strong barrier for fresh or frozen foods, while lid sealing typically uses rigid plastic or foil lids that enhance reusability and presentation. Your choice depends on the packaging material's heat resistance, seal integrity, and product shelf life requirements, with tray sealing often preferred for vacuum or MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging) applications. Both methods must align with material interactions to prevent contamination and maintain product hygiene.
Efficiency and Speed Comparison
Tray sealing offers higher efficiency and faster processing speeds due to its automated sealing process that accommodates continuous product flow, reducing manual intervention. Lid sealing, while providing robust seal integrity, typically requires slower cycle times and more manual handling, leading to lower throughput in high-volume production environments. Industries prioritizing rapid packaging often favor tray sealing systems for their superior speed and efficiency metrics.
Cost Implications: Tray vs. Lid Sealing
Tray sealing generally offers lower upfront equipment costs compared to lid sealing systems, making it more accessible for small to medium-sized production lines. However, lid sealing can reduce long-term expenses by minimizing material usage and improving product shelf life, which may lead to fewer returns and less waste. Your choice between tray and lid sealing should consider both initial investment and ongoing operational savings to achieve optimal cost efficiency.
Impact on Product Shelf Life
Tray sealing creates an airtight barrier that significantly extends product shelf life by preventing contamination and moisture ingress. Lid sealing, while providing a secure closure, may allow minimal air exchange, potentially reducing its effectiveness in preserving freshness. Choosing tray sealing can better protect Your products from spoilage, ensuring longer-lasting quality and safety.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Tray sealing often uses less plastic than lid sealing, making it a more sustainable option by reducing overall material consumption and waste. Your choice of tray sealing can enhance recyclability and lower the carbon footprint due to optimized packaging geometry that minimizes excess packaging. Materials used in tray sealing frequently incorporate biodegradable or compostable films, aligning better with environmental regulations and eco-friendly disposal methods.
Choosing the Right Sealing Method for Your Application
Tray sealing provides an airtight barrier ideal for products requiring extended shelf life and tamper resistance, making it suitable for fresh foods and medical supplies. Lid sealing offers flexible packaging options, better visibility, and easy reclosability, perfect for retail-ready and consumer convenience applications. Selecting the right method depends on product preservation needs, packaging material compatibility, and consumer usability preferences.
Tray sealing vs lid sealing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com